Home / Labor Law / Payment and benefits / Sick pay
Back
Published: March 23, 2016
Reading time: 7 min
0
14781
The duration of the sick leave issued for the period of rehabilitation after amputation of appendicitis is directly related to the peculiarities of this surgical intervention.
The ability of a particular organism to recover is also of great importance. The doctor’s task is to make sure that the patient’s health is not in danger and he can resume work.
- What affects the duration of sick leave for appendicitis?
- Dependence on the complexity of the operation
- How is such sick leave paid?
Causes
The main culprit behind inflammation of the appendix is its blockage. This occurs due to the accumulation of fecal stones and foreign bodies in the appendix (this is how appendicitis usually occurs in children). The bending of the organ under the influence of various factors, such as scars and adhesions, also plays a role. In rare cases, the provocateur is a helminth or a neoplasm on the tissues of the appendix.
Various types of infections (bacterial, parasitic) can cause an inflammatory process.
There is a theory that the disease is caused by an insufficient amount of plant fiber entering the body with food.
It is possible that the syndrome occurs due to suppression of the body's immune function. The walls of the appendix are permeated with lymph cells, which are part of the immune system. The appendix tissue and lymph cells act as a shield. Disruption of the functions of this shield and the presence of infection provoke inflammation.
When is sick leave issued?
Sick leave or disability certificate is issued to citizens in situations where for certain reasons they cannot perform their work duties. Contrary to its name, sick leave is not always directly related to illness. Today, there are several good reasons why a person can receive a certificate of incapacity for work at a clinic, such as:
- illness of a child who needs constant care and attention from a parent. As a rule, the child’s mother goes on sick leave for this reason, but hypothetically the father can also take advantage of this opportunity;
- pregnancy and childbirth. A certificate of incapacity for work is issued to an employee for a fixed period, but if she wishes, she can leave her work duties later or earlier - if there are objective reasons affecting her health. The duration of sick leave according to BiR depends on how the pregnancy proceeds and whether it is singleton or multiple;
The standard duration of sick leave under the BiR is 140 days
- quarantine. Quarantine can be declared both at the enterprise where the employee is employed, and at the educational institution that his child attends. In both cases, doctors at district clinics cannot refuse to issue a certificate of incapacity to a citizen (or woman);
- stay in an inpatient medical facility. The reasons for being in the hospital can be any - from an exacerbation of an existing disease to the need for prosthetics (and an appropriate referral from a doctor);
- rehabilitation. Different diseases require different amounts of time for the body to recover. Thus, a person will need more time to recover from surgery (and the type of surgery determines the duration of recovery). Some operations on the spine and other parts of the body require long-term rehabilitation, which can take almost a year.
During the rehabilitation period, doctors extend sick leave so that the body fully recovers.
Use the temporary disability benefit calculator.
Symptoms
- acute pain in the lower abdomen on the right;
- nausea, which is accompanied by vomiting;
- a sharp jump in temperature (37.5-38 degrees);
- pulse 90-100 contractions per minute;
- rigidity of the abdominal muscles.
The course of the acute form of the disease is influenced by such conditions
- position of the diseased organ;
- phase of the pathological process;
- changes in the tissue structure of the appendix;
- the ability of the circulatory and immune systems to respond quickly and adequately;
- painful conditions and complications present in the body.
Pain appears unexpectedly and increases quickly, worsening with movement or coughing.
The location of the appendix influences where exactly a person feels pain. When the first signs of appendicitis appear, it is impossible to clearly determine the location of the pain. It is felt throughout the abdomen and only after a while it descends into the iliac region.
In cases of an uncharacteristic position of the diseased organ, the pain may have a different nature and be located in some other place. If the cecum is located low enough, the onset of the attack is characterized by aching or stabbing pain over the pubic area.
When the appendix is located behind the cecum, pain is felt in the lower back, iliac region and lower abdomen on the right.
When the appendix is located behind the peritoneum, the pain is localized in the lower back, but it can be felt in the genital area and in the thigh. In this case, the upper part of the appendix may be quite close to the bladder, right kidney or appendages in women. Because of this, inflammation of the celiac appendix can be mistaken for problems with the kidneys or disease of the uterine appendages.
Another sign of the acute form of this disease is vomiting. It is observed in 30% of those who are diagnosed with inflammation of the appendix. Some time after the onset of pain, loss of appetite and nausea with vomiting are noted, attacks of which are sometimes repeated. If this happens after a relatively long period of time, it is a clear symptom of peritonitis.
At the initial stage of the acute form of the disease, body temperature does not exceed the normal limit or reaches 38 degrees, but if the disease actively worsens, it increases. For those cases of inflammation when destruction of organ tissue is observed, low temperature and rapid pulse are characteristic, which is not the norm. In addition, increasing intoxication borders on inappropriately low blood pressure.
Body temperature rarely rises during acute inflammation of the appendix. Usually it reaches 39 degrees and higher when the process is perforated.
The chronic form follows from the acute one, when the attack subsides without medical intervention.
Types of chronic appendicitis
- recurrent;
- residual.
A recurrent inflammatory process is a kind of return of an acute one, only with weaker manifestations.
Residual inflammation manifests itself as damage to the cecum or adhesions.
Complications
- appendicular infiltrate;
- abscess;
- peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum).
The formation of infiltrate occurs on the third, sometimes on the fifth day from the moment when acute appendicitis occurred. Organs adjacent to the appendix participate in the inflammatory process. When the course of the disease becomes unfavorable, an abscess develops.
An abscess can occur in various areas of the abdominal cavity.
Depending on this, the following types of abscess are distinguished:
- periappendicular;
- localized between the intestines;
- developing under the diaphragm;
- pelvic.
Diffuse peritonitis is the most dangerous complication.
Can provoke diffuse peritonitis
- migrating inflammation;
- rupture of the appendix wall;
- penetration of the abscess into the abdominal organs.
Recovery period
Depending on how exactly the operation was performed, recovery can last from 2 days to 2 weeks. During laparoscopic surgery, patients are discharged on the 2-3rd day, and after laparotomy - on the 10th day .
If complications arise (hernia, peritonitis, inflammation of the suture, low-grade fever, abscess), the duration of hospital stay increases.
ATTENTION! To speed up discharge and avoid complications, the patient needs to adhere to all medical instructions, follow a regimen and eat certain foods.
Regime and diet
After removal of the appendix, patients are recommended to start walking (always in a bandage) within 5-6 hours after the operation. A little physical activity promotes rapid recovery of the body and prevents the formation of adhesions.
