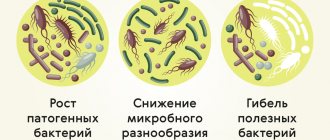
As statistics show, every adult has encountered intestinal dysbiosis to one degree or another at least once. This deviation is characterized by an imbalance in the intestinal microflora, when the number of beneficial bacteria decreases, giving way to pathogenic ones. Since beneficial bacteria perform many important functions in the body (synthesize vitamins, break down dietary fiber), a decrease in their number in the intestines has a detrimental effect on the general condition of the body. Therefore, dysbiosis cannot be left untreated.
Normal microflora
This focus on the tiny inhabitants of the human intestine is explained by the fact that these microorganisms have an extremely positive effect on health. They have many beneficial functions. So, beneficial microflora:
- protect the intestinal mucosa from infectious agents, allergens, and excess opportunistic microbes;
- synthesizes vitamins (especially group B), antitumor substances, enzymes for the breakdown of proteins and sugars;
- neutralizes toxins and harmful metabolic products;
- reduces cholesterol;
- activates immunity:
- produces short-chain fatty acids, which ensure the integrity of the colonic mucosa;
- stimulates the absorption of necessary substances (water, iron, calcium, gases, vitamins E, D).
In addition to beneficial microbes (bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, etc.), opportunistic microorganisms (Klebsiella, Proteus, staphylococci, atypical Escherichia, Serracia, Enterobacter, yeast-like fungi, etc.) live in the intestine. In a healthy person, their number is strictly limited, so they do no harm. But when immunity drops, after intestinal infections, stress, etc. these insidious bacteria and fungi are activated, begin to multiply and have adverse effects, leading to clinical symptoms.
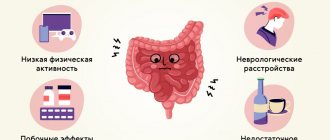
Causes
Dysbacteriosis does not necessarily develop in people with health problems. Quite often, the problem can appear in adults and children who have never previously experienced any problems with the digestive system.
The main reasons for the development of dysbiosis may be the following:
- Incorrect use of certain medications;
- Sudden change in food type;
- Eating poor quality food;
- Lack of fortified and fermented milk foods in the diet;
- Recent intestinal infections;
- Frequent use of antibiotics;
- Insufficient protection of the immune system;
- Having acute or chronic diseases - gastritis, pancreatitis, etc.
At the initial stages of development, dysbiosis may practically not make itself known. A person may only occasionally suffer from minor abdominal pain, bloating, and rare stool disorders.
How to treat flatulence at home?
The main way to treat increased gas formation at home is diet therapy. Avoid legumes, beer, kvass, baked goods, limit the consumption of apples and cabbage. All these products cause fermentation. It will be useful to include crumbly cereals, boiled vegetables, and fermented milk products in your diet.
In the absence of individual intolerance, home therapy can be supplemented with herbal decoctions. Teas based on mint, chamomile, dried ginger, and cumin seeds help relieve increased accumulation of gases. Young children can make dill tea.
The cause of bloating and increased accumulation of gases in the intestines may be a pathological process or infection. Treatment of flatulence includes taking medications prescribed by a gastroenterologist.
Symptoms of intestinal dysbiosis
In adults, the symptoms of dysbiosis are varied in their manifestation and severity. The severity of their manifestations depends on conditions such as age, lifestyle, immune system, and stage of development. In one person, a week of antibiotic therapy will cause only a slight disruption of the intestinal microflora, while in another it will cause severe symptoms of dysbiosis.
- Stage 1 of dysbiosis is characterized by a slight imbalance of normal and pathogenic bacteria. This condition may be due to a short course of taking antibacterial drugs or a change in usual food and water. At this stage, symptoms are mild and may be limited to minor intestinal upset. After completing antimicrobial treatment or getting used to new nutritional conditions, the balance of intestinal microflora is restored independently.
- At stage 2, the intestines cease to produce sufficient quantities of enzymes necessary for normal digestion of food. The result of this may be a fermentation process characterized by bloating, bitterness in the mouth, pain, flatulence, constipation or diarrhea. These symptoms may indicate the development of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, but most often indicate progressive dysbiosis.
- Stage 3 requires medical intervention, since pathogenic flora, affecting the intestinal walls in large quantities, causes inflammation. Symptoms become more pronounced, the patient experiences nausea and vomiting, undigested food fragments can be seen in the stool, patients complain of severe abdominal pain, and body temperature may rise.
