Main symptoms:
- Pain syndrome in the right hypochondrium.
- Itchy skin is also caused by an increase in bile acids.
- Yellow color of the skin and eyeballs (icteric sclera).
- Light stool and dark urine.
- Stool disorder is accompanied by a foul odor.
- Decreased visual acuity.
Diagnosis of the problem is carried out using urine, blood, ultrasound of the liver, cholangiopancreatography, and endoscopic methods.
Causes of pain in the left side
Pain in the left side can be functional or occur due to inflammation. To make a diagnosis, you need to have an idea of what organs may be involved in this process.
Subcostal area
Here are the left lobe of the liver, pancreas, stomach, spleen, part of the colon, small intestine, lower part of the lungs, diaphragm, heart. Unpleasant sensations in this area can be caused by diseases of the heart, lungs (pneumonia and pleurisy), stomach, spleen, pancreas, duodenum, intercostal neuralgia, diaphragmatic hernia. The digestive organs suffer not only from bacteria , but also from unhealthy diet, stress, and bad habits.
A rupture or bruise of the spleen is especially dangerous. The pain is sharp, characterized by the appearance of a bruise around the navel, a hematoma in the left side of the abdomen, colic can radiate to the back. In this case, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Inflammation of the lungs can also be accompanied by dull pain in the left hypochondrium , aggravated by coughing. With pleurisy, they intensify not only during coughing, but also when changing body position and even when breathing.
Intercostal neuralgia is characterized by sharp pain in the side, which manifests itself even with the slightest movement or inhalation. Acute colic is observed with osteochondrosis and neuralgia, myalgia and injuries.
Stitching pain (usually in the muscles) can occur if the load is distributed incorrectly or if there is no preliminary warm-up before training.
Left side
Here are the intestines, kidneys, ureter, spleen, pancreas, stomach, genitals (uterus and ovaries in women, prostate and testes, testes in men). Most of the discomfort in this area is associated with the intestines.
Possible causes of pain in the left side:
- Colitis is accompanied by pain from flatulence, it is acute, cramping, and often occurs after eating. They may also be accompanied by false urges to empty the bowels, diarrhea, sometimes with mucus and blood.
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis - pain is accompanied by general intoxication.
- Intestinal obstruction – pain does not depend on food intake and can occur at any time of the day. Their character is sharp and combative. If help is not provided, they may subside in 2-3 days. But this is not a recovery, but a complication. The clinical picture is complemented by constipation, bloating and asymmetry of the abdomen, nausea and repeated vomiting.
- Colon cancer - in advanced cases.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system - inflammation of the uterus and appendages, sexually transmitted diseases, intestinal infections, atypical appendicitis, cystitis, urethritis, endometriosis, ovarian cysts, tumors, ectopic pregnancy and menstrual irregularities. These pains can radiate to the lower back, anus and groin. Emergencies include torsion of an ovarian cyst and ectopic pregnancy. These pathologies require immediate hospitalization.
Causes of pain
In most cases, pain in the lower back and left leg is caused by injuries or diseases of the spinal region. One of the most common symptoms is muscle spasms, which are interpreted by the patient as a short-term reaction to a sedentary lifestyle or an uncomfortable sleeping position.
Often these reasons are the source of pain. However, there are more serious factors, which include infections, inflammatory processes, and cancer.
These reasons have negative consequences. To avoid them, at the first appearance of lower back pain, you should immediately consult a doctor.
We list the main causes of lower back pain radiating to the left leg:
- Hypothermia. Sudden temperature changes can trigger the appearance of myositis - inflammation of muscle tissue in the lumbar region. The main symptoms of hypothermia include nagging pain that does not go away over time, hardening of muscle areas, and increased pain upon palpation. Often the pain migrates and radiates to the leg and buttock on the affected side. Sometimes myositis entails increased body temperature, redness and itching in the lumbar region.
- Protrusion of intervertebral discs. One of the variants of intervertebral disc herniation, in which the disc bulges into the spinal canal. The dimensions of the protrusion range from 1 to 3 mm. The main prerequisites for the appearance of a hernia are incorrect posture, weak muscular skeleton, obesity, spinal column injuries, high loads on the spinal region, including sports, and past infectious diseases. Symptoms of protrusion include weakness, stiffness of movement, coldness in the legs, and pain spreading to the limbs.
- Diseases of the sciatic nerve. The most common of the spectrum of diseases is sciatica - a pinched nerve, which is accompanied by acute pain and limited mobility of the body. Often there is a shooting pain directed to the back of the thigh or lower leg. The causes of pinching are systematic hypothermia, heavy lifting with weight transfer to the back, sudden unnatural movements in the lower back.