Heavy physical activity and lifting loads are strictly contraindicated for up to 3 months, as all this can lead to the suture coming apart or a hernia occurring.
Patients are advised to sleep at least 8 hours a day, not drink alcohol for 3-4 weeks, and lead as healthy a lifestyle as possible. The same applies to nutrition: it should be light, balanced and of high quality.
In the first 12 hours after surgery, when the body recovers from anesthesia, you should not eat . In the first 3 days, meals are very gentle, light and frequent: at least 5-6 times a day. It can be:
- chicken broths (with a small amount of fat, for example, from chicken breast);
- chicken meat: only boiled and pureed;
- vegetable purees: from potatoes, pumpkin, zucchini;
- dairy products: low-fat and sugar-free (kefir and yogurt);
- boiled rice in water.
A week after the operation, slimy porridge with water, liquid unleavened soups without salt, pureed vegetable soups, a small amount of fresh herbs, boiled carrots, dried fruits, and baked apples can be introduced into the diet.
Gradually, the menu is expanding, and more products can be introduced into it, but it is better to avoid fatty, spicy and salty dishes in principle.
ADVICE! In addition to nutrition, pay attention to water. The more you drink, the better it is for the body: all toxins are more actively removed from it, it is cleansed and restored faster.
Water can be supplemented with herbal teas, fresh natural juices and sugar-free compotes. You need to drink 1.5-2 liters per day .
Temperature after intervention
After surgery, an increase in temperature is normal. A focus of inflammation occurs in the body, and the immune system is actively involved in its work. During this, the temperature rises to 37-38 degrees and lasts from 2 to 10 days.
After laparoscopy, the temperature goes away naturally on the 2-3rd day, and after laparotomy it can last up to 10 days . Sometimes the temperature can last for 3-6 months. The reason for this may be a violation of thermoregulation or other complications.
In such cases, treatment is carried out with antibacterial drugs, anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed, or treated symptomatically with antipyretics. It all depends on the cause, which is determined by the doctor.
When are stitches usually removed?
The abdominal wall is sutured with absorbable threads, and the skin with strong silk or synthetic threads. If wound healing proceeds without complications and the wound is covered with a crust, the sutures are removed within 7-10 days.
Appendicitis in men
Diagnosis of appendicitis in men
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe a series of examinations. In particular, these are blood and urine tests. A blood test is a fairly informative diagnostic method, which mainly monitors the presence of leukocytes and their level, as well as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. A urine test can detect the presence of protein (which should normally be absent).
X-ray is an outdated diagnostic method, since all it can reveal is the presence of fecal stones. Therefore, the patient will be referred for an ultrasound examination, which is the most optimal diagnostic method today. Using ultrasound, you can most accurately identify signs of appendicitis in men, in particular, an increase in the appendix up to 5 mm. However, in approximately 50% of patients, ultrasound will not detect appendicitis due to an unnatural position or obesity.
Therefore, the most productive research method can be prescribed - computed tomography. It makes it possible not only to see the inflamed appendix, but also the inflamed tissue itself near the appendix.
Laparoscopy is the most objective diagnostic method. However, they resort to it in very complex and controversial cases, when standard methods do not give the whole picture of the problem. A probe with a camera is inserted into the patient under anesthesia through a small incision, with the help of which the doctor will accurately see the source of inflammation and provide adequate treatment.
Diseases in men similar to appendicitis
Symptoms of appendicitis in men can be similar to those of other diseases. Even an experienced doctor may not make an accurate diagnosis the first time (which is why an examination is prescribed). In general, along with appendicitis, the patient may be suspected of having urolithiasis or renal colic (a urine test will verify the accuracy of the version). A perforated gastric ulcer may also be suspected (to rule out this possibility, laparoscopy is performed). Another “similar” disease is right-sided pneumonia, which can be excluded or confirmed using x-rays.
Type of appendicitis in men
Signs of appendicitis in men may depend on the type of inflammation. The first stage of the disease is acute catarrhal appendicitis - at this stage the symptoms are quite weak (or do not appear at all). But if the disease is detected at this stage, treatment will be very easy, and recovery after removal of the appendix will be quick.
Destructive appendicitis is an inflammation with pronounced symptoms and unpredictable signs. During the course of the disease, symptoms may change - in particular, sharp fluctuations in body temperature are possible. In any case, discomfort, pain, nausea and other signs should be a signal to consult a doctor. It’s better not to delay - and then the help will be more effective, and you’ll be able to return to your normal way of life faster.
How many days do you get sick leave and how long do you stay in the hospital after appendicitis removal?
When making a decision, the doctor is guided by the recommendations of the Ministry of Health.
The minimum duration of sick leave is only three days, and the maximum is thirty days.
If it is necessary to increase the length of stay of the patient at home or in the hospital, a medical commission is convened. If the patient's condition is unsatisfactory, his sick leave can take a whole year.
Of course, such serious complications are not typical for appendicitis removal. This is a fairly easy operation, the recovery period after which takes an average of two weeks (during this time the stitches have time to completely heal).
The calculation of payments based on a document from a medical institution confirming the fact of the rehabilitation period is based on the provisions of the Labor Code.
Article 183 clearly states that the employer, when paying for any sick leave, must be guided by Federal Law No. 255. According to the provisions of this law, sick leave is paid in full. There are restrictions on payments only in two cases:
- if you have sick leave to care for a child;
- issuing certificates of incapacity for work to employees with disabilities.
The employer does not have the right to refuse payment, check the validity of issuing a medical document, or dismiss an employee.
All of the above actions are violations of the law.
The minimum duration of sick leave is three days, and the maximum is thirty days. To increase the length of stay in the hospital, a medical commission is convened. In some cases, if the patient’s condition is unsatisfactory, sick leave can be extended even up to a year.
But such serious complications are not typical for appendicitis. Appendectomy is a fairly easy surgical procedure, with an average recovery period of fourteen days.
The employer does not have the right to refuse to pay sick leave, dismiss an employee or check the validity of issuing a certificate of incapacity for work.
For appendicitis, laparotomy can be performed - this is an abdominal operation, the essence of which is to dissect the soft tissue located directly above the appendix. Nevertheless, the more preferable method of resection of the appendix is laparoscopy.
The essence of the procedure is that small punctures are made in the area of the navel and appendix. Laparoscopy is less traumatic, which affects the duration of the rehabilitation period and the risks of complications.
With classic surgery to remove the appendix, a small suture remains - about three centimeters. If there are no complications, the sutures are removed on the tenth to twelfth day after surgery. Internal sutures dissolve within two months.