- At stage 4, pathogens almost completely displace the beneficial intestinal microflora. In this case, the mechanism of absorption of nutrients is disrupted, which leads to the development of vitamin deficiency and anemia. In addition, toxins formed as a result of incomplete digestion of food and the activity of pathogenic microflora, entering the blood, cause severe allergic reactions. The previously described symptoms may include rash, eczema, hives, asthma, chronic fatigue, insomnia and problems concentrating. Lack of timely treatment threatens the development of severe intestinal infections.
It must be remembered that it is easiest to eliminate dysbiosis in its initial stages. If you discover a list of suspicious symptoms that do not go away within a couple of days, you should contact a gastroenterologist.
Causes and symptoms
Dysbacteriosis can be caused by a variety of reasons: from pathological conditions in the digestive organs to unhealthy diet and lifestyle.
The most common reasons for deviation are:
- errors in nutrition (strict diets, irregularity, abuse of harmful foods, lack of vitamins);
- long-term use of antibiotics, hormonal drugs;
- the presence of parasitic and other infections in the intestines;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in the chronic stage;
- disturbances in liver function;
- alcohol addiction;
- prolonged stress, depression, overwork;
- general decrease in immunity.
Most often, dysbiosis develops as a result of taking antibiotics. Such aggressive drugs are effective not only against infections, but also against bifidobacteria and lactobacilli in the intestines. Therefore, long-term use, increased dosages, and the use of low-quality drugs always lead to dysbacteriosis.
IMPORTANT!
Prolonged uncontrolled use of antibiotics can also lead to the emergence of treatment-resistant strains of bacteria. This means that it will be extremely difficult to get rid of pathogenic microflora in the future.
Among the main symptoms of dysbiosis:
- decreased appetite;
- pain in the abdomen;
- nausea, vomiting;
- flatulence;
- the presence of constipation or diarrhea with their periodic alternation;
- increased fatigue, feeling of weakness, headache, pain in the joints;
- slight increase in temperature (up to 37.2 degrees).
In general, the state of health with dysbacteriosis worsens, immunity drops, and essential microelements and vitamins cease to be properly synthesized and absorbed. Therefore, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment as soon as the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis.
Chronic dysbacteriosis
Chronic dysbacteriosis is somewhat less common. At the same time, disturbances in the composition and quantity of microflora do not return to normal for a very long time (months, years). As a rule, there are prerequisites that do not allow normal microflora to recover. However, in most cases, this problem can still be solved with proper treatment.
In the chronic course of dysbacteriosis, it is important to pay attention to the presence of the following factors:
- self-medication and unqualified treatment;
- weakened immune system;
- chronic inflammatory bowel diseases;
- non-compliance with the prescribed diet;
- presence of intestinal tumors;
- the presence of a constant source of infection (poor quality drinking water, etc.);
- possible resistance of bacteria to prescribed antibiotics (checked by antibiogram);
- chronic diseases of the liver, pancreas, stomach.
In the presence of the above factors, the prerequisites are created for changes in the composition of the intestinal microflora. If these factors are not eliminated, treatment in most cases will not have the desired effect. The disease takes a chronic course.
Constipation due to dysbiosis in a child
Due to the immaturity and lack of its own immunity, the child’s body is susceptible to various diseases. Intestinal dysfunction occupies one of the leading places among them. Disturbance of microflora can be primary in nature, when the large intestine is colonized by pathogenic microorganisms immediately after birth. The most common variant is a secondary pathology that arises as the child grows older.
The cause of dysbiosis is influenced by various factors
The main causes of childhood dysbiosis lie in:
- late breastfeeding;
- early start of artificial complementary feeding;
- low-quality formulas for feeding;
- infectious diseases;
- use of antibacterial therapy;
- infection with worms and other parasites;
- improper diet;
- low immunity.
If an adult can ignore unpleasant symptoms for a long time, then in a child the clinical picture is more vivid and manifests itself already at the initial stage:
- increased gas formation;
- belching;
- bloated and painful belly;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- irregular bowel movements;
- prolonged absence of stool;
- refusal to eat;
- temperature increase;
- skin rashes;
- moodiness, tearfulness, restlessness.
In infants and small children, frequent changes in feeding formulas lead to an imbalance in the balance of beneficial and harmful bacteria.
Can a child have constipation due to dysbacteriosis? Constipation, as well as diarrhea, are major signs of concern. Normally, a baby has 2 to 7 bowel movements per day; as they grow older, the number of bowel movements decreases to 1-2 per day, but not less. In case of defecation disorders, especially prolonged constipation due to dysbacteriosis in infants, you should immediately contact your pediatrician.
