general information
Currently, doctors identify more than 200 causes of headaches in adults. Pain in itself is not a disease, it is only a symptom of a particular pathology. Diseases of the cardiovascular and central nervous systems, spinal osteochondrosis and inflammation of the sinuses, ophthalmological problems and chronic intoxication - all this can cause discomfort.
Only a full examination, including a thorough examination, consultations with specialists, laboratory, functional and instrumental diagnostics can accurately determine the cause of a severe headache and select the correct therapy. In this case, the medications will not only block the discomfort, but also eliminate its source.
Causes and characteristics of different types of headaches
Headache, nausea, weakness can occur under the influence of stress.
Headache, which is a consequence of anxiety, depression of various types, developing under the influence of everyday and work troubles, is quite common among patients at the Yusupov Hospital. It develops due to excessive tension in the muscles attached to the skull. This disease affects people of all ages, but especially from 25 to 60 years old. Typically, the intensity of the disease remains at the same level and does not increase with physical activity. Pain sensations are concentrated in the temporal, occipital or frontal areas. The pain is either compressive in nature; patients report that their head feels like they are being pulled in by a helmet.
Often headaches and nausea in both men and women occur in the presence of pathology of the central nervous system. This condition can occur due to traumatic brain injury when patients experience increased intracranial pressure. As a result of liquor hypertension, headache, nausea, and vomiting occur, which does not bring relief.
Headache and nausea may be a sign of meningitis. This is an infectious disease in which inflammation of the membranes of the spinal cord develops. In patients with meningitis, body temperature rises to high levels. They experience severe pain when trying to bring their head to their chest or straighten their knees. Infectious disease specialists and neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital carry out a comprehensive examination and adequate treatment of meningitis with the latest antibacterial drugs.
During a hypertensive crisis, women and men complain of headache, mainly in the occipital region, nausea, and dizziness. They vomit, which does not bring relief. During a hypertensive crisis, cardiologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe antihypertensive drugs to patients, drugs that improve brain nutrition and heart function. Stabilizing blood pressure helps prevent acute cerebrovascular accident - stroke.
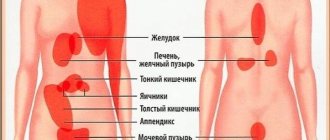
Regardless of the patient's gender, nausea, vomiting and headache can be signs of food poisoning, a side effect of certain medications, anorexia and diabetes.
One of the most common causes of headaches and nausea is cerebrovascular disease. Headache associated with increased intracranial pressure may be an early sign of a brain tumor. It intensifies with sneezing, coughing, tilting the head, and is often accompanied by vomiting without previous nausea and transient visual impairment.
Headache, nausea, and dizziness often bother patients with cervical osteochondrosis, protrusion of intervertebral discs, and spinal hernias. The pain is usually localized in the cervical-occipital region. It often spreads to the temporal and frontal areas of the head, shoulder and upper limb. The headache intensity is moderate. The pain intensifies with prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position, sudden movement of the head, or pressure on the cervical-occipital muscles. Mobility of the cervical spine is limited.
After a traumatic brain injury, headaches may persist for several months. It is diffuse, dull, intensifies with physical activity and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Memory impairment;
- Decreased attention;
- Impaired sleep quality;
- Emotional disorders (low mood, tearfulness);
- Increased fatigue;
- Dizziness.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital identify the cause of headaches and dizziness using modern laboratory and instrumental research methods.
After analyzing the research results, complex therapy is carried out with the latest drugs, which are effective and have a minimal range of side effects. Make an appointment
Types of headaches
Doctors distinguish several types of headaches depending on their nature:
- acute: occurs suddenly, is characterized by high intensity and clear localization;
- aching: has a constant or wave-like character, has medium or low intensity;
- dull: has a more diffuse nature compared to acute pain;
- bursting: characteristic of vascular pathologies, for example, increased blood pressure;
- pulsating: also often of a vascular nature, and can occur against the background of stress or overwork.
Make an appointment
What causes migraines?
