Characteristics and incidence
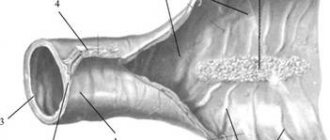
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, a vermiform appendage that emerges from the cecum. One end is closed, the other ends in the large intestine. Its length is about 10 cm, width - 1 cm. It is a “remnant” of the development of the human body, located in the lower abdomen, on the right, and has no significance for digestive activity. The appendix is considered a lymphatic organ that the body can easily do without.
In developed countries, about 7% of the population suffers from appendicitis during their lifetime. The disease is rare in parts of Africa and Asia, probably due to the high fiber content of the diet. In terms of age, the 10-19 age group is most affected. The mortality rate from appendicitis has remained virtually unchanged since the middle of the last century (0.1-0.2%). Recent advances in preoperative and postoperative care have reduced the mortality rate from perforated disease to 2-5%, but postoperative infections still occur in 30% of these forms.
The effect of appendicitis in pregnant women on the fetus
If appendicitis develops in the second trimester of pregnancy, its effect on the fetus is clear. The most common complications include the threat of late pregnancy loss, intestinal obstruction and postoperative infections.
Very rarely there are cases of premature placental abruption in pregnant women with appendicitis. If timely diagnosis and proper treatment are carried out, then there are no threats: the pregnancy will be preserved and completed. If the membranes become inflamed, intrauterine infection of the baby will occur, which will require mandatory antibacterial therapy. Postoperative complications most often occur within 7 days after surgery to remove the inflamed appendix. Therefore, for prevention, pregnant women are prescribed antibacterial therapy.
Forms of the disease
Inflammation of the appendix can be of a dual nature. It comes in an acute form, the symptoms of which develop over several days, and a chronic form, characterized by prolonged abdominal pain alternating with asymptomatic periods.
- The acute form of the disease is rapidly developing. Symptoms appear within a few hours, and their development only takes 2-3 days. Inflammation affects the walls of the appendix. In the absence of timely surgery, perforation of the appendix occurs with subsequent formation of peritonitis. In exceptional cases, inflammation subsides spontaneously and the disease recedes.
- Chronic appendicitis is a long-term disease that lasts for several months. Acute inflammation subsides, but recurs at various intervals. There is often a connection with another affected organ, in particular with an inflamed right ovary in girls.
The chronic form is less common than the acute form. But you cannot underestimate her. Despite the addictive nature of the manifestations, it can lead to the development of complications. Therefore, when typical signs appear, surgical treatment is required.
Signs of acute appendicitis in women
In 30% of cases, symptoms of appendicitis occur suddenly. In such cases, the woman should immediately call an ambulance and go to the hospital. This will help her minimize the risk of complications and even death. You should not endure the pain or suppress it with painkillers - this will only make it worse. You can recognize the acute form of appendicitis by:
- changes and confusion of consciousness;
- vomiting, after which relief does not occur;
- soreness that is wavy in nature;
- abdominal wall tension;
- a sharp increase in body temperature.
If several signs appear at once, the treating specialist should immediately examine you and conduct detailed palpation. If there is any suspicion of such a dangerous disease, you should be immediately taken to the surgical table.
Objective general symptoms
Typically, the disease begins with vague discomfort in the middle upper abdomen, followed by other manifestations, in particular: nausea, loss of appetite, dyspepsia. Over the course of several hours, the pain moves to the right lower abdomen and is limited, causing difficulty moving, walking, and coughing. If vomiting is present, it develops early, several hours after the initial abdominal pain occurs.
The appearance of vomiting before the development of pain casts doubt on the diagnosis of acute appendicitis.
The first symptoms of appendicitis in children and adults are a change in the general condition of the patient with a painful reaction to any movement. A sign of acute appendicitis is an acceleration of the heart rate that does not correspond to body temperature. Assessing the respiratory rate and temperature will not help make a diagnosis (only a temperature above 39-40°C generally indicates against the disease).
Symptoms and manifestations of appendicitis in adults
The location of the appendix is not the same in all people. Anatomical maps describe 6 different locations where the appendix may be located. Therefore, the symptoms of the disease often vary.
The most typical manifestation indicating the development of appendicitis is pain in the navel area, slowly moving to the right in the lower abdomen. Most of the pain is located between the navel and the protrusion of the pelvic bone. This is McBurney's point, named after the American surgeon who first described it.
