From newspapers and magazines, from doctors and notes from various Internet resources, we often hear about the dangers of pancreatic inflammation: there are many cases where the disease was fatal and claimed the lives of many ordinary people, but today we will talk about celebrities who died from pancreatitis . Unfortunately, recently the pathology has been manifesting itself more and more often, and if earlier this disease was diagnosed mainly in people after 40 years, now this mark has dropped to 30. Why is this trend observed and which famous personalities have become victims of this aggressive disease - We'll find out further.
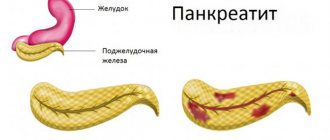
What is the pancreas and its functions
The organ is small in size, shaped like a willow leaf and exhibits two important functions:
- takes part in the digestion of food thanks to digestive juices;
- produces hormones that affect cells in the human body.
Insulin, which controls sugar levels, has become the main pancreatic hormone.
Pancreas
Etiology of the disease
There are two main causes of pancreatitis: drinking excessive amounts of alcohol (about 60%) and cholelithiasis (about 30%).
Additional factors contributing to the development of inflammation are:
- diseases of the duodenum;
- abdominal injuries;
- history of gastric or biliary tract surgery;
- infections – viral hepatitis B and C, mumps (“mumps”);
- helminthic infestations – ascariasis, enterobiasis;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- heredity;
- tumors, narrowing of the pancreatic ducts in the anamnesis.
There are two forms of pancreatitis: acute and chronic.
What types of diseases are there?
There are two types of pathology - chronic and acute pancreatitis.
Chronic pancreatitis manifests itself due to the acute form of the disease. The disease progresses over the years, becoming more and more deformed.
In the acute form, inflammation of the organ occurs almost instantly. The form of the disease is rare. At risk are more often male patients aged forty to fifty years. Chronic alcoholism is often a risk factor for this pathology.
Results and discussion
To our knowledge, there have been no studies evaluating emergency surgical care in the country for a long time. Our results are consistent with previous national reviews [4, 5]. The obtained data are comparable in terms of quantitative and qualitative characteristics with the indicators published by Rosstat in previous years for acute intestinal obstruction (AIO), incarcerated hernia (IH), acute cholecystitis (AC) and acute pancreatitis (AP) (Table 2).
Table 2. Emergency surgical care in the Russian Federation in 2000—2017, thousand people operated on in a hospital* Note. * — Data up to 2021 published by Rosstat; ** — in previous years, data on acute cholecystitis and acute pancreatitis were summarized. The decrease in the number of patients with acute appendicitis (OA) is a long-term trend observed in other countries, which is explained both by the introduction of diagnostic laparoscopy and, consequently, a decrease in the number of unnecessary appendectomies, and by the aging of the population [6]. The decrease in the number of cases of perforated ulcer (PU) is associated with a number of reasons - a decrease in the proportion of the smoking population, the effectiveness of anti-ulcer therapy, but the identified trend requires a separate study [7].
The number of operations for gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB) decreased by 31.4%, which can be explained by more effective conservative treatment and active use of endoscopic hemostasis. However, it is not possible to track the dynamics of this process due to the lack of national data for previous years. In general, the number of emergency surgical interventions decreased by 27.8% during the study period due to OA and complications of peptic ulcer disease.
Since 2000, the ratio of individual forms of acute diseases of the abdominal organs has changed (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. The ratio of individual forms of acute surgical diseases of the abdominal organs in the Russian Federation. Here and in Fig. 2 and 3: OA - acute appendicitis, AC - acute cholecystitis, OP - acute pancreatitis, GI bleeding - gastrointestinal bleeding, OKN - acute intestinal obstruction, UG - strangulated hernia, PY - perforated ulcer. The proportion of OA has decreased significantly - from 40.3 to 26.4%, but so far this is the most common disease in the surgeon’s practice. The share of AC and AP increased to 24.4 and 23.2%, respectively. Gastrointestinal tract infections remain in 4th place in frequency - 8.8%. The proportion of patients with OKN increased to 7.8% and UH to 6.5%, and the proportion of patients with PY decreased from 4.7 to 2.9%.
Postoperative mortality during this time decreased by 1900 (16.5%) people per year and amounted to 10,800 (2.8%) people. A total of 15,500 (2.3%) people died from acute abdominal diseases in 2021. The mortality rate for certain diseases (OP, AC, UG) has decreased and remains stable in OA, gastrointestinal tract, acute intestinal tract (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. Postoperative mortality in acute diseases of the abdominal organs in the Russian Federation.