- Osteochondrosis. This is a disease of the cartilaginous surfaces of the bones of the musculoskeletal system, which often affects the spinal column. Appears as a result of constant sharp turns, bending and straightening of the body, playing sports without mandatory insurance, improper lifting technique and incorrect posture for sleeping and resting. Osteochondrosis causes aching pain in the lower back, which radiates to the legs, numbness of the limbs and increased pain during shaking and sudden movements of the body.
- Neuropathy. This disease occurs due to dysfunction of the sciatic nerve. The causes of neuropathy include injuries to the nerve, surrounding tissues and subsequent compression of the nerve by damaged muscles, as well as degenerative diseases of the nervous system. Neuropathy causes loss of sensation in the foot and impaired movement of the toes. In advanced cases, trophic ulcers form.
- Hernia. Unlike protrusion, it has a size from 3 to 15 mm. Symptoms of a hernia include constant lower back pain, surges in blood pressure, weakness, pain in the heart, dizziness and headache, numbness in one of the legs, and loss of sensation in the genitals. In advanced cases, a hernia of the spine provokes paralysis, paresis, and disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
- Osteoporosis. Consists in reducing bone strength. The bone material becomes more porous and brittle. The causes of the disease can be primary - heredity, disruption of the ovaries in women, old age - and secondary: diabetes, kidney disease, blood disease, thyroid disease, oncology. With osteoporosis, severe pain is observed that spreads to the leg, arm, abdominal area and thoracic region. Fractures and deformation of bones and joints are also possible.
- Sciatica. This is an aching and growing pain in the lumbar region, radiating to one or both legs. People over 30 years of age who are subject to frequent stress and depression are predisposed to this disease. Incorrect posture and heavy physical labor also cause lumbar sciatica. In general, this disease is a consequence of a vertebral hernia. Symptoms include severe migrating pain, limited mobility of the lumbar region, inability to step on the foot, changes in temperature and color of the skin of the legs.
- Oncology. Sometimes the cause of lower back pain that radiates to the left leg is cancer. In this case, pain is caused by metastases located in the bones, multiple myelomas, i.e. tumors, and primary spinal tumors - neoplasms that originally appeared in the spinal column. A distinctive feature of pain caused by cancer is its constant nature and manifestation mainly at night. An increase in temperature to 37-37.5 ° C, weight loss and a decrease in the patient’s height can also be a sign of the development of oncology.
Lower back pain can be caused by a wide range of medical conditions. To minimize risks, preventive measures should be taken.
Localization and nature of pain
Pain is divided according to the mechanism of its occurrence, as well as according to its characteristics. They can feel like cutting, stabbing, dull and sharp, drilling, bursting, shooting, aching and encircling.
Classification of pain by source of origin:
- Visceral - appears due to inflammatory processes, injuries and bleeding from internal organs. It is associated with peristalsis of the intestines and stomach, and occurs during spasms or strains of the muscles of these organs.
- Neurological – occurs when the nerve trunks become inflamed.
- Somatic – constant and clearly localized. The pain is sharp, cutting, appears due to irritation of the peritoneum, for example, with peritonitis.
- Reflected - spreads from distant organs along nerve fibers due to the irradiation of unpleasant sensations. It does not arise in the organs of the left side, but comes here. For example, with left-sided lower lobe pneumonia, pleurisy, heart attack, liver disease.
Classification by pain intensity:
- Acute – intense, cannot be relieved with analgesics.
- Chronic – periodically occurring low-intensity unpleasant sensations that are relieved by analgesics.
Back pain occurs with pleurisy and inflammation of the lung. Lower back pain may indicate kidney pathology.
Pain after eating is usually associated with digestion. They are characterized as heaviness, discomfort and tingling, and may be accompanied by fever, chills, nausea and gas formation. This may also indicate the development of disorders in the pancreas . More often than not, all this is associated with poor nutrition.
When there is aching and pulling on the left side below the ribs in front, this is a symptom of sluggish duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum).
If it stings on the side under the left rib during training or strength training, then this indicates insufficient warm-up. The body simply did not have time to prepare for the increase in blood circulation. They pass quickly and have no consequences.
When the aorta ruptures, the pain is sudden, severe in the abdomen or from the back. Immediately after this, collapse occurs - a sharp drop in pressure. A person can die in a matter of minutes from bleeding. You need to call an ambulance without wasting a second.
Stones and sand in the urinary tract cause sharp pain because the tissue and capsule of the organ are stretched, pressure increases and pain occurs, mainly under the ribs in the back.
Methods for treating and preventing diseases
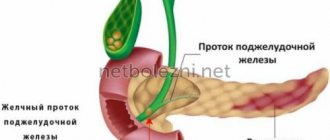
As a treatment for cholestasis, Western medicine suggests taking hepatoprotectors, cytostatics, vitamins, and antioxidants. The subhepatic form of cholestasis requires urgent surgical intervention.
For hepatosis, the main stage of treatment is following a diet that excludes fatty, fried, flour, salty, and alcohol. Depending on the findings of diagnostic tests, allopaths may recommend surgical treatment.