Associated manifestations in adult women and men include:
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- temperature about 37.5°C;
- cardiopalmus;
- constipation;
- flatulence;
- loss of appetite;
- Abdomen sensitive to touch.
Mild diarrhea may sometimes occur. The pain intensifies when walking, sneezing, or other “shocks.” The patient seeks a relieving position, mainly lying on his back with his knees bent.
With inflammation at a late stage, which begins to irritate the abdominal wall, a painful prick occurs after a sharp weakening of the fingers during the previous compression.
In addition to these typical symptoms, the disease in adult men and women can occur in various variations and imitate other abdominal disorders. Appendicitis often imitates renal colic, inflammation of the gallbladder, and gynecological disease.
Symptoms and main signs
To independently determine the primary symptoms, you should pay attention to the following points:
- Localization of pain syndrome . As a rule, at first abdominal pain does not have a clear localization (usually in the periumbilical or epigastric areas). But within several hours, the pain shifts to the right lower quadrant of the abdomen, when the parietal peritoneum is involved in the inflammatory process. The patient feels increased pain when taking a deep breath, coughing or laughing.
- Inability to straighten your back . When the patient feels that it is too painful for him to keep his back straight, because there is a sharp pain in the abdomen, and he urgently needs to take the fetal position (lie on his side and press his legs to his stomach), then an exacerbation of appendicitis can be diagnosed.
- The occurrence of nausea, which ends in vomiting . This symptom may also be characteristic of food poisoning. However, in case of poisoning, vomiting is observed until the stomach is completely emptied. With appendicitis, the gag reflex is constant. On the contrary, in children vomiting can be observed a couple of times, and in older people it may not occur at all. Therefore, diagnosis may become more complicated depending on age.
- Temperature increase . As a rule, during an exacerbation of appendicitis, patients experience a temperature of up to 38 C. If appendicitis is diagnosed in a small child, the temperature can rise to almost 40 C. When the highest temperature is observed in an adult, there is a high probability of developing the consequences of appendicitis (peritonitis).
- Features of the chair . If in adults there are no special changes in stool, then in children, as well as with atypical localization of appendicitis, diarrhea is observed. In this case, food poisoning can be distinguished by loose stools. After diarrhea, the patient will experience a slight subsidence of abdominal pain, which does not happen with acute appendicitis.
- The mouth feels dry . During exacerbation of appendicitis, this is one of the main symptoms.
- Problematic urination . Sometimes painful urination may occur, and unpleasant sensations will occur in the external genitalia.
- Runny nose and cough . These symptoms are atypical signs of appendicitis, and most often occur in children. As a result, diagnosing the disease becomes much more difficult.
It is important! If several of the above symptoms are observed, then you should immediately call an ambulance and not take any medications yourself. If treatment for an exacerbation of the appendix is not provided in a timely manner, an infection of the abdominal cavity may occur, threatening the patient’s life.
Step-by-step instructions for determining appendicitis at home:
- The patient stands up straight and begins to walk, raising his legs bent at the knees very high. If the pain intensifies with each subsequent step, then it is most likely that an exacerbation of appendicitis has occurred.
- The second manipulation involves a flat position on the back. The patient is advised to relax as much as possible. This way you can feel the abdominal area well. If it is appendicitis, the stomach will be swollen and the abdominal muscles will be very tense. On palpation, increased pain is observed.
- At the third step, it is determined whether the patient has the Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom. The patient remains lying flat on his back. The person conducting the inspection should press with his palm near the navel area (a little lower), and then sharply tear off his hand. Signs of appendicitis will be sharp pain radiating to the navel.
It is worth noting that chronic appendicitis is no different from the symptoms of acute appendicitis (vague signs). Therefore, to accurately confirm the diagnosis, mandatory instrumental diagnosis is required in a special medical department.
Features of symptoms of appendicitis in young children and pregnant women
The localization of pain in a pregnant woman will be slightly different, since according to the position of the fetus, the appendix will shift higher than the typical location. However, in young children (up to two years old), pain will be observed in the lower abdomen, in addition there will be bloating and strong gag reflexes. It is typical that the baby will refuse to eat and will be sleepy.
Note! If appendicitis ruptures, the body temperature will rise to 40 C. Very often, appendicitis during pregnancy threatens the life of the fetus.
