What can hurt on the left side?
According to statistics, left-sided pain in the lower abdomen bothers every 6th person on the planet at least once in their life. There are many known diseases that are characterized by the presence of this symptom. Pelvic pain in women can occur as a result of chronic or acute pathologies of the intestines, female reproductive organs or urinary system. Disorders of the pelvic lymph nodes, musculoskeletal system, or blood vessels can also cause problems.
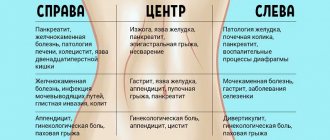
In most cases, the cause of left-sided pain in the lower abdomen is the organs located on the left side of the body:
| Spleen | An unpaired organ of the immune system that performs the functions of hematopoiesis and blood supply, located behind the stomach. The spleen is not a vital organ, since its functions are taken over by the liver and lymph nodes. |
| Small intestine | The section of the digestive tract in which digestion processes occur. The left part of the small intestine may hurt due to blockages and inflammation. |
| Colon | The lower part of the intestine, in which the processes of absorption of water from food debris and the formation of feces take place. Pain in the left lower abdomen can be caused by blockage or inflammation of the left transverse descending colon and its branches. |
| Left hip joint | Located in the area where the left femur connects to the pelvis. Any problems in this area can cause pain, and pathological processes affect not only bone tissue, but also muscles, tendons, cartilage, nerves and blood vessels. |
| Bud | One of the paired organs that perform the function of urine formation, located in the lumbar region. If there are disturbances in the functioning of the left kidney, left-sided pain may occur in the front or back of the body of varying degrees of intensity. |
| Ovary | One of the paired organs of the female reproductive system in which the formation of eggs occurs. With diseases of the left ovary, pain may occur in the lumbar region, radiating to the front of the body. |
| Uterus | The internal genital organ, the main purpose of which is the placement and development of the fetus during pregnancy. Left-sided pain can be caused by pathologies of the uterus itself, its cervix or the left fallopian tube. |
According to statistics, the cause of pain in the left lower abdomen in women is urological or gynecological pathologies. Less often, representatives of the fair sex suffer from disorders of the digestive tract and spinal pathologies.
Causes
Pain in the left side of the lower abdomen in women can occur both for physiological reasons and as a result of pathological lesions of internal organs and systems. In the first case, flatulence and fetal pressure on internal organs during pregnancy can cause discomfort. During menstruation, most women experience pain of physiological origin of varying intensity. There are also many serious diseases that cause pain in the lower abdomen and require immediate medical attention.
Adnexit
Adnexitis is a gynecological disease, which is characterized by the presence of an inflammatory process of the appendages: ovaries and fallopian tubes. The pathology is often diagnosed in women of reproductive age (from 20 to 35 years).
As a rule, the infection first enters the fallopian tube, and from there it affects the ovary. It enters the body through sexual contact or through the bloodstream. The causative agent of the disease can be any harmful microbes, in particular streptococci or staphylococci. The risk of getting sick increases for women who have undergone abortions, improper installation of intrauterine devices and other similar manipulations.
Symptoms of adnexitis:
| Temperature | sharp rise to 38-39 degrees |
| Menstrual cycle | the pain of menstruation increases, delays or prolonged bleeding are possible |
| Urination | pain, purulent or watery discharge |
| Discomfort | abdominal pain that increases during sex or increased physical activity |
The symptoms of adnexitis are similar to those of acute appendicitis, which makes diagnosis difficult. If left untreated, the disease develops into a chronic form, when the intensity of the pain subsides, but it is felt constantly. Against the background of hypothermia and during stress, the risk of complications increases: peritonitis, adhesions, infertility.
Ectopic pregnancy
Pain is one of the main signs of ectopic pregnancy. Unilateral constant or intermittent pain in the left side below the abdomen may indicate that a fertilized egg has implanted in the left fallopian tube. This is a dangerous condition that threatens a woman's life. Discomfort manifests itself even before the delay begins and the accompanying symptoms appear: chest pain, nausea. After physical activity or sexual intercourse, discomfort may intensify.