Attacks of biliary colic are relieved with antispasmodics, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial drugs. Western doctors recommend surgery for frequent exacerbations of the disease.
In case of urolithiasis, Western medicine resorts to surgical treatment (extraction of stones). As a preventive measure, the patient is prescribed drugs that improve microcirculation in the kidneys and relax the urinary tract.
To prevent complications of nephroptosis, wearing a bandage and special exercises that strengthen the muscles of the back and peritoneum are recommended. When bacterial infections develop, antibiotics are needed, and in some cases, surgical treatment.
For chronic pancreatitis, doctors prescribe a special diet, antispasmodics, enzymes, and vitamin therapy.
The left side hurts in a woman and a man: what are the differences?
In men, this may be a consequence of inflammation in the genitourinary system. As a rule, this is accompanied by an increase in temperature.
Sharp pain may indicate:
- prostatitis;
- vesiculitis
- inflammation in the bladder, urethra;
- stones in the prostate gland;
- malignant tumors;
- inguinal hernia;
- gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis.
In women with endometriosis or an ovarian cyst, there is nagging pain (both on the left and on the right). Similar to menstrual ones, but appear at any time. And the periods themselves lengthen and become more painful.
Nagging pain in the lower abdomen in women indicates problems with the left ovary . They get worse when walking. Although this may be due to inflammation of the fallopian tubes and uterine mucosa, and oncology.
In women, pain in the left side of the lower abdomen may occur during pregnancy due to intestinal displacement by the growing uterus. There is no danger if it does not become acute and is not accompanied by spotting and bloody discharge.
Calculous cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder, which is accompanied by thickening of bile and the formation of stones from it. The reasons may be irregular nutrition, hereditary factors, infectious diseases, and a sedentary lifestyle.
The acute form of cholecystitis is accompanied by stabbing pain, vomiting, nausea, and fever. The chronic form is manifested by biliary colic, which occurs when a stone gets stuck in the neck of the gallbladder. The symptoms are the same: acute pain, vomiting without relief, bloating, diarrhea, heartburn. It can be provoked by severe stress and dietary errors. When walking or running quickly, the complaints intensify.
Methods for diagnosing cholecystitis: blood test (determination of liver tests, pancreatic enzymes), cholecystography, ultrasound of the gallbladder.
If your left side hurts, what should be the algorithm of action?
Even if the pain under the ribs, on the left, below, in the navel area or in the center quickly subsides, but is accompanied by vomiting, burning, fever, an ambulance should definitely be called. Any intake of food, water, or pills is not advisable. All this can blur the picture, complicating the diagnosis.
If a rare pain syndrome occurs, you can take painkillers. However, this method is optimal only if the pain is not accompanied by acute symptoms, such as fever, chills and nausea.
Important! Seeing a doctor is mandatory if the pain recurs and all the remedies used are useless.
The most dangerous consequences
Perforation of a stomach ulcer - a peptic ulcer destroys the wall of the stomach, and all the contents leak into the peritoneum. Peritonitis occurs. It is characterized by paroxysmal cutting pain in the lower abdomen, intensifying when lying on the left side, symptoms of intoxication of the body, severe weakness, increased heart rate, and sticky sweat. Emergency hospitalization and immediate treatment are indicated.
Perforation of stomach ulcer
Prevention
As for prevention, the basis is a proper balanced diet. It is advisable to minimize hot and spicy foods. Legumes can irritate the mucous membranes and cause flatulence.
It is important to give up bad habits such as smoking and alcohol , get proper rest and get a good night's sleep. Any training should be carried out only 1.5-2 hours after eating.
To avoid gynecological problems, women need to treat existing inflammation of the genital organs and undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist.
Doctors' advice
Doctors strongly recommend:
- Do not engage in self-diagnosis and treatment.
- In case of acute pain, do not endure it, but call an ambulance. This is the case when it is better to be safe.
- If the pain is not intense, dull, then it is better to consult a doctor at the clinic. You need to describe all your sensations without any embarrassment.
There is no need to assume that the pain in the left side will go away on its own; it is better to consult a doctor and identify the true cause. Taking painkillers gives only a temporary effect, but does not eliminate the disease itself. If pain occurs suddenly and lasts more than half an hour, it is better to play it safe and call an ambulance.
Fatty hepatosis
The condition is characterized by inflammation of liver cells (hepatocytes), metabolic disorders and the formation of fibrous tissue around the hepatic veins. Fat replaces active liver structures, ultimately leading to death. Very often, hepatosis occurs due to alcohol abuse and fatty foods, concomitant pathology (cardiomyopathy, diabetes mellitus). The symptom manifests itself as acute pain in the right hypochondrium after a heavy meal.
For diagnosis, allopaths carry out: clinical blood test, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, liver tissue biopsy, CT scan.