Actions for exacerbation of appendicitis
If it was possible to confirm the diagnosis at home, then you must immediately call an ambulance. When appendicitis worsens, one cannot hope that self-medication can eliminate the disease.
Otherwise, with an inflamed appendix and inaction, death can occur. We must not forget that the patient may have granulosa appendicitis, which is characterized by putrefactive inflammation.
Therefore, there are actions that are strictly prohibited in case of inflamed appendicitis.
| Taking painkillers | Diagnosis of appendicitis, in particular, occurs precisely by the localization of the pain syndrome. This is especially evident upon palpation. Therefore, it will be extremely difficult for a doctor to confirm the diagnosis without determining pain. In this case, only complaints will not be enough. Distortion of the clinical picture under the influence of analgesic drugs can lead to death |
| Applying compresses and various warming agents | Under the influence of heat, the inflammatory process will increase, which will only complicate the patient’s condition |
| Taking laxatives | When one of the symptoms of appendicitis is a problem with stool, then laxatives can only aggravate the clinical picture (may result in a rupture of the appendix) |
| Taking antacids | These medications will only increase the pain syndrome of an inflamed appendix. |
| Eat food and drink | It is not recommended to eat or drink before doctors arrive, as this may lead to aspiration during surgery. |
Carefully! Failure to comply with these rules can lead to complications of the condition, even death.
How is medical diagnosis performed?
After a detailed examination and conversation with the patient, he is sent for additional research. These diagnostic measures are necessary because it is very important to determine the exact location of appendicitis and its differentiation in order to carry out the correct surgical actions.
- Study of blood and urine tests . These tests are required to exclude kidney diseases, but they are not able to confirm the diagnosis of inflamed appendicitis.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity . This examination method is one of the most reliable and accurately confirms the location of the appendix.
- CT scan . This study is prescribed as an additional one if it is not possible to establish an accurate clinical picture using ultrasound.
Reference! Computed tomography may be prescribed when the patient is obese and it is impossible to examine the abdominal cavity in detail using ultrasound.
A competent specialist will tell you about the first signs of appendicitis, which allow you to identify the disease in a timely manner.
Appendicitis can occur at any age, but most often it affects men and women between 19 and 37 years old. Treatment is surgical.
In the absence of proper treatment and timely assistance, perforation of the walls of the appendix is observed, which can cause acute inflammation of the peritoneum and death , so it is important to know what symptoms of appendicitis occur in adults, where and in which side it hurts.
Manifestations of appendicitis in children
Another problem is appendicitis in children - the symptoms of 5-7 years old are difficult to recognize on their own, and a younger child is not able to describe the pain areas. In addition, children often complain of very nonspecific symptoms. Abdominal pain around the belly button is often accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation. In very young children, a swollen, tender tummy may predominate over the accompanying symptoms. Mild fever accompanying inflammation cannot be ruled out. The pain intensifies with other symptoms.
With appendicitis, the symptoms listed above in children 10 years of age and younger are most common. But the disease may occur atypically, with or without some of the described manifestations. In these cases, it is recognized late, at the stage of perforation of the appendix.
The reason why it can be difficult to determine the disease is the atypical location of the appendix. The symptoms described above occur in a number of other disorders. It is important to pay attention to the circumstances preceding their occurrence.
Symptoms of acute appendicitis in children
The signs of appendicitis in a child 11-12 years old differ from the symptoms of the disease in 2-year-old children. Before 2 years of age, it is rare due to the wide connection of the appendix with the cecum. This prevents stagnation of the contents of the appendix. But this condition is dangerous due to the reduced ability to limit inflammation (low immune resistance of the body, poor ability of the peritoneum to produce adhesions, short omentum). In the early stages, the disease manifests itself as drowsiness, irritation, tearfulness, and loss of appetite. As it progresses, vomiting, fever, and pain are added.
There may be a urge to defecate with the passage of a small amount of loose stool, constipation, and a burning sensation during urination.
In children over 2 years of age, the clinical picture is not significantly different from that in adolescents and adults, but their examination is complicated by poor cooperation with the doctor.
You can check appendicitis at home by behavior: the child takes a “relieving” position - half-sitting with legs partially bent. Significant difficulties are created, in particular, by going down the stairs. The temperature rises slightly (usually up to 38°C). Nausea and sometimes vomiting may also be present.