Cysts
Pain in the lower abdomen can occur due to an ovarian cyst - a benign formation that occurs as a result of pathological or physiological processes and has the shape of a thin-walled sac filled with fluid. Ovarian cysts occur in women of all ages. Predisposing factors are hormonal disorders and inflammatory processes of the internal organs of the pelvis.
The following symptoms indicate the presence of an ovarian cyst:
- unilateral pain in the lower abdomen, the intensity of which increases during sex, urination, or increased physical activity
- decreasing the intervals between the urge to urinate
- constipation
- nausea and vomiting (characteristic of the acute course of the disease)
- increase in body temperature when an inflammatory process occurs
- inability to get pregnant
- abdominal swelling
A cyst is diagnosed based on ultrasound and visual examination. Additional tests and examinations may also be needed.
Types of ovarian cysts:
| Name | Peculiarities | Symptoms |
| Follicular | formed in the ovarian follicle, the membrane consists of connective tissue | symptoms are mild or absent, cycle disruptions and pain in the lower abdomen are observed |
| Corpus luteum cyst | formed in women of reproductive age due to impaired blood supply to the corpus luteum at the site of burst follicles, may contain blood clots | symptoms are either completely absent or there is pain in the lower abdomen |
| Paraovarian | occurs in the area of the fallopian tubes and ovaries, more often diagnosed in girls during puberty | pain in the lower abdomen, swelling; menstrual irregularities; infertility |
| Endometrioid | formed when endometrial cells and ovarian tissues grow together, can burst and cause inflammation of the abdominal cavity (peritonitis) | lower abdominal pain; menstrual irregularities |
| Cystic tumor | poses a danger to a woman's life | looks like a cyst |
In most cases, cysts go away on their own within a few months, and complications occur less frequently. If removal of the formation is required, a simple operation is performed - laparoscopy.
Endometritis
Inflammation of the upper mucous membrane of the uterus, which matures every cycle and is shed during menstruation, is called endometritis. Entry of the pathogen into the uterine cavity can cause an acute or chronic course of the disease. Provoking factors are childbirth, cesarean section, abortion, curettage and other similar manipulations. The causative agents of endometritis are harmful microbes and microorganisms: viruses, fungi, bacteria, etc.
Symptoms of the acute course of the disease:
- increased body temperature, fever
- lower abdominal pain
- purulent vaginal discharge
- increased heart rate
- discomfort when urinating
If acute endometritis is not treated, the disease becomes chronic. This pathology often causes infertility, pregnancy failure, and complications during pregnancy.
Endometriosis
The growth of endometrial cells (the inner layer of the uterus) into other tissues of the uterus and nearby organs is called endometriosis. Diagnosed in women of teenage and reproductive age. During endometriosis, endometrial cells form growths that cause pain, discomfort, and complicate the processes of fertilization of the egg and gestation. Growths form in the area of the ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, vagina, rectum, and intestines. During menstruation, these formations are rejected, but do not come out. This leads to internal bleeding and inflammation, and tissue scarring.
Symptoms:
- severe pain during menstruation and sexual intercourse
- irregular or excessively heavy periods
- fatigue, loss of performance
- pain in the stomach and lower back
- stool disorders
To make a final diagnosis, laparoscopy is prescribed, during which the possibility of oncological pathology is excluded.
Pathologies of the genitourinary system, gastrointestinal tract
Diseases associated with the genitourinary system and gastrointestinal tract can cause pain in the left side of the abdomen. There is a large list of such diseases that differ in localization, intensity, and characteristic manifestations. Diagnosis and treatment of such problems should be carried out by a specialist.
