One of the most common health problems among women is pain in the lower abdomen. Often the origin of pain is not fully understood, as its cause can be a number of underlying factors and diseases that need to be diagnosed. Basically, pain in a woman’s lower abdomen is associated with the structure of the body, her genitals and the physiological processes that take place in the reproductive system.
It is important to remember that any pain in the lower abdomen in a female may indicate the presence of a dangerous disease requiring drug treatment or surgical intervention. The consequences of prolonged pain in the lower abdomen can lead to prolonged discomfort, restrictions in movement and action, even disability.
You can make an appointment for the treatment of lower abdominal pain in women at the “MyVrach” medical center. Our qualified doctors will conduct an examination, give advice and determine further diagnosis and treatment for pathologies and inflammatory processes.
Nature of pain
When pain occurs, women consult a doctor. After conducting a general examination, he asks about the nature of the pain. They may be as follows:
- pulling
- characteristic of menstrual syndrome; - acute
- occur during inflammatory processes; - cutting
- occurs with urolithiasis, pancreatitis; - dull
- appear when the inflammatory process enters the chronic stage; - pulsating
- blood vessels enter a pathological state; - aching
- often occur during pregnancy in the later stages of bearing a child due to compression of the internal organs by the uterus.
Based on the nature of the pain, the doctor suggests a diagnosis. But it is impossible to put it on the basis of these data. Additional tests are required using laboratory and instrumental examination methods.
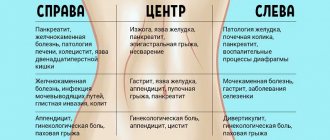
If the organ is paired, pain occurs on the left or right side.
The type of painful sensations is indicated in the medical history in order to identify the trend of their changes at the patient’s next visit. For example, when treating dysmenorrhea, acute pain can turn into aching pain. Then it disappears completely, but with proper treatment.
Pain during pregnancy
Pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy is especially common at the beginning of pregnancy. The causes of discomfort are different:
- stretching of the uterus during fetal growth;
- stretching of the ligaments that support the uterus;
- pressure from the enlarged uterus on the organs located around it.
To relieve pain during pregnancy, pregnant women are advised to walk more often, not do heavy physical work, and not be nervous.
Proper nutrition is necessary. In order not to overload the stomach, you should eat food in small portions, but several times a day. This way, the stomach and intestines will not be overloaded and cause additional pain. If discomfort in the lower abdomen in a pregnant woman does not subside and continues for a long time, you should consult a doctor.
Physiological causes of pain
Discomfort in the lower abdomen does not necessarily mean the development of the disease. The cause may be physiological processes that normally occur in every patient during her life. After a while they pass. The following states are distinguished:
- menstruation - discomfort is caused by rejection of the uterine mucosa;
- ovulation - release of an egg with a change in hormonal levels;
- conception, during which the fertilized egg attaches to the uterus, the hormonal balance is rearranged;
- temporary gastrointestinal changes caused by food intake.
Changes in the digestive tract occur not only due to poisoning or inflammation. Bacteria of opportunistic microflora are located in the intestines. If their ratio changes, increased gas formation occurs. It leads to painful sensations.
Despite the possibility of physiological abnormalities in the condition of the gynecological organs, it is recommended to undergo testing to exclude pathology. An experienced doctor will use a small number of diagnostic tests to rule out an inflammatory process.
Diagnosis of lower abdominal pain
Diagnosis of female pain in the lower abdomen, depending on the root cause in the digestive and genitourinary system, is carried out by an obstetrician-gynecologist or gastroenterologist. It is possible to involve specialists from related fields of medicine.
When examining a woman, the action plan usually includes the following points:
- Collecting the patient's medical history;
- Examination on the chair, palpation;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs in a woman;
- Ultrasound during pregnancy;
- Carrying out endoscopic procedures - hysteroscopy, colonoscopy;
- Carrying out x-rays of the intestinal mucosa and genitourinary system.
Pathological causes of pain
If an inflammatory process develops in the internal organs, pain always occurs. It can be constant or paroxysmal. It is forbidden to use antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs on your own. This will lead to complications and hormonal imbalances. Discomfort may be associated with inflammation of the following organs:
- urinary system (urethritis, cystitis, urolithiasis);
- uterus (endometriosis, bacterial infection);
- ovaries (polycystic);
- fallopian tubes.