Causes and risk factors
Many people are surprised by the fact whether a child can have appendicitis. Of course yes. Most often, children suffer from acute appendicitis.
And this is always very dangerous, because the baby often cannot clearly explain what, where and how it hurts. The main risk group is children aged 13 to 20 years.
The probability of such inflammation is a terrible 75%. However, it's not all bad. If this appendage of the intestine is successfully removed, a person will forget about such acute pain for the rest of his life.
Despite the degree of development of modern medicine, no one can say with 100% certainty what causes inflamed appendicitis in children. However, there are two very specific conditions under which such inflammation definitely occurs: the presence of bacteria and blockage of the lumen of the appendix.
But the reasons for such clogging are quite simple:
- overeating seeds;
- ingestion of fruit and berry seeds and more.
Doctors also identify risk factors in children with reduced immunity or the presence of worms.
First signs and symptoms
Many parents, not knowing the symptoms of inflammation, do not understand how to correctly identify appendicitis in a child. But from the first signs you can understand that things are bad and you need to urgently consult a doctor.
The most important symptom is abdominal pain. Most often the pain begins in the area of the umbilical cord, mostly faintly. Over time, the pain will move to the right and become more intrusive.
Characteristic signs of appendicitis in children are high fever (not always), dizziness, nausea and vomiting. Vomiting may occur several times.
The signs of appendicitis in children are similar, but do not always completely coincide with the signs of inflammation in an adult.
However, an adult can take care of himself, but a child needs careful supervision. If you experience acute pain that does not go away, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Important! In children, appendicitis sometimes does not manifest itself as usual, because not all body systems are fully mature.
What absolutely should not be done
If a parent, using the guide on how to recognize appendicitis in a child, suspects such inflammation and an ambulance is on the way, the main thing is not to harm the patient.
During inflammation of the intestinal appendage, it is strictly forbidden to:
- Take painkillers. They dull the pain, and the child will not be able to clearly explain from memory where and how it hurts.
- Use laxatives. These drugs severely irritate the intestinal mucosa.
- Eat or drink. The stomach should be as empty as possible.
- Apply hot compresses or heating pads.
- Give an enema. Impact on the intestines can result in a ruptured appendix, which is life-threatening.
Diagnostic methods
Even if parents are sure that they know how the stomach hurts with appendicitis in children, in no case should they make a diagnosis on their own.
Even experienced doctors cannot always accurately determine the exacerbation of this appendage without additional tests.
The most common diagnostic method is examining and feeling the child (palpation). By palpating the iliac cavity, the doctor determines the condition of the internal organs and, based on the description of the patient’s pain, can make a diagnosis.
If it is impossible to determine the cause of the pain, suspicion of appendicitis is checked in the laboratory.
Elevated white blood cells in a blood test will indicate a high probability of inflammation of the appendix. However, the most accurate method for determining appendicitis is ultrasound.
When examining a child with the help of ultrasound machines, it is possible to determine not only acute appendicitis, but also the presence of fluids in the abdominal cavity, which will greatly facilitate the operation, because the doctor will be fully aware of the complexity of the situation.
In some cases, diagnosis of the disease can last from 8 to 12 hours.
Treatment methods
After specialists have managed to recognize appendicitis in a child, it is necessary to urgently begin treatment. The main methods of dealing with an inflamed appendix are surgery and laparoscopy.
Standard operation
When acute appendicitis occurs, a small patient is sent for a standard operation, which is performed under general anesthesia.
The surgeon opens the abdominal cavity within an hour, removing the inflamed organ, after which he applies neat, almost invisible sutures. With timely surgical intervention, the prognosis is always positive.
Laparoscopy
A modern analogue of the usual operation is laparoscopy. This procedure is much better and simpler. After laparoscopy, rehabilitation is easier to tolerate.
The essence of this operation is that the surgical intervention is performed through a small hole, avoiding large incisions and, accordingly, sutures. Children recover quickly after such operations, and the body remains neat.
Postoperative rehabilitation
Regardless of the treatment method, the baby still undergoes postoperative rehabilitation, which implies some physical limitations.
The first thing parents ask is: what can a child eat after appendicitis is removed. In each individual case, the diet is different, and the correct diet is always prescribed only by a doctor.
The first day after surgery is always the most difficult: the patient cannot eat or drink anything. After recovery from anesthesia there is always severe dehydration, however, the child can only moisten his lips with a wet cloth or gauze.