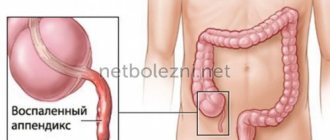
Appendicitis and cholecystitis
The appendix is a ventricular appendage located in the lower part of the intestine. This is a branch of the cecum, narrowed towards the bottom, without a lumen. The appendix is not a vital organ. For a long time it was believed that it does not perform any functions, but modern scientific research proves the opposite. There is reason to believe that this organ is important for the functioning of the immune and endocrine systems, regulating the amount of beneficial microflora in the intestines.
Inflammation of the appendix manifests itself in an acute form; the chronic form of the disease is less common. Due to the accumulation of pus, the appendage increases in size. Often inflammation leads to rupture of the appendix and the development of complications in the future: sepsis, abscess, peritonitis. Without urgent surgical intervention, the likelihood of death increases.
Symptoms:
- acute pain in the lower abdomen (usually on the right, but there are also cases with left-sided pain)
- increase in body temperature
- vomiting and nausea
- Kocher's symptom (movement of the localization of pain in the abdominal area)
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. Its manifestations are similar to those of appendicitis. The disease is caused by a violation of the outflow of bile. In most cases, the provoking factor is stones in the bile ducts. With repeated repetitions of acute cholecystitis, the disease becomes chronic. Pain with cholecystitis occurs after eating fatty or spicy foods or alcohol. Unpleasant sensations increase during stress or excessive physical activity. With biliary colic, the pain is localized in the abdomen, hypochondrium, back, and shoulder blades. Such conditions require urgent medical attention.
Inflammatory process and infections
Infections of the pelvic organs occur as a result of pathogenic viruses and bacteria entering the body, provoking severe inflammatory processes.
Symptoms of infections of the female genital organs include:
- dull pain in different localizations of the abdominal area
- Over time, discomfort moves to the lumbar region
- missed periods
- uncharacteristic vaginal discharge, burning sensation
- redness and itching of the vagina and labia
- temperature increase
- dehydration
- fatigue
- loss of appetite
- severe pain during menstruation
Viral and bacterial infections require urgent treatment and timely consultation with a specialist.
Contraception
While taking some oral contraceptives, hormonal changes occur and pain may be experienced in the abdominal area or below it. If the pain does not go away for a long time, it is recommended to consult a specialist and change the drug. Incorrectly installed intrauterine devices, in particular the IUD, can cause pain on the left side below the abdomen. In this case, you need to consult a doctor.
Types of pain and associated symptoms
The intensity of pain in the lower abdomen indicates the severity of the pathology and can also help in diagnosing the disease. Before the doctor arrives, it is forbidden to independently relieve discomfort with painkillers and compresses.
Aching dull pain
Similar sensations are experienced by women suffering from problems with the reproductive system. Inflammation of the internal genital organs is usually accompanied by an increase in temperature, deterioration in general well-being, and loss of performance. Also, aching, dull pain is accompanied by some non-inflammatory diseases and menstrual irregularities. Discomfort increases during sexual intercourse.
Possible causes of aching, dull pain:
- left lymph node enlargement
- varicose veins
- haemorrhoids
- bladder pathology
Nagging pain
A nagging pain in the left side is usually of low intensity and varies in frequency. Occurs with purulent pathologies, strangulated hernias, and cancer. As the tumor grows, discomfort increases and pain increases. Other serious symptoms may occur: nausea, fever, changes in the size of lymph nodes, etc.
Sharp pain in the side
Spasms of the pelvic organs, increased gas formation in the intestines, effects on nerve endings are the causes of sharp pain in the side below the abdomen. Such conditions indicate an acute course of diseases of the internal organs.
Stitching pain
Colic or paroxysmal stabbing pain in the left side is a sign of kidney or intestinal pathologies. This is a dangerous symptom that may indicate one of the following problems:
- inflammation of joints, cartilage, lower back (shooting pain)
- increased gas formation in the intestines (pain subsides after going to the toilet)
- ovarian cyst rupture
For correct diagnosis, it is necessary to pay attention to the accompanying symptoms that occur in combination with left-sided pain. As a rule, this is a change in temperature, diarrhea, nausea, etc.
