X-ray: types, contraindications
X-ray examination was invented more than a hundred years ago as a method of non-invasive examination of internal organs.
Today, radiography is currently used to diagnose various pathologies in various fields of medicine.
Of course, the development of technology has given doctors the opportunity to use more advanced methods for diagnosing diseases, but even today radiography plays a significant role in clinical practice.
If you compare it with CT or MRI, then the statistics are in favor of this particular research method. The specific gravity of radiography is 15 times higher than that of MRI or CT.
The essence of the method
Radiography is a diagnostic method that is based on the use of X-rays. It must be understood that the radiation exposure of one procedure is not dangerous for humans, but it is necessary to limit the frequency of studies of this kind.
If we talk about classification, the following methods are distinguished:
- Overview – makes it possible to analyze any area of the body;
- Targeted - helps to collect information about the functioning of a specific organ and its structure.
The images obtained as a result of the procedure are called radiographs. The results of the procedure are important in terms of making a diagnosis.
Technology does not stand still, and now digital devices with a computer program are increasingly used. When using them, there is no need to make films by developing them. The picture is displayed on the monitor, but the pictures themselves are stored on electronic media.
Conditions for obtaining reliable diagnostic results
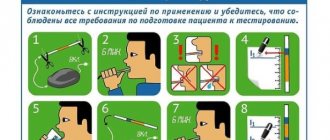
To avoid distorted results of hardware diagnostics of the stomach and intestines, patients are advised to follow a simple diet the day before. Alcohol should be discontinued one day before the test, tobacco and medications that can affect intestinal motility – 12 hours before.
to undergo fluoroscopy of the intestines on an empty stomach, after a three-day slag-free diet. There should be no metal objects in the clothes or on the patient.
The results can be distorted by:
- increased gas exchange;
- full stomach (metabolic disorders, in this case an enema is given a few hours before fluoroscopy of the stomach and intestines);
- metal on the patient (jewelry, crowns, prosthetic plates).
At the end of the study, barium suspension will be released for another 2-3 days. It can cause constipation or mechanical obstruction of the canal, which will aggravate the disease, if any. Therefore, if you experience serious discomfort (bloating, pain, nausea) during this period and (especially) after 72 hours, you should contact your doctor.
Indications
Radiography is also used in oncology. The main purpose of its use is to obtain information about the state of a specific anatomical zone and deviations from anatomical norms.
We can say that the indications for conducting the study are the presence of a malignant neoplasm, the process of its treatment and follow-up.
Patients with cancer are advised to examine a number of anatomical areas:
- Areas of development of the primary tumor process;
- Areas of probable metastasis;
- Areas in which, based on clinical signs or patient complaints, there are likely to be metastases.
We will apply the method during treatment in such cases as:
- The need to select the optimal volume of surgical manipulation;
- In the postoperative period to monitor the condition of the lungs;
- In the postoperative period to control the installation of internal catheters or stents;
- To assess the dynamics of metastases in the lungs and bones during cyclic chemotherapy;
- For monitoring after completion of treatment in areas of probable relapse or metastases.
Symptoms that are referred for fluoroscopy of the gastrointestinal tract
X-ray examination of the intestine and upper tract is mandatory for :
- long-term heartburn;
- symptoms of the acute stage of the disease (blood in the stool, persistent vomiting);
- sudden weight loss, diarrhea;
- lack of appetite;
- pain in the chest and abdomen;
- suspected tumors;
- ulcers;
- ingestion of solid foreign objects.
In some cases, fluoroscopy of the stomach and intestines is performed or not, depending on the expected benefit of the procedure. Contraindications to the examination are perforation, intestinal obstruction and pregnancy.
However, in conditions of high threat to the patient, radiography of the intestines and stomach can be carried out in compliance with special requirements. The same applies to cases of obstruction, when the patient is scheduled to undergo perforation surgery.
Types of research
We list the main types of research:
- Lung examination. Gives an idea of the presence and extent of changes in lung tissue.
- Heart study. Necessary for diagnosing diseases of the cardiovascular system, heart, imbalance of the pulmonary circulation.
- Spine examination. Using it you can indirectly determine the nature of osteochondrosis
- Examination of the stomach and duodenum. It is used to identify ulcers, perforations, foreign bodies, etc.
- Examination of the gallbladder. Important for assessing the condition of the bile ducts.
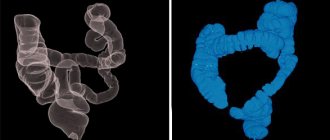
- Colon examination. Necessary for detecting polyps, tumors, foreign bodies, inflammatory foci.
- Abdominal examination. Necessary to clarify the diagnosis when complaining of severe abdominal pain.
- Study of bones and joints. It is used to diagnose fractures, subluxations and dislocations, ligament injuries, joint and bone diseases, etc.
- Dental examination. With its help, the doctor determines the size and location of teeth, abscesses, fractures of the jaw bones, malocclusion, etc.
- Metrosalpingographic study. Detects the presence of adhesions and anatomical changes in the uterus and fallopian tubes.
- Mammographic examination. Important for identifying tumor processes in the mammary gland.
How to prepare for an X-ray examination
An X-ray examination is carried out to identify the disease, clarify the location of the pathological process and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
The internal organs and tissues of a person, depending on their anatomical structure, have different densities, therefore, when X-rays pass through, the degree of their absorption is reflected in the contrast of the resulting image.
The natural contrast in x-ray examination is air, bone and fat tissue. Organs containing such tissues are clearly visualized. In other cases, for example, in order to make hollow organs “visible”, it is necessary to administer a contrast agent. Thanks to this, it becomes possible to obtain their graphic image.