On the second day, you can already drink clean water, and the subsequent diet is prescribed by the doctor (usually chicken broth, unsalted porridge, kefir). On average, complete postoperative rehabilitation takes from 10 to 14 days.
Important! Postoperative gymnastics plays a very important role. It is carried out to prevent adhesions on internal organs.
Possible complications
Acute appendicitis is a dangerous disease that can be accompanied by severe complications, such as:
- Abscesses. In most cases, they resolve on their own, but their danger lies in the likelihood of suppuration.
- Intracavitary ulcers. When suppuration appears, the patient's temperature rises and abdominal pain intensifies. If you experience such sensations after surgery, you should immediately report them to your doctor.
- Peritonitis. The most common and most dangerous complication. In essence, this is a rupture of inflamed appendicitis, which is a direct threat to human life, because fluid from the appendix directly enters the abdominal cavity.
Only a professional can determine appendicitis in a child, but parents should know the symptoms of this insidious disease and consult a doctor in time. If proper treatment is carried out in a timely manner, very little time will pass, and dangerous inflammation will be behind you.
What to do if you suspect appendicitis?
To understand that appendicitis is inflamed, provide timely assistance, and prevent complications, take the following measures:
- Summarize the period before the onset of manifestations with an emphasis on food intake and stool frequency.
- If you experience stomach pain, stop eating.
- Drink sweetened tea or mineral water in small doses at frequent intervals, and avoid carbonated drinks - this temporary diet will prevent bloating, which aggravates symptoms.
- Do not take pain medications (risk of masking symptoms).
- Do not put ice on your baby's tummy!
- If symptoms persist (2-3 hours), you must call a doctor.
Appendicitis often occurs with a typical set of symptoms, but with significant variability. The child complains of pain around the navel. After a few hours, the pain moves to the right lower abdomen and is colicky or constant. Painful palpation and tapping on the abdominal area on the right and left are typical.
Safe tests for appendicitis
The doctor diagnoses appendicitis after a series of tests. An important point is to examine the patient with pressure on various parts of the abdomen. Sharp pain often occurs upon palpation in the navel or iliac region, when lifting the right leg from a sitting position. In the hospital, blood tests, urine tests, and ultrasound examinations are required.
Feeling the stomach on your own or trying to find out the source of pain is strictly prohibited. Severe inflammation can cause appendix rupture.
There are several safe tests that you can do yourself to confirm your diagnosis.
- Cough several times. The pain on the right side should intensify.
- Lie on your right side, press your knees towards you, take the “fetal position”. The pain will gradually ease.
- Turn on your left side, straighten your legs. The pain will immediately intensify.
- Lie on your left side. Using the palm of your right hand, lightly press on the area of pain. Quickly release your palm. The pain increases noticeably.
Diagnosis of appendicitis
If the disease does not manifest itself with typical symptoms, making a diagnosis can be difficult. Diagnostics includes taking an anamnesis, palpation, measuring pulse and temperature.
It is also necessary to do a blood test for leukocytes and other signs of inflammation. Diagnostic recommendations (depending on the complexity of the diagnosis) include:
- imaging methods (ultrasound);
- CT;
- endoscopic examination;
- x-ray (regular or with contrast agent);
- rectal examination.
For adult women, a gynecological examination is recommended to exclude diseases of the genital area (the stomach also hurts with diseases of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries). Similar to how the stomach hurts with appendicitis, fibrous nodes, cysts, ovarian tumors, and inflammation in the pelvis appear.
As part of the diagnosis, it is important to recognize the type of appendicitis:
| Type of disease | Typical manifestations |
| Catarrhal | Inflammation affects the mucous membrane, the appendix is swollen |
| Phlegmonous | Inflammation of muscle tissue, purulent, green appendix |
| Gangrenous | The appendix is black, thickened, fragile |
If there is a rupture, a sample is taken for cultivation and the cavity is rinsed. The patient is treated in the ICU and a nasogastric tube is used. He is discharged within 3-7 days after surgery. He can go to work 10 days after the appendix is removed, and play sports after 6 weeks.
What is appendicitis?
Appendicitis is a diagnosis that characterizes the inflammatory process in the appendix of the rectum .
So far, no clear reasons have been established that cause the inflammatory process, but the factors that provoke it have been identified.