Description of the disease
It mainly affects the left side of a woman when there is a malfunction in the digestive system, urinary tract, or reproductive organs. The possibility cannot be excluded: pinched nerves in the lumbar spine; disruption of innervation due to Crohn's disease; excessive tension in the abdominal muscles; intensive gas production; high sensitivity during ovulation and menstruation.
It is important to clearly determine the reason why the left side hurts and pulls, since this determines which specialist will develop treatment tactics, adequate prescription of medications and the end result - the prognosis for recovery.
Left-sided sensations of pain are a wide group of changes in the peritoneum with local discomfort:
- under the navel, in front of the body;
- under the lumbar area, on the back of the body.
Pain is a complex pathophysical mechanism. It differs in different people, with an identical pathological process. Soreness can be causeless - it does not have an obvious source of the problem, but still, from time to time it can pull on the left side.
The pain focus is concentrated locally in the following cases:
- disruption of blood circulation;
- failure in metabolic processes;
- destructive disorders, inflammation;
- changes in organs of various etiologies.
At the beginning of the development of the disease, unpleasant sensations are concentrated at the location of the outbreak. Further, the pain can be reflected and form secondary foci. This development of pathology leads to a loss of connection with the first symptoms. At the final stage, an expansion of trophic disorders and an increase in the volume of the focus of pain concentration are observed.
When the left side of a woman’s abdomen is pulled, this means that the patient may well suffer from diseases in the field of gynecology, urology, have problems with the digestive organs, or be a patient in the surgical department. According to statistics, a large proportion of patients experience symptoms due to dysfunction of the reproductive organs for various reasons, and urological ailments. Up to 15% of patients complain of pain in the left side due to orthopedic diseases.
Every person at least once in his life has encountered pain, a pulling sensation in the side or lower abdomen. On the left side there are various organs that, due to pathology, can cause pain.
The doctor must identify the organ or systemic disorder that provokes the formation of spasm. The first person a patient usually sees is a family therapist. If your left side feels tight during pregnancy, this is not always considered a pathology, but full attention should be paid to the problem.
What to do
If the pain in the lower abdomen is mild or caused by increased gas formation, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines. You can take a special drug to reduce the symptoms of bloating with a sufficient amount of water.
Dangerous symptoms in which it is recommended to urgently consult a doctor:
- sharp sharp pain
- presence of accompanying symptoms: deterioration of health, diarrhea, fever, loss of appetite or vomiting
- abdominal pain during pregnancy
- persistence of pain for more than 1-2 days
- bowel disorder: diarrhea or constipation
- urinary disorders
- prolonged bloating
- pain radiating from the left side of the abdomen to the neck, shoulders, chest
Treatment of left-sided lower abdominal pain in women should be carried out as prescribed by a specialist. If you feel a sharp sharp pain, you need to take a comfortable position, relax and wait for the doctor to arrive. You can treat menstrual pain on your own after consulting your doctor. For this, painkillers and sedatives, compresses to the abdominal area, and light massage are indicated. During this period, it is recommended to limit physical activity and get more rest.
Which doctor should I contact?
If there is discomfort in the left lower abdomen, a woman should seek medical help. First of all, it is recommended to visit a general practitioner or family doctor, who will issue a referral for a consultation with a specialist doctor:
- gastroenterologist
- gynecologist
- urologist
- proctologist
- surgeon
- oncologist, etc.
In the future, the patient is shown a comprehensive diagnosis, based on the data of which treatment is prescribed.
Classification of pain
It should also be remembered that pain in the lower abdomen can be different.
Therefore, it should be remembered that its character is of great importance in making a diagnosis:
- Aching. Pain is characteristic mainly of inflammatory pathologies.
- Stabbing. This can be either an acute inflammatory process or a pathology associated with a space-occupying formation.
- Sharp. In this case, pain in the lower abdomen occurs due to non-inflammatory diseases. These include ectopic pregnancy, cyst rupture, etc.