Sharp pain in the middle of the abdomen may occur in pregnant women. This is due to excessive fetal movements in the last stages, the onset of the labor process, and the risk of premature birth.
When the kidneys are damaged, the pain is localized not only in the abdomen, but also on the side.
In addition to the genitals, the lower part of the digestive system is located in the lower abdomen. Intestinal dysfunctions are possible, causing acute pain. The reason is inflammation, infection, malignant or benign neoplasms, injuries.
Painful menstruation as a cause of pathology
The woman experiences discomfort or severe pain. It intensifies when bending, squatting, or standing. This is called dysmenorrhea. Unpleasant sensations increase with any movement, sneezing, coughing.
The first painful signs in the back occur 1 day before the rejection of the uterine mucosa. The next day, stabbing attacks occur, radiating into adjacent tissues. For example, sacrum, lower back.
There are 3 stages in the pathological process, described in the table.
| Stage of dysmenorrhea | Description |
| 1 | Discomfortable sensations that do not create sharp pain. Do not take painkillers |
| 2 | The patient's body temperature rises and chills occur. Taking medications to relieve vasospasm |
| 3 | Pain when moving. Tachycardia and arrhythmia occur. This is due to hormonal changes and inflammation of internal organs. Taking painkillers |
A severe process is formed due to pathology. Instrumental and laboratory examinations are required to identify the cause. More often it goes like this:
- sexual infections;
- inflammatory process in the vagina, uterus, ovaries;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- cysts, abscesses;
- the presence of a spiral as a method of contraception;
- thyroid dysfunction.
Improved nutrition, sleep, and exercise help in treatment. This will not help with diseases of the internal organs. Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and hormonal therapy is required.
Damage to the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries
Many diseases of the uterus and fallopian tubes are accompanied by pain. Some of them lead to infertility caused by the formation of adhesions due to inflammation. The following pathological conditions are distinguished:
- oophoritis - an inflammatory process of the ovaries with the presence of a cyst;
- myometritis - damage to the muscle tissue of the uterus;
- endometritis - inflammation of the endometrium of the uterus;
- salpingitis is a lesion of the fallopian tubes, often resulting in adhesions.
These pathologies are caused by bacteria and fungi that cause an immune response, damage to cells and tissues. Of the microbes, sexually transmitted sexually transmitted diseases are especially dangerous. In addition to pain on a certain side, the disease can be suspected based on the following clinical symptoms:
- discharge mixed with pus, blood (can be brown, green, yellow, red);
- painful sexual intercourse accompanied by bleeding;
- painful urination;
- dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain);
- fever.
If we are talking about paired organs, that is, the fallopian tubes or ovaries, they look at the area where the discomfort is strongest. For example, if a patient experiences pain on the left side of the lower abdomen, polycystic ovarian disease in this area may be the cause. The condition can be confirmed by ultrasound and other instrumental studies.
Gastrointestinal diseases
A common cause of acute pain is poisoning. It can occur due to the consumption of low-quality products or alcohol intoxication. There are other diseases:
- intestinal infection - penetration of salmonella, dysentery, and other bacteria;
- pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas;
- intestinal dysfunction;
- benign neoplasms in the intestines (polyps);
- mechanical damage to the mucous membranes.
If an attack is caused by an imbalance in the intestinal microflora, colic occurs. That is, air bubbles move throughout the organ, forming swellings. Irritable bowel syndrome appears.
Based on the symptoms, the doctor determines the pathology of the digestive tract; additional dyspeptic signs distinguish it from gynecological diseases.
Frequent diseases are accompanied by impaired stool formation. This could be constipation or diarrhea. The appearance of vomiting dehydrates the body and leads to malaise. Gastroenterologists and infectious disease specialists determine pathology by the symptoms that appear. If a misdiagnosis is suspected, it is best to perform diagnostic tests.
Causes of symptoms
Heaviness in the lower abdomen can occur for many reasons, for example, as a harbinger of menstruation or as a result of serious organ diseases. Some people have very enviable patience and can endure pain for so long that irreversible processes begin in the body. There is no need to start the situation by realizing the pain; you need to try to understand its origin in order to go to the right doctor.