At the same time, with a 2-fold reduction in the number of patients with PY during the analyzed period, a negative trend was the increase in postoperative mortality from 4.8 to 9%, although in absolute numbers the mortality rate does not change - 1700 deaths per year.
In 2021, emergency surgical care was provided to 669.2 thousand patients with acute diseases of the abdominal organs, of which 387.9 thousand people were operated on (Table 3).
Table 3. Acute diseases of the abdominal organs in the Russian Federation in 2021. Note. The percentage is indicated in parentheses.
Both general and postoperative mortality directly depend on the timing of delivery of patients with acute diseases of the abdominal organs to the hospital. Mortality in the group of patients hospitalized after 24 hours from the onset of the disease was 2-3 times higher compared to the group of patients admitted on the first day of the disease. The proportion of those who applied late varied from 23.4% for OA to 45.2% for AP (Fig. 3),
Rice. 3. Proportion of patients with late hospitalization. at the same time, the proportion of this group of patients is increasing: in 2000 - 32.9%, in 2010 - 36.1%, in 2021 - 37.8%.
Acute appendicitis
In Russia, the number of appendectomies has decreased by 1.8 times over the past 17 years. This led to a 2-fold decrease in the number of deaths (see Table 2), but the mortality rate did not change (0.13%) and is largely the same as in other countries, as is the incidence rate [8, 9] . In Western countries, OA occurs with a frequency of 100-120 cases per 100 thousand population per year. When comparing the incidence rate of OA and the share of laparoscopic appendectomy in a number of regions and federal districts, an inverse relationship was revealed ( r
=−0.9;
p
=0.002) (Fig. 4).
Rice.
4. The ratio of the incidence of acute appendicitis and the use of laparoscopy in the federal districts of the Russian Federation. Routine use of the laparoscopic approach eliminates unnecessary appendectomies and has not only clinical but also economic advantages over open appendectomy [10]. Currently, Moscow has the highest proportion of laparoscopic appendectomy (89.6%) and the lowest incidence (83 cases per 100 thousand population). The minimum share of laparoscopic operations was in the Volga Federal District (8.3%), and the incidence, on the contrary, was the highest - 140.8 cases per 100 thousand population. When analyzing mortality, a higher level is also noted in federal districts where laparoscopy was used less frequently - the Southern Federal District (0.17%), the Volga Federal District (0.15%), while the best rate was achieved in Moscow - 0.05%.
Thus, it is necessary to increase the national average (21.1%) share of the use of laparoscopy in the treatment of OA to the level that has been achieved in a number of regions - Novgorod (63.8%), Arkhangelsk (55.7%), Tula (53.6). %), Tyumen (52.7%), Pskov (50.7%) regions.
Perforated ulcer
The number of cases of PJ has decreased by 2 times since 2000 (see Table 2). The incidence rate in the federal districts is quite even, with the exception of the North Caucasus, where it turned out to be significantly lower than the national average (Fig. 5),
Rice. 5. The incidence of perforated ulcers in the Russian Federation in 2021; however, regional differences also exist among European countries [11].
Over the studied period of time, the frequency of complications of gastric and duodenal ulcers in the form of perforation decreased in Russia from 26.9 to 13.7 cases per 100 thousand population, but it remains 2 times higher than in Western countries [7, 12] .
The main reason for the increase in mortality in PO (9.7%) is the increase in the proportion of late presentation of patients. A slightly higher overall mortality rate (10.6%) was noted in the USA in 2006, but with a clear downward trend [13]. Among those who died from PY in 2021, 62.4% of patients sought medical help after 24 hours from the onset of the disease. Postoperative mortality in this group was 25.8%. The differences in mortality rates across federal districts (from 8.3% in the North Caucasus to 11.3% in the North-West) are not as great as the differences in the level of use of laparoscopic access (from 2.9% in the Far East to 17.2% in the North-West, with an average of 7%. The maximum level of laparoscopic operations was achieved in the Arkhangelsk region (32.5%), St. Petersburg (30%), Khakassia (29%). In recent years, the percentage of suturing perforated ulcers using laparoscopic access is constantly increasing, although it is advisable to select patients for laparoscopic surgery [14].