Diagnostics
In order to determine the presence and nature of dysbiosis, it is necessary to find out which microbes populate the intestines and in what quantity. Today, two main diagnostic methods are practiced:
- The method for examining microflora metabolites is based on determining the substances (volatile fatty acids) that microbes secrete during their development. This method is highly sensitive and easy to determine microbes and allows you to get results within a few hours. In addition, it is not as expensive as bacteriological.
- Bacteriological research. With the bacteriological method, depending on the specialization of the laboratory, from 14 to 25 species of bacteria are determined (this is only 10% of all microorganisms). Alas, you will receive the result of this analysis only after 7 days; on average, this is the time it takes for bacteria to grow in special nutrient media and be identified. In addition, the quality of the results of this analysis also depends on compliance with delivery times and the quality of the material; there are also difficulties in cultivating certain types of bacteria.
It must be remembered that the composition of the intestinal microflora is individual for each person. It depends on age, food consumed, and even the time of year. Therefore, making a diagnosis based solely on tests is a mistake. Additional examination is needed to determine the cause of dysbiosis.
Development of constipation due to dysbiosis in adults
In an adult, constipation is asymptomatic for a long time. Minor discomfort and periodic bowel movements are rarely taken into account. But these are the first signs of illness. Constipation with dysbacteriosis at the first stage appears periodically, without causing any special problems. But as the pathology develops, it becomes chronic. Sluggish intestinal motility and digestive problems speed up the process.
Constipation can occur for many different reasons, and it is not always caused by a microflora disorder
In the second and third stages, constipation is usually accompanied by:
- strong hardening of feces;
- when passing through the rectum, they damage the walls, causing hemorrhoids and fissures;
- dense stool is followed by a shapeless mass with a fetid odor;
- Each act of defecation is accompanied by prolonged straining and painful sensations.
Not without additional unpleasant symptoms:
- heaviness in the stomach;
- flatulence;
- feelings of incomplete bowel movement.
Irregular stool with a delay of more than two days leads to damage to the body by toxins. Feces stagnate in the intestines and cause poisoning, followed by fever, anemia, and general malaise.
Elderly people and pregnant women are at particular risk. Natural aging of the body is accompanied by loss of intestinal tone, deterioration of digestion and the development of chronic constipation. It is impossible to do without supportive drug therapy and a special diet. During pregnancy, similar disorders occur, but laxatives should be avoided. It is important for a woman to adjust her diet and carefully monitor her well-being. Dysbacteriosis in both cases can significantly complicate the health condition.
Complications
The most serious consequences can be caused by the following complications of dysbacteriosis:
- Losing weight. Progressive weight loss due to malabsorption is common in chronic dysbiosis. In some cases, patients become malnourished as a result of diarrhea. Regardless of the mechanism of exhaustion, the important thing is that the body weakens and becomes more susceptible to other diseases (acute respiratory diseases, chronic diseases worsen). Gaining body weight after prolonged dysbacteriosis is a slow process. More often, severe exhaustion is observed in children with severe forms of the disease.
- Dehydration. This complication is rare and occurs only in some severe types of dysbacteriosis. The fact is that long-term loss of water as a result of diarrhea can have very serious consequences for the body. Typically, dehydration is said to occur when there is a loss of 3% fluid or more. With a loss of 12% of fluid, the patient's condition becomes very serious and there is a high risk of life. Prolonged diarrhea with pronounced water loss is usually a consequence of the addition of dangerous pathogens that are not normally found in the intestines.
- Parasitic diseases. To a lesser extent, normal microflora protects the body from some parasitic diseases. We are talking about various helminthiases that are often found in children.
- Secondary intestinal infections. There are a large number of dangerous intestinal infections that do not affect the body, partly due to the presence of normal microflora. If this line of defense weakens, the likelihood of severe intestinal diseases increases. The most common infections that can aggravate dysbacteriosis and pose a threat to life are salmonellosis, shigellosis (dysentery), cholera, yersiniosis, etc. These diseases pose the greatest danger to children.
- Developmental disorders in children. In young children, dysbiosis without adequate treatment often becomes protracted. Because of this, the child may lack certain nutrients or vitamins for a long time. Given the high rate of growth and development in early childhood, such problems lead to delays in mental and physical development. Proper treatment can usually correct this deficiency in a child.