There are a number of potential triggers that can trigger a migraine:
- Wine, dark chocolate, cheese, honey, coffee;
- Bright or flashing lights are a common migraine trigger;
- The sound is too harsh or loud;
- Menstruation. In women with this type of migraine, attacks occur in the first days of the cycle;
- Too much or too little sleep. For migraine patients, it is important to know your sleep norm and try to stick to it;
- Stress.
But in this matter everything is individual. Migraines can occur suddenly even after waking up and being well rested.
Causes
The list of the most common causes of headaches includes:
- sudden changes in hormonal levels (puberty, pregnancy, menopause, certain phases of the menstrual cycle);
- severe or prolonged stress;
- overwork, lack of sleep;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia (impaired functioning of the autonomic nervous system);
- high or low blood pressure;
- inflammatory processes in the brain and its membranes, sinuses, upper respiratory tract, muscles of the head and neck, and oral cavity;
- pathology of the thyroid gland;
- ophthalmological diseases, in particular glaucoma;
- head or spine injuries;
- increased or decreased blood glucose levels;
- infectious diseases;
- pathology of the cervical spine: osteochondrosis, protrusion or herniation of intervertebral discs;
- benign and malignant tumors, etc.
Depending on the cause, headaches are classified as:
- primary: does not have a clearly identified mechanism of occurrence (migraine, cluster headaches or tension pain);
- secondary: is a consequence of disease or injury.
Causes of migraine
75% of all patients with migraine reported having migraine in their immediate family. The hereditary factor plays an important role here. The likelihood that a child of one of the parents with migraines will also develop migraines is also 75%.
To date, a connection between migraine and the neuropeptide CGRP, which is involved in the development of a migraine attack, has been discovered. During a migraine, the patient's level of only this protein increases, and after artificial administration of CGRP, the subjects began to experience a headache attack.
The reason why the level of this neuropeptide increases is still unknown.
Diseases
There are many diseases that can cause constant or recurrent headaches.
Migraine
This disease is characterized by periodic attacks of severe headaches, often localized in one half of the head. The condition can last from several hours to several days and often disrupts the usual rhythm of a person’s life. Characteristic features of migraine pain are:
- one-sided nature (in most cases);
- pulsating character
- Occurrence due to stress, overexcitation, hormonal imbalances;
- increased pain with excessive stimulation of the senses: bright light, loud sounds, strong, pungent odors.
The disease most often occurs in young women.
Tension headache
Perhaps the most common type of headache. The condition is associated with prolonged overstrain of the muscles of the head and neck and is characterized by a constant, aching headache without other symptoms. Its intensity is usually high, and the provoking factor is stress.
Cluster headache
Cluster headaches manifest as multiple attacks, one after the other. The duration of each attack ranges from 15 minutes to several hours, and the intensity is so great that some patients seriously think about suicide. A series of attacks lasts 2-3 months, and then there is a long break.
The epicenter of pain in cluster pain is located in the temple area and extends to the orbit. The condition is often accompanied by severe redness of the mucous membranes of the eyes, lacrimation and nasal congestion.
Vascular diseases
Diseases of the cardiovascular system often cause headaches. Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, vegetative-vascular dystonia, hypertension, ischemic stroke or cerebral hemorrhage - all these conditions cause pain of varying intensity. Their epicenter is usually located in the temples or occipital region, and each attack is accompanied by:
- tinnitus or hearing loss;
- flashing of flies before the eyes or temporary blindness;
- dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting.
The severity of symptoms may vary. Often pain becomes the first obvious sign of developing vascular pathology.
Disturbances of venous outflow
Stagnation of blood in the vessels of the head can be a symptom of the development of a benign or malignant tumor, hematoma, or a stroke. The pain in such diseases is dull in nature, accompanied by a feeling of fullness or heaviness in the head, a general feeling of lethargy and drowsiness. At the height of the attack, dizziness occurs.
Cervical osteochondrosis
The disease is associated with a progressive decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs, and at an advanced stage - with the formation of protrusion and herniation of the disc core. In the process, compression occurs on the nerve roots extending from the spinal cord and passing in the bone canals between the vertebrae, which leads to pain in the neck, radiating to the head.
Headaches are also caused by insufficient oxygen supply to the brain tissues. It is associated with partial compression of the vertebral arteries by a deformed disc, a displaced vertebra or a spasmed muscle. Subsequently, the person develops vertebral artery syndrome, in which pain is accompanied by severe dizziness, nausea and vomiting, and in severe cases, fainting.