Strangulated hernia
The number of patients with abdominal hypertension in the country is not decreasing - 41 thousand patients are operated on annually. Mortality increases 2-3 times with late hospitalization in all federal districts (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. The ratio of overall mortality, mortality among those hospitalized after 24 hours and the proportion of late hospitalization among patients with a strangulated hernia. Early detection of complicated abdominal hernias is the best way to reduce mortality [15].
There is a moderate inverse relationship between the number of elective surgeries performed in federal districts and the incidence of UH ( r
=–0.37;
p
=0.001). The lowest frequency of UH was in the Ural Federal District, where the highest level of elective hernia repairs per 100 thousand population was noted (Fig. 7).
Rice. 7. The ratio of the incidence rate of strangulated hernia and the number of planned operations per 100 thousand population.
Acute intestinal obstruction
The number of operations for intestinal obstruction has not decreased - 27.4 thousand operations per year for 17 years. The number of deaths from acute respiratory failure increased from 2.4 to 2.5 thousand people per year. In the reporting form, there is no division of intestinal obstruction by etiology into tumor and adhesive. In this regard, the revealed dependence of lethality on operational activity ( r
=0.64;
p
=0.0001) needs clarification (Fig. 8).
Rice. 8. The ratio of operational activity and mortality in acute intestinal obstruction by federal districts, %. Mortality was lower where fewer patients with intestinal obstruction are operated on. This trend is probably more true for tactics for adhesive intestinal obstruction [16].
Acute cholecystitis
In Russia, more than 160 thousand patients with AC are hospitalized during the year, and almost 100 thousand patients are operated on. When compared across federal districts, the dependence of the mortality rate on the level of operational activity is noted (Fig. 9).
Rice. 9. The ratio of operational activity and mortality in acute cholecystitis, %. The higher the operational activity, the lower the mortality rate. The identified trend confirms the feasibility of earlier active surgical tactics using minimally invasive technologies [17]. More active surgical tactics for AC in recent years and the active introduction of endoscopic and minimally invasive technologies have led to a decrease in postoperative mortality by almost 2 times. In 2000, the mortality rate was 2.6% with operational activity of 48.5%, in 2021 - 1.4 and 59.8%, respectively. Of course, the reduction in mortality is primarily influenced by an increase in the proportion of laparoscopic cholecystectomy [1].
Despite the obtained statistical significance ( p
=0.0002), we believe that the data are not absolutely reliable: according to the reporting form, the share of laparoscopy in gallstone surgery was 65.8%, without division into planned and emergency operations.
Acute pancreatitis
In 2021, more than 155 thousand patients were hospitalized with a diagnosis of AP, and more than 4 thousand people died (see Table 3). A direct relationship was revealed between operational activity and overall mortality ( r
=0.65;
p
=0.0003). The values of operational activity vary significantly across federal districts. There is probably no unity in approaches to treating O.P. The highest operational activity was in the Urals and Siberia, but the overall mortality rate was above average. However, it did not specify which operations were most often used. To answer these questions, of course, it is necessary to introduce new criteria for statistics: first of all, to distinguish necrotizing pancreatitis, and the diagnosis should be based on CT data with contrast, and not on ultrasound data. It is necessary to take into account the etiology - alcoholic and biliary pancreatitis. In the future, it would be advisable to divide interventions in the reporting form into minimally invasive and traditional ones [18].
And yet, it should be noted that there has been a decrease in postoperative mortality in AP over the studied period of time: in 2000 - 22%, in 2010 - 18.7%, in 2021 - 15.4% (Fig. 10).
Rice. 10. The ratio of overall mortality and operational activity in acute pancreatitis, %. Probably, surgeons began to more clearly formulate the indications for operations. The level of operational activity in AP during the study period changed slightly: in 2000 it was 10.3%, in 2010 - 8.7%, in 2021 - 11.2%.
Gastrointestinal bleeding
The incidence of bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract (GIT) in the world is characterized by great geographical diversity - from 48 to 160 cases per 100 thousand population [14]. Our data demonstrate not only significant differences in incidence, but also uneven quality of care for patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding across federal districts (Table 4).