- Inflammatory processes. In rare cases (usually in the presence of concomitant inflammatory bowel diseases), serious changes in the microflora can lead to the development of an inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity. It is believed that chronic dysbiosis plays a role in the development of appendicitis, diverticulitis (inflammation of a diverticulum - a protrusion of the intestinal wall), and the formation of abscesses. Any inflammation in the abdominal cavity is potentially a very dangerous condition and requires intensive treatment (often surgical).
Considering the lack of vitamins and weakened immunity that occur with dysbiosis, there is a risk of other complications that are not directly related to disorders of the intestinal microflora. In general, we can say that dysbiosis is not a dangerous disease, but you still shouldn’t start the disease.
What is dysbiosis?
Dysbacteriosis is a pathological condition of the intestine in which its microflora is disrupted. It does not arise as a separate disease, but as a complex reaction of the body to an imbalance of harmful and beneficial microorganisms. It manifests itself in a number of unpleasant symptoms associated with indigestion and defecation.
Normally, the intestines contain both pathogenic and beneficial bacteria. Microflora is very important for:
- food processing;
- absorption of useful and nutrient substances;
- timely removal of waste products;
- ensuring metabolic processes, metabolism, immune protection of the body from adverse factors.
Constipation due to dysbiosis often occurs in both adults and children
For normal functioning, harmful and beneficial microorganisms must be in relative balance. When for some reason the balance is disturbed in favor of pathogenic microflora, dysbiosis develops. As a result, harmful bacteria actively multiply on the intestinal mucosa, causing various disorders and reducing the body's defenses.
The pathology does not appear suddenly, it develops over a certain period of time, so it is difficult to detect it at an early stage. The first obvious signs appear already with serious damage to the colon, when problems with stool and dyspepsia occur for a long time. It is important to consult a doctor in time and begin therapy to avoid general intoxication of the body.
Treatment of intestinal dysbiosis
In case of confirmed intestinal dysbacteriosis, planned treatment is carried out using drugs that restore normal intestinal flora and correct other disorders in the body (using enzymes, sorbents, vitamins).
Groups of drugs prescribed for intestinal dysbiosis in adults:
- Sorbents are prescribed for severe signs of intoxication. Activated carbon is prescribed 5-7 tablets at a time, for 5 days.
- Prebiotics - have a bifidogenic property, i.e. contribute to the stimulation and growth and reproduction of microbes that are part of the normal intestinal flora. Representatives of this group include: Hilak-forte, Duphalac. Hilak-forte is prescribed 40-60 drops 3 times a day.
- Antibacterial drugs are used for the 4th degree of intestinal dysbiosis, to destroy pathogenic flora. The most commonly used antibiotics are: tetracyclines (Doxycycline), cephalosporins (Cefuroxime, Ceftriaxone), penicillins (Ampiox), nitroimidazoles: Metronidazole, prescribed 500 mg 3 times a day, after meals.
- Symbiotics (Bifidobak, Maltodophilus) are combined preparations (prebiotic + probiotic), i.e. simultaneously stimulate the growth of normal flora and replace the missing number of microbes in the intestines. Bifidobac is prescribed 1 capsule 3 times a day, with meals.
- Bacteriophages. To eliminate the symptoms of dysbiosis, you can take medications containing viruses that attack a specific type of bacteria. They are combined with antibacterial treatment or used as an alternative therapy.
- Enzymes are prescribed in case of severe digestive disorders. Mezim tablets, 1 tablet 3 times a day, before meals.
- Antifungal drugs (Levorin) are prescribed if there are yeast-like fungi such as Candida in the stool. Levorin is prescribed 500 thousand units 2-4 times a day.
- Multivitamins: Duovit, 1 tablet 1 time per day.
The dosage, duration of treatment and group of drugs are prescribed by the attending physician, depending on the degree of dysbacteriosis. Below are the dosages of drugs for adults; for children, the dosage depends on the weight and age of the child.
How to treat flatulence during pregnancy?
Flatulence in pregnant women is not dangerous, but can lead to muscle spasms and cause nagging pain in the lower abdomen. Treatment is usually not required; it is enough to adjust the diet by eliminating foods that cause increased gas formation. It is recommended to eat food often (5-6 times a day), but little by little and slowly. Decoctions of chamomile, mint, weak ginger and dill teas help against flatulence.
Dysbacteriosis is not an independent disease, but a consequence of poor nutrition or disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. The success of treatment directly depends on correct diagnosis and following the doctor’s recommendations.
0
3
5
Article rating:
4.43 out of 5 based on 7 ratings
Author: Mulchenko Elena Viktorovna
Gastroenterologist. Highest category. Work experience 24 years.