Meningitis
Of all the infectious diseases accompanied by headaches, meningitis is one of the most dangerous. The pain is intense; many patients compare it to a constant fire inside the skull. The condition is accompanied by constant nausea, uncontrollable vomiting, which does not bring relief, and fever. One of the distinguishing signs is spasm (stiffness) of the neck muscles, due to which the patient cannot press his chin to his chest.
Migraine symptoms
The first symptom of migraine is the so-called migraine aura. This is not a mandatory symptom, but according to statistics, it occurs in more than 30% of patients. A migraine aura can manifest itself as:
- Visual disturbances - circles, zigzags, blind spots before the eyes;
- Hearing disorders - tinnitus, slight loss of coordination;
- Olfactory disturbances - a sharp increase in the sense of smell, a feeling of an obsessive smell nearby;
- Tactile disturbances - pain or increased sensitivity of the skin, goosebumps, numbness in the face or limbs.
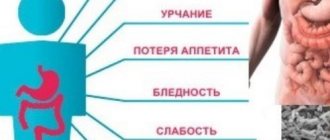
Some patients feel a migraine in advance - they experience weakness, irritability, tearfulness, increased appetite or complete loss of appetite.
Subsequent symptoms of an already occurring migraine:
- Severe, sometimes simply unbearable headache in one side of the head (usually the right). If you concentrate, you will be able to clearly feel the source of pain. It can last from several hours to 3 days.
- Nausea, abdominal discomfort, sometimes vomiting. Complete lack of appetite.
- Photophobia. Even dim light can increase pain or cause discomfort.
- Sound phobia. During a migraine, even a whisper nearby can be painful.
- Weakness. The stronger the pain increases, the stronger the feeling of weakness. During a severe attack, fainting may occur.
Patients with migraine are advised not to wait for an attack to develop, but to stop it in a timely manner. If possible, at the aura stage or the first signals of a developing migraine.
Pain in various parts of the head
The location of the pain can tell a lot about its cause.
- Back of the head. Discomfort or pain in this area is most often associated with diseases of the cervical spine (osteochondrosis, spondylosis), vascular development abnormalities, and occipital neuralgia. Sharp pain often accompanies a hypertensive crisis.
- Whiskey. Pain in this area may be unilateral or bilateral. It may indicate migraine (usually unilateral), otitis media, inflammation or injury of the temporomandibular joint, or damage to the temporal artery (autoimmune arteritis). A sudden attack may indicate a stroke.
- Forehead. Pain in the frontal region is most often a sign of acute respiratory viral infection (in this case, it is accompanied by an increase in body temperature). Ophthalmic diseases, sinusitis and migraines can also provoke attacks.
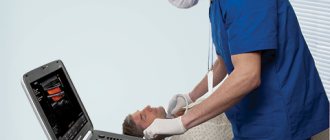
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of headaches, especially chronic ones, is a long and complex process that requires the participation of specialists in various fields: therapist, neurologist, ophthalmologist, ENT specialist. The process of finding the cause includes:
- identification of the main complaints: intensity, duration, localization, nature of pain, conditions of appearance and cessation, what is accompanied;
- medical history: when the first attacks occurred, how often they occur, etc.;
- life history: previous injuries, acute and chronic diseases, allergies, heredity;
- examination: assessment of blood pressure, pulse, temperature, neurological examination, etc.;
- laboratory diagnostics: general blood and urine analysis, basic biochemical blood parameters (glucose, cholesterol, bilirubin levels), if necessary, assessment of hormonal and allergic status, etc.;
- Doppler ultrasound (duplex scanning) of the vessels of the head and neck to identify possible narrowings, spasms, atherosclerotic plaques, structural features;
- EEG (electroencephalogram): makes it possible to evaluate the electrical activity of the brain, identify signs of epilepsy, etc.;
- MRI or CT scan of the head: allows you to identify tumors, ischemic areas, hemorrhages and other abnormalities;
- X-ray of the vessels of the head with contrast to identify the features of the anatomy of the vessels in this area.