- Bursting. This type of pain is characteristic of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract or one of the stages of the inflammatory process.
Diagnostics
For pelvic pain of any intensity, it is recommended to urgently undergo a comprehensive examination. In some women, diseases of the pelvic organs are completely asymptomatic. Without timely medical care, severe complications develop from the genitourinary, lymphatic, digestive and other systems of the body.
The diagnosis for left-sided pain in the lower abdomen is based on:
- data from a visual examination of the patient by a doctor
- ultrasound data of internal organs
- results of blood and urine tests, which help determine the presence of an inflammatory process
Depending on the severity of the disease, the examination is carried out by one or more specialists. Based on the examination results, a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed.
What to do in case of pain attacks
To find out why the left side hurts and pulls, diagnostic tests are performed. The therapist determines which specialist to refer the patient to after conducting a thorough examination, listening to complaints, and collecting an anamnesis.
The doctor is interested in:
- is there a delay in menstruation;
- Is your left side cramping until your period?
- Does your left side feel tight after eating?
- does the left side feel tight after ovulation?
- does the left side pull when walking?
- does the left side pull when bending over?
- Does your left side hurt after ovulation?
It is necessary to understand that if the left side feels tight in the early stages of pregnancy, this can be caused not only by physiological displacement of organs, but also by all possible pathological causes that should be identified without delay.
Additional diagnostic methods are also prescribed:
- general tests;
- blood biochemistry;
- CT (diagnostic method, computed tomography);
- MRI (diagnostic method, magnetic resonance imaging);
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination);
- ECG (diagnostic method, electrocardiography);
- gastroduodenoscopy (colonoscopy).
But usually the pain comes unexpectedly and requires emergency measures. The patient’s condition and the further outcome of treatment depend on the confident actions of nearby people. Algorithm of actions when providing first aid:
- the patient should be reassured, told that medical help will arrive any minute;
- position the patient in a horizontal position;
- Apply a cold compress to the painful part;
- in case of hyperthermia, it is allowed to take antipyretics;
- In order not to smooth out the clinical picture, taking pills is extremely undesirable.
Further actions are carried out by medical workers.
Treatment
Treatment of left-sided lower abdominal pain in women is aimed at relieving unpleasant symptoms and getting rid of the cause of the problem.
Treatment methods for lower abdominal pain:
- Conservative therapy is taking medications in combination with traditional medicine prescriptions as prescribed by a doctor.
- Physiotherapy is the use of special healing techniques to relieve pain symptoms and combat the cause of the disease.
- Surgical intervention is carried out in emergency cases, if there is a threat to the patient’s life.
For diseases of the genitourinary system, careful adherence to the rules of intimate hygiene is indicated. During treatment it is necessary to abstain from sexual acts. For intestinal diseases, it is important to regulate your diet and exclude foods that cause increased gas formation and fermentation. The daily diet should be selected in accordance with the recommendations of a specialist.
Prevention
Prevention of pain in the lower abdomen involves timely consultation with a doctor at the first signs of illness. To avoid increased gas formation, you need to adhere to a special diet. It is usually recommended to exclude dairy products, raw vegetables and fruits, legumes, fatty, fried, salty or sweet foods from the diet. Observing personal hygiene rules will help you avoid diseases of the genitourinary system. Women need to visit a gynecologist for preventive purposes at least once every 6 months. Pregnant women should register with a doctor in a timely manner and undergo all necessary examinations.
Prevention of lower abdominal pain
Preventive measures:
- Lifestyle changes.
- It is necessary to regularly visit specialists and at the first pathological symptoms it is worth starting to diagnose it and treat it in a timely manner.
- In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to the quality of sexual life , casual sexual intercourse should be avoided, as well as the lack of protective equipment with people who have not been tested for sexually transmitted infections.
- Maintain personal hygiene measures , especially when traveling.
- Monitoring the state of immunity , regular nutrition, adequate sleep, prevention of respiratory and other types of infections.