Most often, an attack of appendicitis occurs due to blockage of the appendix:
- Foreign bodies;
- Neoplasms;
- Fecal stones;
- Helminths.
The disease occurs due to infection with certain pathogens . This most often occurs when hit by:
- Escherichia coli;
- Staphylococcus;
- Streptococci.
In some cases, blockage of the lumen of the appendix leads to the proliferation of bacteria , which indicates the relationship between the first and second causes of appendicitis.
If there are disturbances in the vascular system that nourishes the walls of the appendix, inflammation also occurs, leading to tissue necrosis. Excessive production of serotonin in the mucous membrane of the appendix can cause inflammation.
The disease appendicitis is a consequence of a malfunction of the body or its infection with pathogenic bacteria . It is very difficult to determine what caused the inflammatory process in a particular case - and for this purpose the appendage is sent for examination after the operation.
At-risk groups
Any malfunction of the digestive system can cause inflammation of the appendix. Various intestinal infections can cause this disease.
The risk of developing appendicitis is high in people who have any inflammatory process in the body and do not treat it. Pathogenic bacteria can migrate through the bloodstream throughout the body and cause a purulent infection in the appendix.
In most cases, appendicitis occurs in people who suffer from constipation . Most often, constipation is caused by protein foods, which cause putrefactive deposits.
Fecal stones block the junction of the appendix and the rectum. Remains of undigested food and the accumulation of helminths can lead to this. Appendicitis can be caused by various tumors in the rectum and appendix area.
Symptoms at different stages
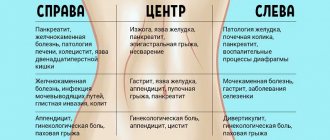
When appendicitis occurs, acute pain occurs on the right side in the iliac region of the abdomen . As a rule, such a symptom appears at the stage when the disease has turned into a phlegmonous form - and emergency surgery is required.
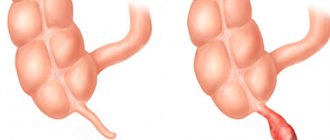
Catarrhal
Acute form of appendicitis , the duration of development of which is no more than 12 hours. At this stage, changes occur only in the mucous membrane of the appendix. Initially, the pain appears in the stomach area - and after a short time it covers the entire abdominal cavity.
A person cannot indicate a clear location of pain. Characteristic symptoms:
- Nausea and vomiting that do not bring relief;
- Dry mouth and increased body temperature;
- On palpation the pain intensifies;
- Pain increases when moving the body and walking;
- A defecation disorder occurs - a person cannot empty his bowels.
Phlegmonous
There is acute pain in the right iliac region of the abdomen. She is sharp in nature. This indicates the beginning of perforation of the walls of the appendix and purulent inflammation . Phlegmonous appendicitis develops within 24 hours from the onset of the disease.
This stage of the disease can only be diagnosed during surgery. The patient's condition is very serious - the exacerbation covers the entire appendix, purulent masses can lead to its rupture.
All signs of intoxication are observed:
- Increased body temperature;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Diarrhea or constipation;
- Increased body temperature.
On palpation, you can notice tension in the appendix area . During breathing, the right part of the iliac region lags behind the left. The pain intensifies when pressing on the area of the appendix.
In people who have a thin build, the surgeon may feel the appendix , which will resemble a thickened cushion.
Rupture stage
The person feels relief - the pain disappears. This indicates a rupture of the walls of the appendix, and after some time the patient’s condition will worsen significantly.
Peritonitis develops - purulent inflammation of the peritoneum, sepsis is possible. Tissue necrosis and damage to all abdominal organs are observed. Emergency surgery required.
Atypical forms of the disease
Typically, the appendix is located in the right iliac region of the abdomen, but due to the long mesentery that connects it, it can be displaced .
The appendix may attach to the right kidney, lower back muscles, or ureter. In this case, the disease is called retrocecal appendicitis .
With the development of this form, the pain is localized at the location of the appendix - and the organs that are located nearby suffer. If it is the kidney, then the person experiences frequent urination, acute pain, and elevated leukocytes in the urine test.
The appendix can be located in the pelvic region and in the intestinal plexuses. Sometimes it moves to the left. In cases of atypical location of the appendix, diagnosis of the disease becomes more complicated .