If specific diseases are suspected, specific tests and consultations with specialists are prescribed (examination by an ophthalmologist for signs of glaucoma, spinal puncture if there is a possibility of meningitis, etc.).
Make an appointment
Treatment
Treatment for headaches depends on the cause. Specific diseases require appropriate therapy. If we are talking about long-term, chronic processes, for example, cerebral ischemia, migraine, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, etc., the following groups of drugs can be prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): necessary for quickly relieving pain and eliminating inflammation;
- Unlimited use of NSAIDs leads to side effects in the form of gastritis, ulcers of the gastric mucosa, gastrointestinal bleeding, and long-term use of NSAIDs leads to the appearance of ABUSE HEADACHES - arising from taking painkillers.
- antispasmodics (including combined): effective for vascular spasms of any origin, including migraine, arterial hypertension, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- sedatives: help reduce stress levels, normalize sleep, enhance the effect of analgesics, often enough to relieve headaches;
- antidepressants, tranquilizers: necessary if the drugs of the previous group are ineffective;
- nootropic drugs: improve metabolism in the brain, increase resistance to stress; required for encephalopathy, cerebral ischemia, vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- B vitamins: improve the conduction of nerve impulses, improve the functioning of the brain and spinal cord;
- Agnioprotectors and blood thinners: improve blood fluidity, increase the supply of tissues with oxygen and nutrients.
The following may be used as an adjunct to drug therapy:
- physiotherapeutic procedures: magnetotherapy, electrophoresis, phonophoresis, laser therapy, electrosleep, diathermotherapy, etc.;
- restorative or therapeutic massage, especially effective for pathologies of the cervical spine;
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- manual therapy;
- Spa treatment.
Surgical techniques are necessary for advanced osteochondrosis, malignant and benign tumors and other conditions that cannot be corrected by conservative methods.
Prevention
Effective headache prevention is, first of all, lifestyle changes. Doctors recommend:
- normalize sleep: you need to sleep at least 8 hours every day and at night;
- have a good rest;
- minimize stress as much as possible;
- avoid physical inactivity: walks in the fresh air, moderate sports at the amateur level, swimming will help improve blood circulation and strengthen the muscle corset;
- eat right: avoid overeating, minimize the consumption of spicy, salty, canned foods, smoked foods, etc.; the diet must contain a sufficient amount of vitamins, macro- and micronutrients;
- normalize body weight;
- minimize or eliminate smoking and alcohol consumption;
- Drink at least 2 liters of clean water daily.
In addition, it is necessary to regularly visit doctors, monitor chronic diseases, and, in their absence, undergo a comprehensive check-up diagnosis.
What to do if you have a migraine?
- Take a drug that stops the attack as soon as possible. NSAIDs may help in the early stages, but triptans are the best treatment today;
- Lie down comfortably in a dark and cool place, provide access to fresh air;
- If necessary, place a towel moistened with cool water on your forehead;
- Avoid exposure to light and sounds;
- Try to sleep;
- If medications and sleep do not help, and the attack becomes more and more painful, you need to call an ambulance.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
Even a mild headache can affect lifestyle and be a symptom of serious illnesses. Doctors at the Energy of Health clinic invite you to undergo a comprehensive examination and identify the cause of the discomfort. We offer modern, combined treatment methods, including:
- drug therapy according to indications;
- various types of physiotherapy;
- group and individual physical therapy classes, compiling sets of home exercises;
- therapeutic and general massage;
- manual therapy and osteopathic services if necessary;
- therapeutic procedures for sinusitis and other diseases of the ENT organs;
- ophthalmological care, etc.
Working together with the patient, we will find the cause of the pain and try to eliminate it as quickly as possible.
Advantages of the clinic
The main priority of the Health Energy clinic is effective, affordable and qualified medical care for each patient. We do everything to make you comfortable and comfortable within the walls of our center. At your service:
- experienced doctors and nursing staff;
- modern equipment for diagnosing and treating diseases;
- all types of laboratory tests;
- comprehensive diagnostic programs;
- organization of rehabilitation and sanatorium-resort treatment;
- Reception by appointment without long queues.
Don't let headaches become a part of your life. Get diagnosed at the Health Energy clinic and let us choose effective treatment.