Probiotics
Probiotics (eubiotics) are preparations containing live microorganisms (i.e. bacteria of normal intestinal flora), they are used to treat grade 2-4 dysbacteriosis.
- 1st generation drugs: Bifidumbacterin, Lifepack probiotics. They are liquid concentrates of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria and are not stored for long (about 3 months). This group of drugs is unstable under the influence of gastric juice or enzymes of the gastrointestinal tract, which leads to their rapid destruction and the intake of insufficient concentrations, the main disadvantage of 1st generation probiotics. Bifidumbacterin is prescribed orally, 5 doses of the drug 2-3 times a day, 20 minutes before meals;
- 2nd generation drugs: Baktisubtil, Flonivin, Enterol. They contain spores of bacteria of normal intestinal flora, which in the patient’s intestines secrete enzymes for the digestion of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, stimulate the growth of bacteria of normal intestinal flora, and also suppress the growth of putrefactive flora. Subtil is prescribed 1 capsule 3 times a day, 1 hour before meals;
- 3rd generation drugs: Bifikol, Linex. They consist of several types of bacteria from the normal intestinal flora, and therefore are highly effective compared to the previous 2 generations of probiotics. Linex is prescribed 2 capsules 3 times a day;
- 4th generation drugs: Bifidumbacterin forte, Biosorb-Bifidum. This group of drugs consists of bacteria of normal intestinal flora in combination with an enterosorbent (with activated carbon or others). Enterosorbent is necessary to protect microorganisms when passing through the stomach, it actively protects them from inactivation by gastric juice or enzymes of the gastrointestinal tract. Bifidumbacterin forte is prescribed 5 doses 2-3 times a day, before meals.
Treatment of intestinal dysbiosis is prescribed comprehensively depending on the degree of the disease. Since dysbiosis develops under the influence of many factors, it is important to eliminate the cause of its development, otherwise taking probiotics will not have a positive effect. Elimination of foci of infection and chronic diseases is the main task in the treatment of dysbiosis.
Other folk remedies for getting rid of dysbiosis
whey helps a lot with dysbacteriosis.
. To obtain it, a liter of kefir is heated in a saucepan over low heat until it separates. Then remove the pan from the heat and leave to stand for 10-15 minutes, and then strain the contents through cheesecloth or a colander. The whey will drain, and the curd will remain in the colander. The resulting cottage cheese can be eaten, and the whey can be drunk in the morning on an empty stomach, one glass warm. The result of treatment will be the gradual normalization of microflora, elimination of symptoms of dysbacteriosis and improvement of the general condition of the body.
Another effective remedy is bee honey.
. It combines anti-inflammatory, antibacterial activity, regenerating properties, and is also endowed with a huge amount of useful microelements. The value of honey is its ability to simultaneously eliminate pathogenic microflora and nourish beneficial ones.
The simplest honey recipe is to dissolve a teaspoon of honey in a glass of warm water and drink immediately. The product should be taken twice daily, 25-35 minutes before meals.
IMPORTANT! Treatment with honey is contraindicated if you are allergic to bee products.
Natural antibiotic garlic
also showed good results in the treatment of dysbiosis. The phytoncides it contains have powerful anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activity, leaving no chance for pathogenic microorganisms.
It is enough to swallow one medium-sized clove of garlic per day, washed down with a glass of kefir or fermented baked milk.
Important! Garlic is an aggressive remedy, and therefore it is contraindicated for people suffering from stomach ulcers, duodenal ulcers, or erosions on the gastric or intestinal mucosa.
To get rid of dysbiosis and prevent further relapses, it is most effective to use an integrated approach. A combination of medications prescribed by a doctor, traditional medicine, and a balanced diet will help quickly establish metabolic processes and forget about the discomfort caused by dysbacteriosis. Read about itching without discharge on our website.
Diet for dysbiosis
How to treat intestinal dysbiosis? With a mild degree of imbalance in the intestinal microflora, it may be sufficient to eliminate these causes through a balanced diet, taking prebiotics or probiotics.
In case of severe disorders, dietary nutrition is also indicated simultaneously with complex antimicrobial therapy. Basic Rules:
- Products are steamed, boiled, baked, stewed. No frying!
- Drink plenty of fluids, mostly clean water. For diarrhea, it helps against dehydration, and for constipation, it softens clotted stool.
- The food is balanced, rich in foods containing proteins, carbohydrates, vegetable fats, minerals, vitamins necessary for the full functioning of the body.