But in any case, in order for the contrast and visibility of a tissue or organ to be as close as possible to “anatomical” indicators, high-quality preparation for the study is required.
Preparation for x-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT)
1. Preparation for gastric examination
- The study is carried out on an empty stomach, and you need to completely refuse food 6-8 hours before the study;
- 3 days before the study, you should give up hard-to-digest foods such as legumes, mushrooms, pickles, olives, brown bread, etc. Plus, you need to stop drinking alcoholic beverages 2-3 days before the test.
- on the eve of the study, you need to limit smoking, consumption of spicy and fiery foods;
- It is advisable to conduct the study in the morning (before 11.00);
- before the study, you should not
eat food or take tablets (with the exception of patients with diabetes), or drink (even a sip of water); It is advisable not to brush your teeth to avoid liquid entering the stomach.
2. Preparation for the examination of the small intestine
- It is necessary to limit food intake after 19 pm.
- 2-3 days before the test you should avoid foods that cause gas formation. These are legumes, vegetables and fruits, black bread, fresh milk, herbs, etc.;
- 2-3 days before the study you need to stop drinking alcoholic beverages and limit smoking;
- It is advisable to conduct the study in the morning (before 12-13 pm).
3. Preparation for examination of the colon (irrigoscopy and irrigography)
- It is necessary to limit food intake after 7 pm; a light breakfast is recommended in the morning;
- 2-3 days before the examination, you should avoid foods that contribute to gas formation. It is recommended to switch to boiled meat, fish, omelets, cereals, etc. It is advisable to take an infusion of chamomile and thyme on the eve of the test;
- The study is recommended to be carried out in the morning (before 12-13 pm);
- Before the study, it is recommended to cleanse the colon in any of two ways:
Cleansing enema
On the eve of the examination - at approximately 16.00 - it is advisable to take a mild laxative with plenty of water. This could be 30 g of petroleum jelly (or castor) oil or the drugs Regulax, Bisacodyl, etc. It is advisable to consult a doctor first.
In the evening, after dinner, at approximately 19.00, you need to give an enema with boiled water at room temperature using an Esmarch mug (1.5 liters of water). Perform the enema while lying on your left side. In the morning - 2 hours before leaving the house - repeat the enema.
Colon cleansing by taking Fortrans powder orally
The dosage of the drug depends on the patient's weight. One powder dissolves in 1 liter. boiled water at room temperature and drink in small sips for 1 hour.
If the patient’s weight is up to 60-65 kg, then it is necessary to take 2 powders (the evening before the test), dissolved in 2 liters. boiled water at room temperature for 2 hours. And in the morning - 2-3 hours before leaving the house - give a cleansing enema, as described above.
If the patient’s weight is from 70 to 80 kg, then on the evening before the test it is necessary to take 3-4 powders, which dissolve in 3-4 liters, respectively. water and taken within 3-4 hours. In the morning - 2-3 hours before leaving the house - a cleansing enema is performed.
If the patient’s weight is more than 80 kg, then it is necessary to take 4 powders in the evening according to the scheme described above, and in the morning - perform a cleansing enema.
Preparation for x-ray examination of the urinary tract (excretory and survey urography)
- before the study, it is necessary to limit food intake after 7 pm; in the morning, a light breakfast is required, which may include porridge, white bread with cheese, hard-boiled egg, tea, etc.;
- 3 days before the test, exclude foods that stimulate gas formation: legumes, vegetables and fruits, brown bread, fresh milk, herbs, etc.;
- Do not take saline laxatives;
- In the evening, it is recommended to take Fortrans orally (as described above);
- It should be borne in mind that if you have an allergic reaction to iodine or iodine-containing drugs, the study is contraindicated.
Preparation for examining the patency of the fallopian tubes (hysterosalpingography), as well as for radiography of the lumbar spine, is the same as for examining the urinary tract (described above).
Preparation for fluorography (lung examination) is not required.
You can learn more about the indications and contraindications for a particular study, as well as the nuances of preparing for it, from an ON CLINIC radiologist.
Features of the event
Today, both large-sized and compact devices are used for research. The patient is in one room, the radiologist is in the adjacent one, from where he gives the necessary commands.
If the study is contrast, it is performed in the morning, usually on an empty stomach. A non-contrast study can be performed at any time.
The procedure is short, only a few minutes, except in cases where it is necessary to perform a series of photographs.
The position of the patient depends on which area needs to be examined.
Scintigraphy
To ensure accurate images, you need to remove metal jewelry; they can distort the results.
Conditions for performing fluoroscopy of the gastrointestinal tract
X-rays are taken at intervals of twenty minutes to an hour. The process may take several hours. The subject periodically needs to change position on the table (lying, standing, on his side) and wait from half an hour to an hour for the contrast to move to the next section of the digestive canal.
Depending on the areas studied, there are several types of fluoroscopy of the stomach and intestines :
- irrigoscopy - x-ray of the colon (the suspension is administered by enema);
- fluoroscopy – images of the upper gastrointestinal tract (pharynx, esophagus, stomach, first part of the small intestine);
- esophagography – pictures of the esophagus, pharynx.
During intestinal fluoroscopy, general photographs and targeted ones are taken from different angles for a better examination of pathologies or disorders of the examined area. A suspension of pure barium sulfate is used as a contrast.
Contrast in intestinal fluoroscopy
X-ray diagnostics can be conventional (contrast), with double and air contrast.
- The patient takes part of a pre-prepared barium suspension orally. To better distribute the solution throughout the gastric mucosa, the patient’s abdomen is thoroughly massaged.
- Double contrast - taking the solution through a perforated tube. X-ray of the intestines and stomach with 2nd contrast allows you to study in detail the disturbances in the relief of the organ lining.
- Air contrast - taking a solution of crystalline soda instead of barium.