Table 4. Gastrointestinal bleeding (morbidity, mortality, treatment methods) in federal districts Note. 1 - incidence, number of cases per 100 thousand population per year; 2 — overall mortality, %; 3 — endoscopic hemostasis, number of procedures per 100 patients; 4 — operational activity, %; 5 — postoperative mortality, %. With the highest incidence in the Southern and Central Federal Districts (more than 50 cases per 100 thousand population) and equal use of endoscopic hemostasis, mortality was 2 times higher in the Southern District with higher operational activity (25.7% versus 14.6%). There was no direct relationship between the mortality rate and the frequency of use of endoscopic hemostasis in certain regions. Thus, the mortality rate for gastrointestinal tract diseases in the Novosibirsk region was 3.3%, and the frequency of use of endoscopic hemostasis was 64 procedures per 100 patients, which is significantly higher than the national average. At the same time, the frequency of use of endoscopy for the purpose of hemostasis in the Irkutsk region was even higher - 89 procedures per 100 patients, but the overall mortality rate (9.4%) significantly exceeded the average. The reason is probably not only the number of procedures performed. The ratio of operations and endoscopic interventions was 1:3.
Emergency surgical care for gastrointestinal tract diseases is declining: in the UK, the rate of surgical operations fell from 8 to 2% between 1993 and 2006. During the same period in the United States, hospitalization for ulcer bleeding decreased by 28.2%, the use of endoscopic treatment increased by 58.9%, and the rate of emergency surgery decreased by 21.9% [14].
It should be noted that there are no clear criteria for recording this disease in the reporting form we used. It is necessary to highlight the etiology and localization of bleeding, as well as the method of treatment (surgery, endoscopic or endovascular hemostasis).
Alcoholic pancreatitis
Alcoholic pancreatitis develops due to alcohol abuse. The type and cost of alcohol does not affect the course of the disease. You can get sick from both beer and expensive cognac if you drink regularly.
In chronic pancreatitis, mortality has been recorded for twenty years. During this period, half of the population suffering from pancreatic disease dies. Moreover, people of mature and young age have to die. The causes of death are not the disease, but the diseases that appear due to alcohol abuse.
The effect of alcohol on the pancreas
As a result of alcohol entering the body, pancreatic cells are deformed. The cause is substances formed during the breakdown of ethyl alcohol or surrogates.
Pathogenesis
Cell deformation occurs through the activation of enzymes produced directly by the gland. Then the enzymes act on the organ itself. The result is necrosis, the death of large areas. The gland becomes inflamed and increases to pathological sizes. The pancreatic tissue is deformed and replaced by fat cells, destroying the endocrine system. Diabetes develops due to pathology.
Alcohol, which is abused by diagnosed patients, has an extremely negative effect on cells. Tobacco, which often accompanies alcohol, causes vascular spasms, which increases tissue damage. Foods filled with fats activate secretory activity, causing a harmful effect on the gland.
The functions associated with the functioning of the pancreas are interconnected. It is impossible to say that the patient died from pancreatitis without finding out the true cause of death.
Classification of pancreatitis caused by alcoholism
The pathology is divided into two stages - acute and chronic. As a result of one-time consumption of alcohol in large doses, intoxication of the body occurs. This happens in the acute form of the disease. Signs of the acute form of the disease are similar to those of a conventional diagnosis.
The causes of chronic pancreatitis are mostly due to alcohol abuse. Symptoms of this type of disease may not appear for a long time. If you drink alcohol in small doses but regularly, the disease progresses daily. With chronic pancreatitis, patients live without realizing the presence of the disease for many years.
How dangerous is alcoholic pancreatitis?
During attacks of pain, many patients complain of acute pain in the upper abdomen, arising in the back and hypochondrium. Painful sensations intensify in the “lying on your back” position.
Due to impaired absorption of nutrients into the body, patients experience a sharp weight loss. To avoid death, you need to consult a gastroenterologist.
What are the complications of the disease?
Complications that arise lead to the formation of cysts and abscesses. With pancreatitis, if the disease is not treated, adenocarcinoma, pancreatic cancer, develops. The result of the pathology is often fatal.
Is it possible to cure pancreatitis caused by alcohol?
Treatment of the disease occurs under the strict supervision of a number of doctors. Professionals in the field of gastroenterology, endocrinology, and surgery are considered competent. In severe cases, ask for help from a radiologist or psychotherapist.
The main condition for effective treatment is the exclusion of alcoholic beverages from the diet. You cannot drink beer or other low-alcohol drinks.
Pancreatitis: probable mortality from the disease
Mortality due to inflammation of the pancreas accounts for 40 percent of all cases of acute inflammation of the pancreas. These are very high numbers, indicating the danger of this pathology, the need for timely diagnosis, treatment and prevention of pancreatitis.