It is necessary to conduct a number of studies to exclude the risk of developing other diseases with similar symptoms.
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to examine the body by a qualified specialist . Typically it includes:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal area;
- Analysis of urine;
- Blood analysis;
- X-ray.
diagnostic laparoscopy may be prescribed , during which, in case of inflammation of the appendix, it is removed.
Women are advised to be examined by a gynecologist to eliminate the risk of ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage, which often have similar symptoms. In addition, additional examinations may be necessary to exclude diseases such as:
- Crohn's disease;
- Food poisoning;
- Renal colic;
- Adnexitis;
- Acute endometritis;
- Cholecystitis;
- Colitis;
- Peptic ulcer;
- Intestinal colic.
It is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own - an examination of the abdominal cavity, urine and blood is required.
But for pain in the epigastric region or at the location of the appendix, which is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, chills and problems with bowel movements, you must immediately call an ambulance.
Treatment of appendicitis
Currently, there are several ways to remove the appendix.
- The classic operation used in most cases is appendectomy . The vermiform appendix is removed through an incision in the peritoneum. The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
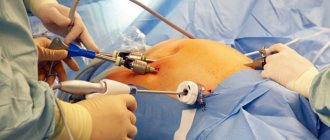
- A more modern removal technique is laparoscopic appendectomy . Small punctures are made in the abdominal area, into which instruments and special optical equipment are inserted. The surgeon performs the operation while watching his actions on the monitor.
The recovery period takes about 10 days. After the patient's stitches are removed, he is discharged from the hospital. In the future, he is registered with a surgeon for some time.
With laparoscopy, the recovery period is shorter, and the patient can be discharged after three days.
The first day after surgery, the patient can get out of bed only with the permission of the attending physician. A diet is indicated - you can only eat liquid and jelly-like foods. In the future, you can include porridge, fish, broths and fermented milk products in your diet.
A person is prohibited from lifting weights for about 3 months.
When surgery is performed at the stage of catarrhal appendicitis, the prognosis of the disease is positive. In cases of late diagnosis, the development of an abscess in the abdominal cavity and the formation of infiltrate are possible.
Dangerous complications of appendicitis are peritonitis and pylephlebitis, which are acute inflammatory processes in the peritoneum.
If there are complications during surgery, drainage is done, and after removal of the appendix, antibiotic therapy is indicated. The recovery period can be extended to a month.
If in case of peritonitis a person does not seek medical help, general intoxication of the body is observed, which can lead to death.
Possible complications after surgery:
- Formation of adhesions;
- Wound dehiscence;
- Postoperative hernia.
If all recommendations of the attending physician are followed, complications after surgery are extremely rare. The period after surgery should be aimed at restoring the body's strength . At this time, heavy physical activity, unhealthy foods and frequent stress are contraindicated.
Prevention
Appendicitis can occur in any person who has not had the appendix removed. It is impossible to protect yourself from this disease due to unclear reasons for its occurrence. In general, preventive measures boil down to:
- Proper nutrition;
- Preventing frequent constipation;
- Timely treatment of inflammatory diseases;
- Antihelminthic therapy;
- Healthy lifestyle.
Monitor the condition of your lymph nodes, preventing them from becoming inflamed. Read more about this here.
In the absence of gastrointestinal problems and normal intestinal motility, the risk of appendicitis is very low. People who do not have inflammatory problems, as well as vascular failures, rarely suffer from this disease.
Quite often, appendicitis is confused with other diseases of the stomach or intestines (colic, poisoning, etc.), but a ruptured appendix is deadly.
If inflammation of this part of the intestine is not recognized in time, the consequences can be dire. Therefore, every parent needs to know the enemy by sight.
Chronic appendicitis
Chronic appendicitis differs from the acute form of the disease in the variety of symptoms, the complexity of the examination, the surgical approach, and the duration of hospitalization and recovery. It occurs slowly or at intervals, with symptomatic periods alternating with asymptomatic ones.
Inflammation is often associated with urinary tract diseases and gynecological disorders. Its diagnosis is difficult; it is necessary to exclude other diseases similar to chronic appendicitis. The operation can be carried out as scheduled.
The advantage of removing a chronically inflamed appendix is the laparoscopic technique. The doctor works with a camera and 2-3 instruments inserted into the abdominal cavity through small incisions. The advantage of this technique is the possibility of better examination of the abdominal cavity than with classical surgery. The positive cosmetic effect after laparoscopic surgery (smaller scars), shorter hospitalization, and recovery period are also important.