So, heaviness in the lower abdomen can occur for the following reasons:
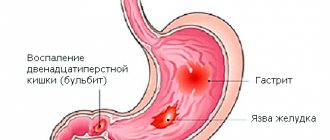
- Stomach diseases. In this case, the heaviness in the lower abdomen is accompanied by nausea and lack of appetite. These symptoms may mean exacerbation of gastritis, stomach ulcers, or the appearance of a tumor. In this case, you need to seek examination from a gastroenterologist.
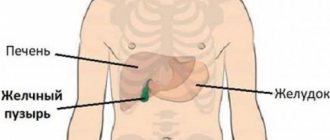
- Heaviness in the lower abdomen can cause diseases in other organs of the digestive system. In this case, there is nausea, headache and a feeling of bitterness in the mouth. All this indicates liver disease, gall bladder or problems in the duodenum.
- If the temperature rises, chills begin, in addition to a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen, then there is no need to endure it, you should urgently consult a doctor. After all, all this indicates inflammatory processes in the pelvis. Perhaps the problems are related to the rectum.
- If discomfort occurs in the lumbar region, there is also pain when urinating, there is blood in the urine, the reasons for this are kidney disease. A urologist will help here. You cannot delay this, because pain, in case of kidney inflammation, can cause shock, and this can lead to cardiac arrest.
- Pain in the lower abdomen in women can cause inflammation of the female genital organs. They can occur both from banal hypothermia and from a more serious disease: cancer. A gynecologist will help you deal with the problem.
- Pain in the lower abdomen may be associated with diseases caused by fungi (staphylococcus and streptococcus) in the vagina. This is the so-called vaginosis. In this case, pain in the vagina occurs, often with discharge.
- The pain may be caused by an ovarian or Bartholin gland cyst. Such diseases rarely manifest themselves. The only symptom is pain in the lower abdomen.
- The resulting polyps on the cervix can also be manifested by the presence of discomfort in the lower abdominal cavity.
- Pain in the lower abdomen can be caused by uterine fibroids, a benign tumor formed from connective tissue. Fibroids can grow to a significant size and put pressure on the organs around the uterus.
- Varicose veins in the pelvis can also cause pain. The reasons for the occurrence of such a disease may be that a woman often experiences severe physical overload. If she has gone through several abortions or, conversely, is a mother of many children, and also if she has no sex life, all this leads to varicose veins.
- An ectopic pregnancy may present with pain in the lower abdomen. It is very difficult to diagnose such a disease in the early stages, since it occurs in the form of a normal pregnancy. However, after 6-8 weeks, the fallopian tube, in which the fetus has consolidated and developed, bursts and severe bleeding occurs. In this case, there is no time to waste; you must immediately call an ambulance, otherwise the woman may die from blood loss.
- Inflammation of the cecum, or simply appendicitis, can also cause a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen.
- The causes may be harmless, familiar and predictable. For example, such pain occurs during menstruation or in early pregnancy.
Thus, any pain in the lower abdomen must be examined in a specialized institution using medical equipment and undergoing the necessary tests.
After all, pain can mean a serious illness, often incompatible with life.
Diagnostics of deviations
When a patient comes to the doctor with complaints, it is not always possible to make a diagnosis based on a general examination and complaints. Therefore, comprehensive research is carried out. They prevent the risk of prescribing the wrong treatment.
- General inspection. Assessment of the genital organs, skin, mucous membranes.
- Palpation. The localization of pain is determined by palpation and pressing. The doctor taps the stomach with his fingertips, identifying the area of discomfort. They start with the kidneys, gradually going lower.
- General clinical examination of urine and blood, biochemical test. Identification of cellular composition and foreign elements.
- Smear from the vagina, uterus. Diagnostics of microflora contents, identifying bacteria and fungi.
- Biopsy of the uterus. The test is carried out in the presence of erosion. It excludes malignancy.
- Colposcopy. The condition of the intestines, the presence of new formations, and the inflammatory process are assessed.
- Ultrasound. The screen shows the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, urinary system, and intestines. Determine the inflammatory process on the left or right.
- Hysteroscopy - assessment of the internal contents of the uterus.
- Laparoscopy. A small hole is made on the woman’s stomach through which a probe is inserted to examine the internal contents.
Using methods, a diagnosis is made. Pathogenetic and symptomatic treatment begins. Repeated studies evaluate the quality of therapy.