Causes of appendicitis in children
- fractional meals: little by little, but often;
- eat food warm;
- food should be fortified and balanced;
- exclusion of food products that provoke fermentation and gas formation processes.
As for physical activity, you shouldn’t completely exclude it, but, on the other hand, completely giving up activity would be stupid. Minimal mobility is indicated only in the first days after surgery. Within six weeks, muscle fusion occurs. During this period, the risks of adhesions and hernia are high.
For this reason, heavy lifting is strictly prohibited during this period. On the other hand, therapeutic exercises and walks in the fresh air will help reduce the likelihood of adhesions forming. The return to physical activity should not be abrupt; the intensity should be increased gradually.
10 days - this is the period for which sick leave is issued after removal of appendicitis, however, this is an average figure.
The attending physician decides how long a particular patient will spend on forced rest, based on the state of health and the method by which the operation was performed.
But full recovery will take more time than the Labor Code provides, therefore, if the work involves physical activity, the person will not be able to perform it in full immediately after returning to the workforce.
Treatment of appendicitis
Like another similar disease (appendicitis is essentially an inflammation of one of the processes of the cecum), it can be stopped with the help of antibiotics.
But most medical institutions do not have equipment that allows accurate monitoring of the healing process, and since the likelihood of inflammation moving into the acute phase is quite high, doctors prefer the already proven method - surgery. There are two types of surgery used for appendicitis:
- Laparoscopy is when an unnecessary organ is removed through three small incisions and an endoscope (a device that allows the surgeon to observe everything that is happening on a monitor) is inserted into the abdominal cavity. It lasts about half an hour.
- Laparotomy is an old and unloved method by patients, which requires an incision up to 10 cm long. It is usually used for complicated appendicitis, which requires not only removing the appendix, but also washing the intestines from residual pus. After such an operation, the patient needs long-term care.
Accordingly, recovery occurs. To return to normal life, the patient may need up to 4 weeks, whereas after laparotomy it takes 10-14 days.
In addition to the short recovery time, the minimally invasive technique is also attractive because the internal tissues are almost not damaged, so there are no noticeable marks left after the operation.
After surgery, to prevent worsening, the doctor prescribes medications.
From the operating table, patients are transferred to the intensive care unit.
It does not matter the method used by the surgeon, because complications can develop with any of them. In addition, general anesthesia used for appendicitis has a negative impact on the general condition of the patient.
The doctor’s goal at this stage is to prevent deterioration, so medications are actively used:
- painkillers - to relieve postoperative pain;
- antibiotics - to prevent infections;
- glucose and vitamins - to maintain vitality and restore the body.
On the second day, the patient is transferred to a regular ward and the further recovery process depends on how successful the surgical intervention was. If appendicitis was diagnosed on time, and the patient complies with all the instructions of the medical staff, there is every chance of a favorable outcome.
If there are no problems (constantly elevated temperature, purulent discharge), on the 3rd day the patient can get out of bed and take the first steps. At this moment, the presence of a doctor nearby is not necessary, but it is desirable.
Also, on the third day, the sutures are removed after laparoscopy, and if the operation was performed using the standard method, you will have to wait a few more days.
Caring for a scar does not require much effort; it is enough not to wet it during hygiene procedures and periodically treat it with an antiseptic. On the tenth day the patient is discharged home.
Until complete recovery, which takes about 2 months, he has to exclude fatty, floury foods and sweets from his diet, and also postpone visits to the gym and any physical activity until later.
Most complications appear a few days after surgery. The most common among these is inflammation of the incision site with the formation of pus in the abdominal cavity.
A sharp increase in temperature and throbbing abdominal pain are the first symptoms and require immediate response.
Treatment started on time will last 2-3 days; in advanced cases, you will have to resort to surgery again.
If after the operation the pain does not subside, but intensifies, this indicates the development of peritonitis or internal bleeding. There are no options - only a repeat operation can save the patient’s life.
Sometimes, in the postoperative period, complications arise that cannot be avoided without repeated surgery.
Sometimes complications occur that are not directly related to the abdominal organs or wound healing.
Typical examples are pneumonia, bronchitis, cardiovascular diseases and genitourinary problems. Pathologies are treated by specialized specialists. Therapy is carried out according to the standard regimen, but the patient is in the surgical department.
How long they stay in the hospital in such cases is determined individually for each patient, based on their medical history.
The sick leave includes not only the time spent in the hospital. A certain period of rehabilitation takes place at home, and the duration depends on the patient’s condition.
In the absence of complications, the period of “legal absenteeism” is no more than 14 days, but if after this period the patient’s health does not allow him to go to work, it is possible to extend the sick leave. But this will require a decision by a medical commission and the presence of important reasons. The maximum period for which sick leave is given after appendicitis is 12 months, but in practice this happens very rarely.
Despite the apparent simplicity of the operation, about 4 months must pass after discharge for the patient to return to his normal lifestyle.
Until then, he will have to limit himself to drinking alcohol, playing sports, lifting heavy objects and having an active intimate life.
A diet is required, although not as strict as in the first days and weeks.
An important part of rehabilitation is caring for the postoperative scar. To make it less visible, it is recommended to lubricate it with special ointments, creams or oils, but not earlier than two months after appendicitis.
The fact is that first the internal sutures, which are fastened with self-absorbable threads, must heal.
In the first days of staying at home (if the stitches have not yet been removed), you need to make sure that the edges of the wound do not separate and that infection does not get inside.
The complexity of appendectomy and the method of its implementation is directly related to how much sick leave will be given after appendicitis:
- If an inflammatory disease is detected in a timely manner, a standard operation is performed. Small incisions are made. In this case, sick leave is given for a period of five to ten days;
- emergency amputation is performed if the appendix bursts or peritonitis develops. In this case, a longer recovery period will be required. In this case, patients stay in a medical facility for up to thirty days;
- if complications arise, the patient may be kept in the hospital for even more than thirty days. One of the serious complications of appendicitis is appendicular infiltration. It is a collection of inflamed tissue around the appendix.
Treatment of appendicitis
Appendicitis in women
The main signs of appendicitis in women:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- acute abdominal pain;
- muscle tension;
- Shchetkin-Blumberg syndrome;
- heat.