Patients die due to severe acute inflammatory pathology or exacerbation of a chronic inflammatory process, with the development of severe complications:
- pancreatic necrosis,
- internal bleeding, especially in the case of its severe complication - hypovolemic shock,
- acute intoxication with decay products as a cause of infectious-toxic shock, more often relevant in pancreatitis of alcoholic origin,
- abscesses, ulcers on the surface of the pancreas or nearby organs (omentum, liver, gall bladder, stomach), purulent inflammatory process in the ducts of the gland, when ruptured or spread, a serious condition develops - peritonitis,
- pain shock,
- pancreatic cancer due to long-term chronic pancreatitis.
If you do not seek medical help in time, do not diagnose these serious conditions in a timely manner and do not begin to treat the patient correctly, then the risk of death is very high.
What are the prognosis for treatment?
The prognosis of chronic pancreatitis is often unfavorable. Pancreatic necrosis, or death of gland cells, is especially difficult to treat. A fatal outcome in the described case is likely.
To avoid tragedy, patients need to clearly understand that the causes of chronic pancreatitis depend on the quality of food. When diagnosed, you should not drink alcoholic beverages or eat fatty foods. The diet includes protein (mandatory) and a minimum amount of fat.
How long do people with pancreatitis live is a question that worries every sick person. Life expectancy is influenced by a number of reasons:
- Patient's age. The earlier a person gets sick, the higher the chance of recovery.
- Drinking pattern - how often ethanol is consumed.
- The degree of damage to the gland.
A young guy who recently turned 20 years old and does not drink alcohol can live with this diagnosis into old age. A man in his declining years who regularly drinks alcohol shortens his life by ten or more years.
Factors influencing life expectancy:
- Life expectancy depends on the form of the disease. Acute attacks are often fatal. In severe forms, death from pancreatitis occurs in thirty percent of patients.
- The severity of the disease affects the general condition of the body.
- Complications in the form of cyst formation, bleeding from a damaged organ, and problems with the gastrointestinal tract aggravate the situation, mainly in older patients. The mortality rate reaches 20%.
- Age category of patients.
- Regular, thoughtful treatment.
- Compliance with the doctor's requests for treatment.
- Consumption of products prescribed by a gastroenterologist.
- Refusal to drink strong and low-alcohol alcoholic beverages.
Material and methods
To collect information, we used a reporting form developed and used since 2013 in the Central Federal District. The questionnaire method is used to obtain data on surgical care in other countries [3]. Based on data for 2021, a comparative analysis of emergency surgical care was carried out, covering 80 regions of the Russian Federation, where 99.3% of the country's population lives (information was not provided from the Republic of Buryatia, the Republic of Tyva, the Sakhalin Region, the Jewish Autonomous Region, the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug) . The analysis took into account quantitative and qualitative indicators of surgeons’ work both in absolute numbers and per 100 thousand population. The dynamics of a number of indicators for a 17-year period starting from 2000 are presented. To determine the relationship between indicators, a regression analysis was carried out with the calculation of the regression coefficient ( r
).
Statistical significance was checked using t
test; the data were considered statistically significant at
p
<0.05.
A comparison of indicators was carried out for federal districts - territorial entities that have common geographic and demographic features. These features of the territories should be taken into account not only in assessing indicators, but also in organizing emergency surgical care (Table 1).
Table 1. Geodemographic characteristics of the federal districts of the Russian Federation
What can cause acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis?
This pathology is characterized by the death of pancreatic tissue. As a rule, with this type of disease, the mortality rate among patients is high. The cause of the disease is surgical interventions, various wounds and injuries, and alcoholism. With pathology, a sharp enlargement of the gland occurs, resulting in hemorrhage and the formation of blood clots.
If acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis is suspected, patients feel chills and the temperature rises. Vomiting and weakness in the body appear. Pain sensations radiate to the shoulder blades and back. Sometimes the pain reaches the heart area. As a result of pressure on the front of the abdomen, acute pain occurs. Most patients with this type of disease are in serious condition. If treatment is not provided in a timely manner, the patient runs the risk of dying.
Pancreatitis is a disease whose course can be controlled. If you follow doctors' recommendations, there is no risk of death. Among other things, you need to monitor your emotional state, follow healthy eating rules, avoid stressful situations and undergo scheduled examinations on time. It is possible to live with such a diagnosis if the patient has a desire to live.
Signs of severe forms of the disease
- Of the main types of the disease, the acute phase of pancreatitis is distinguished; it is considered a dangerous form in which the death of the patient occurs.