Treatment of pathologies
The method of therapy depends on the presence of a physiological and pathological process. In the first case, symptomatic treatment in the form of painkillers will be required. If a woman has a disease, temporary pain relief will not work. It is necessary to identify the source of tissue damage and eliminate it.
The therapist makes the diagnosis and refers the patient for examination. After determining the cause, the help of specialized doctors will be required. These include a gynecologist, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, urologist, and neurologist. The choice of doctor depends on the area of development of the disease.
If therapy is not carried out in a timely manner, inflammation and bacterial infection can spread to neighboring tissues. For example, women often experience bacterial or fungal vaginosis.
This causes discomfort that sometimes stops. But further damage spreads to the tissue of the uterus and ovaries. This causes adhesions and the formation of infertility.
Diseases of the urinary system
The organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Inflammatory processes can occur in any department. The following methods of drug therapy are used:
- antibiotics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs based on diclofenac;
- steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs based on dexamethasone, hydrocortisone;
- diuretics - increase diuresis, reduce swelling (Furosemide);
- herbal mixtures that eliminate the inflammatory process, sand, bacteria (Cyston, Canephron).
The drugs are taken orally, they act systemically on the body, but the greater effect is on the urinary tract. Sometimes the use of medications is not enough. Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. Electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, and infrared radiation are common among them. Blood flow and metabolism improve, and the regeneration of damaged cells is stimulated. Surgery is rarely performed. It is indicated for tissue necrosis and a sharp decrease in organ function.
Diseases of the reproductive system
Therapy is selected with caution to eliminate the risk of infertility. This is especially true for women of childbearing age. The following medications are used:
- antiseptics, antibiotics in suppositories (Sintomycin, Clindacin);
- antifungal drugs in suppositories or tablets for intravaginal use (Livarol);
- oral antifungals (Irunin);
- anti-inflammatory medications for vaginal use;
- hormonal oral drugs (Duphaston).
If erosion develops on the uterus, cauterization is used to remove the source of damage and prevent it from developing into a malignant form. Surgical interventions are used, most often using laparoscopy. A small incision is made in the woman's abdomen through which manipulation is carried out. This eliminates lengthy recovery time after the procedure.
A surgical method may be needed to remove part of the uterus, ovaries, eliminate polycystic disease, and adhesions.
Physiotherapy methods are also used in gynecology. The uterus has many blood vessels that supply it with blood. With the help of heating, blood flow increases, additional capillaries appear, and the tissue is restored.
If the patient develops dysmenorrhea, she is indicated for therapy. A painful menstrual cycle can lead to serious consequences. It is recommended to use hormonal therapy and injections of painkillers.
Pathologies of the digestive tract
Pain in the lower middle of the abdomen may be a sign of intestinal dysfunction. To eliminate it, you may need medications taken orally or anally. The following categories of drugs are used:
- antiseptics, antibiotics;
- sorbents for removing toxins, bacteria, viruses (Polysorb, Enterosgel, activated carbon);
- strengthening medications to eliminate diarrhea (Motilium);
- laxatives against constipation (Duphalac), used orally or as suppositories;
- products that restore intestinal microflora (Linex, Normobakt).
If the pain is caused by obstruction, benign intestinal formations, or mechanical damage, surgical interventions are used. It can be performed using large incisions or using laparoscopy.
Doctors recommend medications used in the form of suppositories. They act only on the affected area and do not affect the body. In severe conditions, it is recommended to use tablets and suspensions to quickly ease a person’s well-being. For example, when the gastrointestinal tract is infected with the formation of vomiting, diarrhea, and fever.
The importance of timely identification and treatment of pathology
When the source of damage just begins to develop, it is easy to eliminate it. This requires medications and physiotherapy. Gradually, the inflammatory focus increases, spreads to neighboring tissues, and causes complications. At this stage, the use of heavier medications will be required.
When the patient does not see a doctor for a long time, using only painkillers. Dire consequences arise. They can lead to loss of kidney function, the appearance of large stones in the bladder, infertility, and intestinal obstruction. These pathologies sharply worsen the standard of living and can cause death.
If antibiotic therapy is used, the dosage is strictly adhered to. You should not take medications for more than 7-10 days. This will lead to resistance of pathogenic microflora, which will cause abundant spread throughout the body. Bacteria can enter the systemic circulation. The same rules apply to other drugs. If the medication does not work or your health worsens, the therapist will replace the medication; changing it yourself is prohibited.