It is important to identify appendicitis in women in time in order to put her health at risk as little as possible. One of the most important signs is pain. At the very beginning of inflammation, the pain is pulling and pressing. They occur not only on the right side; it is quite normal for the pain to radiate to the left side or concentrate around the navel. In pregnant women, pain often occurs in the upper abdomen. After some time, the pain can spread throughout the abdomen, and then concentrate in the appendix area. At this time, they can be either constant or attacks similar to contractions. Another feature of pain with appendicitis is that it intensifies when coughing or even laughing.
Another sign by which you can understand how to determine appendicitis in women is vomiting and nausea. This is a completely typical manifestation of appendicitis. Vomiting occurs once or twice during the course of the disease. In addition to nausea, pregnant women also experience severe shortness of breath.
Appendicitis provokes an increase in body temperature. The normal temperature for this disease is 38 degrees. Quite often, the inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity provokes tension in the abdominal walls, as a result it becomes hard. In pregnant women, such a belly is a sign of uterine tone, so confusion often arises.
Another sign of how appendicitis manifests itself in women is lack of appetite. In addition, there is general weakness and poor health. The first signs of acute appendicitis in women most often appear in the late afternoon or even at night.
Signs of chronic appendicitis in women
The main symptoms of chronic appendicitis in women are pain in the right iliac region. The nature of pain varies. Attacks occur both at night and early in the morning. Moving with chronic appendicitis is extremely difficult. In addition, the woman simply cannot lie on her left side, as very severe pain occurs.
In addition to pain with chronic appendicitis, women experience constipation or intestinal upset. Frequent urination also appears, which is also accompanied by quite painful sensations. When examined by a gynecologist, intense pain occurs. On palpation, the compacted and painful process can be clearly felt.
Features of the course of appendicitis in women
Acute appendicitis in women is characterized by severe pain in the right hypochondrium and a tense abdomen. The disease in women is difficult to identify due to the characteristics of the female body. Diagnosing a disease during pregnancy is a rather difficult task, because all organs are displaced from their usual places, which means it is problematic to determine the localization of pain. It is worth noting that abdominal pain during pregnancy is quite common. After all, they are provoked by: fetal tremors, tissue stretching. And nausea and vomiting are quite traditional companions of pregnant women.
In order to identify appendicitis in women, you should not focus specifically on pain. But the presence of painful nausea and vomiting are some of the signs of appendicitis in women. In most female diseases, despite abdominal pain, these signs are absent.
Do not forget that any female inflammation and appendicitis can provoke peritonitis, as well as other serious consequences. This means that if you have any acute abdominal pain, you must immediately consult a surgeon.
Diagnosis of appendicitis in women
The examination of the patient usually begins with a general examination. The presence of inflammation of the appendix can indicate:
- palpation of the abdomen, which causes the patient pain in the area of the right ilium;
- the occurrence of painful sensations when palpating the area of the cecum when the patient lies on his left side;
- increased pain when simultaneously pressing on the stomach and lifting the straight right leg;
- increased pain after pressing and abruptly releasing the painful area.
Of course, the most informative are modern methods for diagnosing appendicitis: ultrasound, computed tomography, endoscopy. Laboratory tests are also needed that can confirm the picture of the inflammatory process in the body.
Quite often, even doctors can confuse acute appendicitis in women with right-sided pyelonephritis, rupture of an ovarian cyst, intestinal obstruction, etc. To make a final diagnosis, laparoscopy is performed - instruments and video cameras are inserted into the abdominal cavity through microcuts, with the help of which the cecum is examined and neighboring organs. If a hypertrophied appendix is detected, it is immediately removed.
Causes and risk factors for appendicitis in children
The cause of inflammation of the appendix is its narrowing or blockage with the further development of bacterial flora in its cavity. Obstruction of the appendix can be caused by the ingress of foreign objects, fecal stones, parasites, or congenital anomalies of the cecum.
Closing the lumen of the appendix leads to a deterioration in the blood supply in it, stagnation of venous blood, and proliferation of microbial contents. 12 hours is enough for inflammation to develop. If surgery is not performed within 1-3 days, the appendix will rupture and pus and fecal matter will enter the abdominal cavity.
Acute appendicitis is very rare in children under 2 years of age. This is due to the feeding habits and anatomical characteristics of the appendage (it is shorter and wider).
Risk factors for developing inflammation of the appendix in children:
- binge eating;
- lack of fiber in the diet;
- increased sugar consumption;
- frequent constipation;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- dysbacteriosis;
- ascariasis.
On what day are you discharged after appendicitis?
The duration of the sick leave issued for the period of rehabilitation after amputation of appendicitis is directly related to the peculiarities of this surgical intervention.
The ability of a particular organism to recover is also of great importance. The doctor’s task is to make sure that the patient’s health is not in danger and he can resume work.
Many people do not associate surgery to remove the vermiform appendix with a sufficiently high degree of severity of the intervention. This is an erroneous opinion, since any surgical operation, especially one involving penetration into the abdominal cavity, carries a certain degree of risk and, therefore, the approach to such an operation must be the most serious. No one can guess in advance what day they will be discharged on after appendicitis.
We will write today about how quickly you can be discharged from the hospital following surgery to remove appendicitis, and about some other nuances.
It would be imprudent to talk about specific and clearly defined periods of hospitalization after surgery for appendix removal.
After all, each patient has his own body with unique immunity and resistance.
This means that for one, everything can heal quickly and without complications, while for another, the temperature may rise or some other illness may occur after surgery.
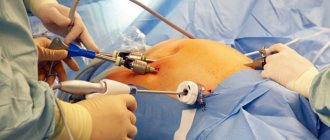
1Laparoscopy. The operation is performed through a very small incision in the abdominal wall using a lighted endoscopic probe and microsurgical instrument. 2The classic method is appendectomy. An incision is made in the right ilium, through which the vermiform appendix is removed.
With this method, you will have to stay in the hospital for about 10 days, and with laparoscopic removal this period is reduced to 3-5 days.
After a successful operation, the hospital regime is observed. At that time:
- You should not eat food on the first day. You can't drink either. But to relieve thirst, the surface of the patient’s lips is moistened.
- If the patient's condition is excellent, after this period he is allowed to drink tea or broth.
- Three days after surgery, the patient is transferred to food in small portions five or six times a day with an interval between meals of no more than 2.5 hours.
- In the early postoperative period, the patient should eat according to dietary table No. 5. Below we will describe a list of food products that are acceptable in this case.
- Patients are transferred to normal nutrition no earlier than 4 months after surgery.
Even after switching to regular food, some nutritional rules are strictly followed, which include maintaining a balanced diet, warm food temperature, thoroughly chopping or chewing food and some other simple rules. If this is not followed, recovery after surgery will take longer. In such cases, treatment continues upon discharge from sick leave after appendicitis for a number of days.