- With unbearable pain in the abdomen of different locations - near the navel, under the rib on the left side or on the right. Often the pain is girdling, radiating to the lumbar area, both shoulders, and sternum. The pain syndrome can be so severe that it provokes the development of pain shock with a change in consciousness, the formation of multiple organ dysfunction, which leads to death;
- Dyspeptic manifestations are characterized by nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief, increased formation of gases in the intestines, bloating, and diarrhea. A severe form of dyspepsia with prolonged profuse vomiting and diarrhea leads to dehydration of the body, and essential microelements and vitamins are lost. This often develops as a result of insufficient or untimely infusion treatment. Dehydration of body tissues and lack of minerals negatively affect the functioning of all organs and systems; in serious cases, this can lead to death;
- General intoxication syndrome is manifested by various severe symptoms that indicate damage to all body systems. The main manifestations of poisoning of the body are increased temperature, a weakened body, pressure decreases to the point of collapse, shortness of breath, skin changes - pallor, jaundice, icterus, headache and dizziness, impaired consciousness;
- Laboratory and instrumental tests worsen if there is severe inflammation of the pancreas. The CBC reveals obvious leukocytosis with a painful disorder of the leukocyte formula, a rapid increase in ESR due to inflammation. When the liver is affected or internal blood flow rapidly increases, the level of liver enzymes, amylase and other indicators that indicate damage to the organ increases. Ultrasound and computed tomography reveal symptoms of swelling, disorder of pancreatic tissue, abscesses and other painful disorders.
The onset of severe pain before the ambulance arrives cannot be dealt with using strong medications. It is also impossible to lower the increased temperature; vomiting occurs after eating. When the canals become clogged, many foci, purulent formations, and clots of coagulated skin are observed in the parenchyma. As a result of severe development of pancreatitis, both the pancreas fails and the functionality of the liver, kidneys, stomach, and intestines changes.
The cholangiogenic type develops immediately after eating food. This pathology is caused by the presence of excrement in the bile ducts. The course of the chronic alcoholic type of pancreatitis is often detected when the patient abuses alcohol too much.
Symptoms of this type appear quite clearly and occur if you eat fresh fruits, vegetables, or spicy or sour foods.
Early manifestations of the pathology are accompanied by endless constipation along with hypomotor dyskinesia of the colon and bile excretion passages. Constipation is often replaced by diarrhea. Diarrhea with this type is an invariable phenomenon and a typical symptom.
Death from pancreatic necrosis occurs in 1/3 of patients - these numbers are terrifying. Death with toxic pancreatitis of the gland is observed in 100% of cases.
The patient's death occurs within 7 days if treatment is not prescribed immediately. Patients who do not pay attention to emerging signs die. Often occurs as a result of cholangiogenic and alcoholic type of disease.
Let us look at the appearance of the acute form, which leads to 50% of deaths, using an example.
The patient constantly drinks alcohol and fatty foods, spicy and salty foods. He also smokes cigarettes, feeling normal for some time. However, colic occurs, bitterness in the mouth, and nausea is present all the time.
Signs of the disease go away after a certain period of time, and the person again drinks alcohol and smokes. Not understanding that the gland is signaling a problem, that it is not too late to change everything for the better.
Since no action is taken, the destruction of the pancreas continues until outbreaks of pathology force one to think about leading an unhealthy lifestyle.
It is important not to waste time if an acute course is suspected, so that the death of gland cells and the subsequent death of the patient from pancreatic necrosis does not occur.
Is it possible to die from pancreatic necrosis - statistics
The incidence of death from pancreatitis in its acute form occurs in one third of patients - these numbers are terrifying. Death with infected pancreatic necrosis of the pancreas occurs in 100% of cases. The statistics of deaths from this disease speaks for itself.
A greater number of patients with suspected fatal pancreatic necrosis of the pancreas require urgent surgical intervention. Timely and competent assistance increases the chances of recovery. The surgeon drains or excises areas of necrosis, but often the necrosis spreads again. After surgery, the patient is admitted to the intensive care unit and continues to be treated conservatively to delay or prevent death as much as possible.
In conservative treatment, antibiotics are used, fasting is prescribed for several days, and nutrients, hemodez, and polyglucin are administered parenterally. The blood is cleansed of toxins and breakdown products by transfusion. Somatostatin is prescribed, a hormone that stops the breakdown of pancreatic cells.
So, pancreatitis is fatal - they can follow each other and this must be remembered, especially for elderly patients, you should follow a diet and not abuse alcoholic beverages, then you can extend your life for many years.