Special forms of inflammation
The clinical picture of appendicitis depends on the atypical position of the appendix, changes in the patient's response due to age, pregnancy, and medication use. It is impossible to recognize a special form on your own; a specialized examination is required.
| Form of inflammation | Clinical picture |
| Retrocecular appendicitis | Pain, muscle contraction, painful extension of the limbs in the thigh when examining the patient on the left side |
| Laterocecal appendicitis | Pain on the right side of the abdomen (due to muscle contraction, pain may radiate to the lumbar region) |
| Pelvic appendicitis | Localization of pain near the symphysis, inguinal ligament, painful hip rotation, dysuric problems, diarrhea |
| Mesocoelial appendicitis | Pain around the navel, often without muscle contraction |
| Left-sided appendicitis | Pain, muscle contraction in the left hypogastrium, clinically simulating diverticulitis. Often it is possible to understand that it is the appendix that is inflamed only by examining the abdomen using imaging methods |
| Senile appendicitis | Possible absence of classic symptoms, in particular muscle contractions; inexpressible pain. The course of the disease is more severe, purulent complications and perforations are common |
Testing for inflammation in old age is difficult due to the body's reduced ability to respond to it. In children, the problem is inappropriate reporting of symptoms.
Particular symptoms of appendicitis in women
Any attending physician can tell exactly where appendicitis is located and its symptoms in women. With the right approach to diagnosis, this inflammation can be recognized even in its inception stage by:
- bloating caused by obstruction of the digestive tract;
- white or yellow coating on the tongue;
- unpleasant pulling sensations in the right side;
- loss of appetite;
- dry mouth;
- general malaise;
- rapid heartbeat;
- high blood pressure;
- pain in joints and bones.
How clearly you will experience the symptoms and signs of appendicitis depends on the degree of inflammation and the general condition of the body. In some cases, people may experience seizures and loss of consciousness. Manifestations of appendicitis of infectious origin develop most quickly.
Complications of acute appendicitis
Common complications in adults and children include:
- perforation of the appendix;
- peritonitis;
- periapendicular abscess;
- post-inflammatory adhesion;
- pylephlebitis.
The first signs of perforation are higher temperature and pain than with “simple” appendicitis. Perforation can lead to generalized peritonitis. Peritonitis leads to increased pain and contraction of the abdominal wall. The patient has a high fever and signs of severe toxemia.
A periapendicular infiltrate may develop over several days. The omentum and surrounding intestinal loops are gradually glued together with fibrin from the exudate. A painful, noticeable swelling forms in the right hypogastrium.
A periapendicular abscess is characterized by the presence of pus in a cavity bounded by the omentum and intestinal loops. The symptoms get worse by the day. A palpable, clearly defined, painful tumor of soft consistency develops in the right hypogastrium. The diagnosis is confirmed by ultrasound or CT.
Post-inflammatory adhesions can lead to recurrent ileosis or infertility in women.
Purulent pylephlebitis is thrombophlebitis of the portal venous system. Characterized by chills, high fever, and later liver abscesses. This is a rare but serious, even fatal complication.
Complications require immediate specialized therapy; attempts to alleviate them at home, in non-professional conditions, are unacceptable.
What can you take away from the information received?
Appendicitis is a common disease, incl. in children. It is important to recognize the signs of inflammation in a timely manner and to operate on it in a timely manner. This will help prevent complications from developing. To identify the disease, it is important to know on which side appendicitis is located in a child and an adult, and where it hurts. In most patients, acute appendicitis occurs with a typical clinical picture; its diagnosis is not difficult. But there are cases with a different clinical course, in which the diagnosis is confirmed or excluded only by surgery.
Causes of inflammation of the appendix
Acute appendicitis develops when the lumen of the appendix becomes blocked by a foreign body, parasites or tumor. Mucus accumulates inside, pathogenic bacteria multiply excessively, and the mucous membrane itself and adjacent tissues become inflamed.
The lumen can be closed by fecal stones, seed husks, small bones, and other solid objects that enter the digestive organs along with food.
The inflammatory process can also begin as a result of a chronic disease: colitis, enteritis, adnexitis. It has been statistically proven that acute appendicitis develops more often in people who have problems with bowel movements.