- Remove foods that irritate the gastrointestinal tract, have a laxative or fixative effect.
- Avoid products that cause gas formation, fermentation, and rotting.
- Remove sauces, hot spices, smoked meats, marinades, and strong alcohol. No fast food, semi-finished products, dry food, on the go. Rich broths, confectionery, baked goods, whole milk, strong tea are prohibited.
- Eat foods that create favorable conditions for the growth of beneficial bacteria. They place emphasis on fermented milk products (kefir, yogurt, acidophilus milk), and foods rich in plant fiber.
- They refuse fresh vegetables and fruits. Any heat treatment is preferred. Baked apples are an excellent dessert, rich in vitamins and healthy elements.
- Eat food regularly, every 2.5-3 hours in small portions. Long intervals between meals should not be allowed.
- The temperature of the food should be pleasant and warm. You can't eat hot, it's too cold.
Diet is an important condition for the successful treatment of dysbiosis in adults and children. Food consumption is not limited, its composition is changed. A balanced diet and properly prepared food will help restore the lack of vitamins, increase hemoglobin, normalize digestion, and ensure complete excretion of bile.
Correcting nutritional errors
Treatment should always begin with establishing a diet. In many cases, the intestinal microflora is able to recover on its own over time, but it needs help. Whatever option for getting rid of dysbiosis is chosen, without following the rules of a healthy diet, treatment will be ineffective.
To begin with, you should exclude fasting and strict restrictive diets, because during dysbacteriosis the body already suffers from a lack of vitamins.
In this case, you should remove from your daily diet:
- fatty meat and fish;
- fried and spicy;
- smoked meats and canned food;
- baked goods, sweets, white bread;
- eggs in the form of fried omelettes and scrambled eggs, as well as hard-boiled ones;
- vegetables that have an aggressive effect on the gastrointestinal tract (radish, raw onions and garlic (except for swallowing a whole clove), sorrel);
- mayonnaise and sour sauces (ketchup);
- alcohol, carbonated drinks.
The above products have an irritating effect on the already damaged intestinal mucosa, and also feed the pathogenic microflora that has colonized the intestines.
Basic principles of proper nutrition for dysbiosis:
- eating regularly at the same time;
- eating warm food (within 25-40 degrees) and avoiding too cold or hot food;
- avoiding aggressive and spicy foods;
- chewing food thoroughly;
- eating food frequently (every two and a half hours) and in small portions;
- drink plenty of fluids, but not during meals (so as not to interfere with the digestion of food).
Compliance with these simple rules is the key to quickly and completely getting rid of dysbacteriosis, as well as preventing its relapses.
Can the patient do without treatment?
Cases of independent voluntary disposal of minor disturbances in the intestinal microflora are recorded quite often in medical practice. But most of these examples are associated with disorders due to emotional shocks or rapid acclimatization.
Please note that dysbiosis can stop progressing only in the first phase of its development. This is the big problem, because during this period it is almost impossible to notice characteristic changes in the intestinal microflora. And if the patient already has pronounced symptoms of the disease, then he needs medical help, since we are talking about a seriously advanced process.
Prevention
The most important method of prevention is timely and rational antibacterial therapy. In this way, the patient can protect himself from the symptoms of dysbiosis and the development of the disease.
A common case of dysbacteriosis is long-term use of antibiotics. To prevent the disease, it is recommended to take the following measures:
- eat fermented milk products;
- start using antifungal drugs;
- take probiotics, multi-enzymes and multivitamins.
The complex of drugs must be prescribed by a doctor; it is not recommended to use any medications on your own.
Natural analogues of drugs
To cure dysbiosis, avoiding taking a large number of pharmaceutical medications, you can resort to consuming natural sources of beneficial bacteria - familiar foods.
Foods rich in prebiotics
:
- fermented milk products (ryazhenka, kefir, cottage cheese);
- chicory (raw root);
- cereals, wheat bran;
- raw asparagus;
- dried apricots, prunes;
- fruits (apples, citruses, bananas);
- berries (strawberries, black and red currants, plums).
Products containing sufficient amounts of probiotics and synbiotics
:
- flax seeds;
- corn;
- figs;
- grape;
- sauerkraut;
- bulb onions;
- soft cheese, cottage cheese, fermented baked milk.
Antiseptic products
:
- onion and garlic;
- cardamom;
- ginger root;
- dill and fennel (seeds and herbs);
- walnuts, hazelnuts and almonds;
- rowan, blueberry and other berries with a tart taste