In the hospital canteen and for the first time after being discharged home, table No. 5 should include such products as pureed soups with vegetable broth, lean beef, steamed or boiled, ripe and not sour fruits, compotes, boiled and crumbly natural porridges . You should not put stress on the gastrointestinal tract immediately after discharge from the hospital.
After the patient is discharged, he is given a sick leave certificate after appendicitis. Many patients are interested in the question of how long sick leave can be after removal of appendicitis and how many days it is given for. This issue is resolved personally and directly with the treating doctor.
Any operation can bring certain troubles into the patient’s life in the form of complications. The skill and professionalism of surgeons minimize possible problems, but, nevertheless, they sometimes arise.
The most dangerous of them is peritonitis. Its onset is indicated by an increase in temperature after removal of appendicitis.
This condition is an emergency and requires immediate medical intervention and assistance. Otherwise, even death is possible.
Other complications include suppuration of the surgical suture several days after the operation, sepsis as an extremely severe complication, intraperitoneal bleeding of varying intensity, and the development of adhesions between the layers of the peritoneum and internal organs. All these situations keep the patient in hospital rooms and after discharge he is given sick leave to restore his health.
What can be advised in order to avoid the risk of inflammation of the appendix? Unfortunately, there are no specific prevention methods. But, nevertheless, it is possible to reduce the risk of this disease if you follow some recommendations.
So, for example, if we consider that inflammation of the appendix can occur if it is damaged, it is recommended to avoid eating sunflower seeds or hard-shelled nuts.
It is also not recommended to eat foods that are too fatty or smoked. Prevention and timely treatment of helminthic infestations also prevents and prevents the occurrence of inflammation of the appendix.
Postoperative period | Vasily KhrapachAppendicitis postoperative period. Surgeon Platon: treatment of appendicitis - review
In cases of acute appendicitis, patients are operated on as quickly as possible.
The operation to remove the inflamed appendix is called an appendectomy.
It is the most common surgical procedure performed without delay, since untreated acute appendicitis often leads to peritonitis, a fatal complication.
With peritonitis, pus from the inflamed appendage of the cecum can enter the sterile abdominal cavity and the patient will die from sepsis.
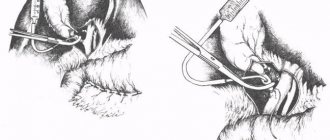
An appendectomy is performed as follows: the surgeon cuts out the inflamed appendix under general anesthesia through a small oblique incision in the right side. If the appendix has not ruptured and its contents have not entered the abdominal cavity, the appendectomy takes no more than forty minutes.
Otherwise, the surgeon has to thoroughly rinse the entire cavity to remove even the slightest contamination.
After removal of the appendix, sutures are placed on the incision and the patient is sent for observation to a hospital ward, where he will spend a certain time until complete recovery.
After an appendectomy, the patient may feel weak, tired and generally unwell, including pain in the incision area, but this condition quickly passes.
If there are no postoperative complications, the patient is discharged from the hospital five to seven days after surgery and can begin to carry out normal daily activities.
Sutures after an appendectomy are usually removed painlessly on the tenth day.
Today, with an unruptured appendix, doctors are increasingly resorting to endoscopic removal of the appendix, in which they make not an incision, but several punctures in the right places.
After a standard appendectomy, a scar is left, the length of which is from 7 to 9 centimeters. The scar will be dark red in color for the first six months, but over time it will fade and become invisible.
If desired, an unsightly scar from appendicitis can be corrected in any plastic surgery clinic.
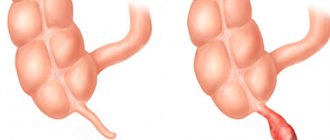
The appendix is the vermiform appendix of the cecum, located on the border between the large and small intestines. Its length on average ranges from 5 to 15 centimeters, and its diameter is about 1 centimeter.
In case of inflammation of the appendix - appendicitis - urgent removal of the affected appendix is necessary.
The main task of the appendix is to protect the small intestine from a variety of bacteria found in the rectum.
Inflammation of the appendix is very common and can occur in anyone, regardless of their age or health condition.
Also, appendicitis can be caused by blockage of the lumen of the appendix with fecal stones or undigested food particles, which is often found with constipation in older people.
Usually, such a diagnosis can be made immediately after examining the patient, but women will have to undergo a consultation with a gynecologist - the symptoms of appendicitis and the symptoms of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary tract can be very similar.
When the first symptoms resembling appendicitis appear, the patient is left in the hospital under observation, postponing the operation for twelve hours or a day.
Appendix removal
In well-equipped clinics, for the most accurate diagnosis, the laparoscopy method is used, when a probe is inserted into the abdominal cavity through a small incision, with which the surgeon examines the condition of the appendix. If the diagnosis is confirmed, removal of the appendix can also be performed using a laparoscopic apparatus under local or general anesthesia.
An appendectomy is a common surgical procedure in which the surgeon makes an incision on the right side of the abdomen and removes the inflamed appendix.
Appendix removal
Types of appendicitis in children
Inflammation of the appendix in children is usually classified according to the characteristics of the destructive processes, as well as the degree of severity:
- simple (catarrhal) – appendicitis without complications, manifested in the form of slight thickening of the walls with a mild inflammatory process;
- destructive - can be phlegmonous (increase in the size of the appendix, vascular thrombosis) and gangrenous (tissue necrosis);
- empyema is an acute purulent inflammation of the appendix.
In the second and third cases, perforation of the appendix (rupture) is possible, but this does not happen all the time - the integrity of the rudimentary organ may well be preserved. Occasionally, cases of spontaneous recovery are recorded. There is also a risk of inflammation becoming chronic, with relapses occurring periodically.
When diagnosing appendicitis in children, one should take into account a characteristic feature - a large selection of options for localizing the appendix. It can be located in various places in the abdominal cavity: in the right or left hypochondrium, in the pelvic space, under the liver, etc. This makes diagnosing appendicitis in children very difficult.
Main symptoms and diagnosis of appendicitis in children
Acute appendicitis in children is a disease with frequent cases of misdiagnosis. On the one hand, vague symptoms do not give the doctor the opportunity to immediately suspect appendicitis (plus, not all children can accurately describe complaints). As long as the doctor doubts and makes other diagnoses, appendicitis will progress until it reaches dangerous stages.
However, on the other hand, the symptoms of appendicitis in children are similar to the symptoms of other diseases, so a child with a preliminary diagnosis of appendicitis may develop a completely different disease. Modern methods of ultrasound diagnostics greatly facilitate the solution of these problems.
Classic symptoms of appendicitis in children, characterized by their ability to progress:
- Pain around the navel or in the pit of the stomach, which is then localized on the right side in the iliac region (the standard location of the appendix). The child tries to change the position so that the pain is felt less (most often on the right side or back). In young children who cannot indicate the location of pain, the first signs should be discomfort, crying, lack of appetite, and sleep disturbances.
- Vomiting, after which there is no feeling of relief. Vomiting can be repeated (typical of small children) or single (most often in older children).
- The inflammatory process in young children is most often characterized by elevated temperature. The temperature also rises in older people if appendicitis is complicated. In its simplest form, the temperature can fluctuate in the sub-range.
- One of the indicators of inflammation is the condition of the tongue. Most often, the disease can be recognized by an abundant white coating. The more severe the inflammation, the larger the area of the tongue turns white. With gangrenous appendicitis, not only whitening is diagnosed, but also dryness of the tongue.
- Abnormal bowel movements: diarrhea in small children and constipation in older children. If the appendix is located close to the urinary organs, there may be problems with urination.
Symptoms of appendicitis in children of different ages
Even a professional doctor will practically not be able to identify signs of appendicitis in newborns or infants. True, at this age appendicitis develops only in exceptional cases. Characteristic symptoms are expressed only as signs of general malaise. These are: monotonous sharp crying, short and restless sleep, sluggish sucking or complete refusal to eat, frequent belching, rapid movements of the legs or pulling them towards the stomach (a symptom of abdominal pain). Most often, the diagnosis is confirmed only during surgery. The appendix erodes quickly enough and there is a risk of peritonitis.
Signs of appendicitis in children 3 years old manifest themselves in the form of changes in general condition. The presence of pain itself is very difficult to establish. Symptoms of appendicitis in children 5 years old are also expressed in a deterioration in the general condition, and the child cannot describe the pain. Given the similarity of symptoms with a large number of other diseases, appendicitis is difficult to diagnose not only for parents, but sometimes also for doctors. To begin to suspect appendicitis in a child, you should look for the following signs:
- peculiarities of behavior (whims, causeless crying);
- constant change of position in order to reduce pain, restlessness;
- refusal to eat (even your favorite dishes);
- single or repeated vomiting;
- diarrhea (however, this occurs rarely);
- sleep disorders - the child cannot fall asleep because pain interferes;
- an increase in body temperature to 37°C in the absence of a runny nose and cough.
Symptoms of appendicitis in children 8 years of age and older do not need to be tracked by changes in general condition - the child is already able to describe his sensations and point to the area of pain. Most often, the child names the following symptoms of appendicitis: pain, initially localized throughout the abdomen, and then descending to the lower sections - and specifically to the right side (can point with a finger); increased pain when changing position, bending, turning from back to side; painful nausea and refusal to eat; slightly elevated temperature. Simply put, the symptoms of appendicitis in children 10 years old almost completely coincide with the signs of this inflammatory disease in adults.
Symptoms of appendicitis in children with an atypical location of the appendix
In this case, pain is observed in other places (and not just in the right side of the lower abdomen). In addition, other typical signs may be blurred: pain when palpated and abdominal tension. If the process of the cecum is retroperitoneal, symptoms of pain will appear in the lumbar region (on the right side), in the area of the ureters, and in the groin. In the pelvic position, pain will occur above the pubis, in the perineum. Diarrhea with mucus and pain when urinating are possible. With a subhepatic location, the pain will be in the right hypochondrium.
With atypical localization of the appendix, the gangrenous form of appendicitis is especially dangerous. Her picture is unclear: moderate pain, no abdominal tension, satisfactory condition of the child.
Regardless of the nature of the external manifestations, you cannot delay it - if you have any manifestations of restless behavior or complaints of pain, you should immediately consult a doctor. Considering the rapid development of appendicitis in children, this will allow the disease to be diagnosed in time and measures taken before complications arise.
Registration procedure
Registration of a certificate of incapacity for work for appendicitis is standard. In the line “Cause of disability”, code “01” is indicated (illness that does not allow the employee to attend the workplace). Information about the nature and course of the disease, as well as the manipulations required to eliminate it, is a medical secret. The doctor has no right to disclose it to anyone, including the employer.
Removal of the appendix is considered an ordinary simple operation, so the duration of the certificate of incapacity most often does not exceed 2 weeks. The issue of extending sick leave is resolved individually with the involvement of medical workers.
It must be remembered that the employee’s independent introduction of any amendments to the sick leave is unacceptable . Such a document is considered invalid.
Gangrenous appendicitis
Symptoms of gangrenous appendicitis
Necrosis (death) of tissue in the gangrenous form of acute appendicitis leads to the death of the nerve endings of the appendix. Because of this, patients begin to feel relief: the pain syndrome decreases and a false feeling appears that suspicions of appendicitis were in vain.
However, gangrenous appendicitis is accompanied by putrefactive inflammatory processes, and therefore the patient may experience symptoms of general intoxication: severe weakness, multiple vomiting, which does not bring relief. Body temperature is not an indicator - it can remain within normal limits. The tongue in the gangrenous form of appendicitis is dry, covered with a white or yellowish coating (this is especially noticeable at the root).
The gangrenous form of acute appendicitis is characterized by the occurrence of the “toxic scissors” syndrome: with a general serious condition and normal body temperature, the development of pronounced tachycardia is observed with a heart rate of up to 120 beats per minute, with a norm of 70-80 beats.
The symptoms of primary gangrenous appendicitis are different. Initially, the patient experiences sharp pain in the right iliac region. The pain goes away very quickly, but the general condition remains severe, and the body temperature is high in most cases. The abdomen is tense, painful, with obvious signs of peritoneal irritation.
Who can issue sick leave?
I would like to separately highlight the fact that not every medical institution and not every doctor is authorized to issue sick leave. Thus, the patient can receive an official certificate of incapacity for work, which will have legal force in the following organizations:
- public clinic - is the main place where employees receive sick leave;
- private medical institution - this type of clinic has the right to issue sick leave certificates only if it has the appropriate accreditation and license. Many private clinics currently do not have the appropriate powers, therefore, when choosing a medical institution for obtaining BL, it is important to take into account its specifications;
- dental clinics - since dentists are specialized doctors, they have the right to issue sick leave for up to ten days;
- psychiatric and other hospitals with a certain bias.
In most cases, doctors from district clinics are responsible for issuing certificates of incapacity for work.
If we talk about those places where the patient will not be able to receive the appropriate document confirming his illness, then these include the following organizations:
- blood transfusion points;
- Bureau of Forensic Medical Examination;
- health care centers;
- mud baths;
- consumer protection institutions.
Emergency doctors do not have the appropriate authority to issue sick leave
In addition, it is important for the patient to take into account the fact that ambulance workers also do not have the right to issue certificates of incapacity for work. All that is in their power is to provide quick medical care and/or move the patient to a hospital, where he can be under the supervision of the attending physician. Therefore, the only thing such specialists can provide to a citizen is a certificate confirming the fact that an ambulance was called. Such a certificate will not be taken into account in the accounting department of the enterprise where the employee works, and is not a valid reason for taking time off.
Gangrenous-perforated appendicitis
If treatment is not carried out at the stage of gangrenous appendicitis, the stage of gangrenous-perforated appendicitis occurs. During this process, the wall of the appendix is pierced (perforated). At this moment, the patient feels a sharp pain in the right iliac region. The pain syndrome is constant, with intensification spreading throughout the abdomen. Intoxication of the body increases, which is expressed by increased body temperature, tachycardia, and repeated vomiting. The tongue is dry and has a brown coating on it. Abdominal bloating is constantly increasing, peristalsis is absent.
Consequences of gangrenous appendicitis
The gangrenous form of acute appendicitis is a very dangerous disease that provokes severe complications:
- purulent diffuse peritonitis (inflammatory process in the peritoneum). This is a dangerous condition that can only be treated with urgent surgery. If timely assistance is not provided, sepsis (blood poisoning) quickly develops and death occurs;
- appendiceal infiltrate - the formation of a local conglomerate of tissues and organs around the inflamed appendix. This complication is treated conservatively. The infiltrate can resolve only after 3-4 months of treatment - only after this can the appendix be removed;
- local purulent abscesses in the abdominal cavity - in the pelvic cavity, between intestinal loops, in the subdiaphragmatic region;
- septic thrombophlebitis (inflammation of the venous walls with further formation of blood clots in the lumens of the portal vein and tributaries).
Grounds for extending a certificate of incapacity for work
If two weeks are not enough for recovery, the period of forced leave is increased.
You can count on 30 days of sick leave if postoperative complications arise, these include:
- hernia, serious adhesions, etc. As a rule, in such situations there is a need for repeated surgery;
- abscess. With such a complication, a course of antibiotics and special physiotherapy are needed;
- pylephlebitis is a serious pathology that can lead to death. Requires complex treatment;
- purulent peritonitis;
- inflammation and bleeding at the suture site.
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilyeva
Civil law expert
In extremely rare cases, treatment may take longer than 1 month. In this case, the patient’s condition is assessed by a special medical commission. She also decides to extend the sick leave.
Dear readers! To solve your problem right now, get a free consultation
— contact the on-duty lawyer in the online chat on the right or call:
+7
— Moscow and region.
+7
— St. Petersburg and region.
8
- Other regions of the Russian Federation
You will not need to waste your time and nerves
- an experienced lawyer will take care of solving all your problems!
Diagnosis of gangrenous appendicitis
Initially, the doctor listens to the patient and conducts a general examination. To more accurately determine the form of appendicitis, the patient will be advised to undergo tests and examinations. After confirming the diagnosis, an appendectomy (removal of the appendix) will be prescribed, which can be performed traditionally or by laparoscopy.
In order to quickly restore the body after surgery to remove gangrenous appendicitis, you must strictly follow all the recommendations of the attending physician on rehabilitation and dietary nutrition. The recovery process takes up to 3 months - during this entire period, reboots and heavy lifting are prohibited.
Time off from work
The duration of the rehabilitation period, which is prescribed on the sick leave and frees the patient from work, depends on the patient’s condition and on the method by which the operation was performed:
- with laparotomy it is 5-7 days;
- with laparoscopy – 10-15 days;
- for complications during surgery or the postoperative period – up to 30 days.
How to renew?
To request an extension of the terms specified on the sick leave, you need:
- contact the head doctor of the hospital or your attending physician;
- come on your own or wait for a medical commission to conduct an examination;
- the certificate of incapacity for work is updated depending on what decision the commission makes.
Only the attending physician or medical commission who work in the institution where the patient was operated on and treated has the right to extend sick leave. Independent amendments to the sick leave certificate are unacceptable ; such a document is considered invalid.
Reasons for extension
Extension of sick leave is possible only in case of complications that appeared during surgery or during the rehabilitation period: diffuse or local peritonitis, rupture of the appendix, thrombophlebitis, appendiceal infiltrate (appearance of fluid).
If the patient is diagnosed with such complications, he continues to be treated in the hospital.
Depending on what decision is made by the doctors after the service, sick leave may be extended for up to 30 days . In particularly severe cases, this can be several months.
REFERENCE! The maximum period for which sick leave can be extended is 12 months.
Appendicitis in pregnant women
Symptoms of appendicitis during pregnancy
In medicine, a distinction is made between catarrhal and destructive forms of appendicitis. Each of them has its own characteristic development of the process. In the catarrhal form, inflammation develops within 6-12 hours, in the destructive form - from 12 to 48 hours, after which perforation can occur and intestinal contents enter the abdominal cavity.
There are no specific symptoms of appendicitis in pregnant women, since each woman’s body is individual, not everyone’s appendix is located in the same place, therefore, changes in the appendix may be different.
If the inflammation begins in the appendix itself, without affecting the abdominal cavity, a pregnant woman is most often bothered by pain in the upper abdomen, gradually spreading to the lower right region. Symptoms of appendicitis include: vomiting. Stomach upset, nausea. Pain can sometimes be insignificant and occur in all areas of the abdomen. A woman may experience painful sensations while lying on her right side. During a medical examination, the source of pain will not be immediately determined.
With the gradual development of inflammation, pain will manifest itself along the entire right iliac region, often moving into the lower and upper parts of the abdominal cavity, and sometimes into the hypochondrium. The severity of pain depends on the stage of pregnancy. It is important to note that the standard symptoms of acute appendicitis in pregnant women may appear mild or appear late.
The location of the appendix also influences pain. If the appendix is located under the liver, the pregnant woman will have symptoms resembling gastritis (pain in the upper abdomen, vomiting and nausea). If the appendix borders the urinary system, the pain will radiate to the perineum and legs, the woman will experience a frequent urge to urinate and other symptoms usually characteristic of cystitis.
The most common question is the cause of appendicitis
The main task of the appendix is to protect the small intestine from a variety of bacteria found in the rectum. Inflammation of the appendix is very common and can occur in anyone, regardless of their age or health condition. The most common causes of appendicitis are inflammatory bowel disease, abdominal trauma, various infections and an overly mobile appendix.
Since appendicitis is a disease of the gastrointestinal tract, it needs to be “taken” to a gastroenterologist, but in acute cases only a surgeon can help.
Usually, such a diagnosis can be made immediately after examining the patient, but women will have to undergo a consultation with a gynecologist - the symptoms of appendicitis and the symptoms of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary tract can be very similar. X-ray and ultrasound examination of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity can confirm the presence of appendicitis.
Block: 4/5 Number of characters: 1300
The effect of appendicitis in pregnant women on the fetus
If appendicitis develops in the second trimester of pregnancy, its effect on the fetus is clear. The most common complications include the threat of late pregnancy loss, intestinal obstruction and postoperative infections.
Very rarely there are cases of premature placental abruption in pregnant women with appendicitis. If timely diagnosis and proper treatment are carried out, then there are no threats: the pregnancy will be preserved and completed. If the membranes become inflamed, intrauterine infection of the baby will occur, which will require mandatory antibacterial therapy. Postoperative complications most often occur within 7 days after surgery to remove the inflamed appendix. Therefore, for prevention, pregnant women are prescribed antibacterial therapy.
Causes of elevated temperature after appendicitis removal
Fever after appendectomy may occur due to wound infection. This is the most common reason that occurs due to non-compliance with the medical regimen. Damage to internal organs during surgery may also be the cause. As a result, the traumatic inflammatory process develops further.
Also, a fairly common cause of fever after surgery for appendicitis can be a decrease in immunity, since any surgical intervention puts quite a lot of stress on the body. During the recovery period, the human body begins to use all internal reserves. For this reason, additional diseases may occur in the form of viral or acute respiratory infections.
Fever may also occur due to severe bleeding during surgery. An infectious process may also occur during surgery. Drainage, which may be installed during surgery, can also cause increased temperature. Once the drainage tubes are removed, your body temperature should return to normal. Often the inflammatory process develops due to poor nutrition. The patient must fully adhere to the diet established by the doctor, otherwise there is a danger of the occurrence and development of general intoxication of the body. In addition, your doctor may prescribe antipyretic medications to combat symptoms.
Typically, fever after appendicitis may also be accompanied by profuse sweating and chills. In order to diagnose the causes of inflammation, the following methods are used:
- a clinical blood test that confirms the presence of severe inflammation;
- Ultrasound, which allows you to see the inflammatory process in visualization.
We receive sick leave
The procedure for issuing and filling out sick leave is regulated by the following regulations:
- Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation No. 624n dated June 29, 2011;
- Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation No. 31n dated January 24, 2012;
- Article No. 183 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
According to the law, a certificate of incapacity for work is issued by an employee of the health care institution where the patient was treated . After appendicitis, sick leave is issued by the attending physician upon discharge from the hospital.
How long does sick leave last after appendectomy? The duration of the certificate of incapacity for work is also determined by the attending physician on the basis of the law and depending on the general condition of the patient. It is calculated using the formula “length of hospital stay + rehabilitation period.”
Sick leave after appendicitis, how many days? The average number of days for rehabilitation varies:
- during laparoscopy – 5 – 7 days;
- for laparotomy - 10 - 15 days.
You may also be interested in the article “How much sick leave is given for chickenpox?”, which will surprise you, because with chickenpox the number of sick days is much greater.
It also happens that an employee of a medical institution made a mistake on the sick leave certificate, so we strongly recommend that you carefully check the document. If there is an inaccuracy in the name of the company, then read the article “Place of work on the sick leave certificate,” where you will learn how to correct this mistake.
Symptoms of adhesions after appendicitis
Most often, adhesions occur after appendicitis. The symptoms are as follows:
- pain - it may be absent for a long time. As a rule, it is localized in the area of the postoperative scar. Most often it has a pulling nature and can intensify after physical activity;
- dyspeptic syndrome - digestion is disrupted due to improper bowel function;
- violation of defecation - constipation appears, no stool for more than a day;
- complete absence of stool for more than two days.
Possible complications of the adhesive process
Adhesions after appendicitis can lead to serious complications. For example, acute intestinal obstruction may develop. It occurs due to compression of the intestines, which in turn prevents the passage of food in the intestines. In addition, necrosis of a section of the intestine is possible. Due to a disruption in its blood supply, which is provoked by an artery pinched by a commissure, the walls of the intestine die. This condition requires immediate removal of this section of the intestine.
How is your recovery going?
Even if a person “goes off” without consequences and the stitch heals quickly, in the first two to three months he should severely limit physical activity. This is especially true for those who work physically or play sports. Fast walking and running, as well as lifting weights weighing more than 5-7 kilograms are not allowed.
In practice, the seam stops bothering people after an average of a month, and after this period they can gradually return to their usual loads.
But in terms of nutrition and diet, everything is a little more complicated. During the first month of rehabilitation you will have to eat according to dietary table No. 5. This means that you can only eat the following foods:
- rye or wheat bread and crackers without added sugar;
- low-fat cottage cheese and milk with minimal fat content, as well as low-fat kefir and yogurt;
- vegetables - cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkin, potatoes, tomatoes;
- The preferred fruits are pomegranate, prunes and sweet apples;
- any types of greens;
- lean meat (chicken, turkey, rabbit, veal), and dishes made from such meat must be steamed;
- lean fish;
- buckwheat, rice, oatmeal;
- soft-boiled eggs or as a steam omelet.
Following a diet is an important point in the recovery process and the key to a speedy recovery.
Only after three to four months can you return to your usual diet. Despite the ban on serious physical activity and restrictions on sports, I do not recommend strict bed rest. A sedentary state during rehabilitation also has its negative sides.
In particular, peristalsis suffers: in the absence of physical activity, intestinal activity decreases, which can result in constipation.
Not only is this phenomenon unpleasant in itself, but in such situations pathogenic microorganisms multiply in stagnant feces.
Considering that in the first few weeks the junction of the cecum with the now missing appendix is still a healing wound, the entry of such bacteria into it can result in infectious inflammation.
It is important to know! Dieting is an important point when
restorative
process and the key to a speedy recovery.
In particular, peristalsis suffers: in the absence of physical activity, intestinal activity decreases, which can result in constipation.