Helicobacter pylori infection and its symptoms
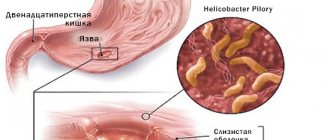
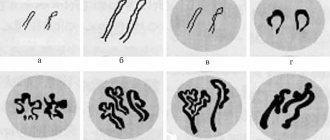
In appearance, the bacterium resembles a spiral surrounded by hairs. With their help, it quickly moves along the walls of the organs and chooses the pylorus of the stomach as its abode - the pyloric lower tier, which smoothly passes into the duodenum.
If a person has a strong immune system, then when a bacteria appears, the body can cope with it. However, it can cause harm that will be global in the future. In the area where the microbe resides, the amount of protective mucus is significantly reduced, hydrochloric acid actively moves towards it, and subsequently inflammation of the mucous membrane appears.
Routes of transmission of the bacterium helicobacter pylori.
Symptoms of the presence of bacteria in the body are as follows:
- heartburn, belching;
- bleeding gums, coated tongue;
- nagging pain in the stomach;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- constant nausea.
These symptoms are characteristic of a disease called helicobacteriosis. They may indicate the appearance of ulcers and chronic gastritis.
How does bacteria work in the stomach?
The microorganism colonizes the gastric mucosa. It often leads to inflammatory processes. Helicobacter pylori is recognized as the etiological factor of gastritis, which is why gastritis began to be called an infectious disease.
Depending on the state of the protective functions of the stomach, the infectious process can occur with pronounced symptoms of inflammation or latently. Scientists now believe that Helicobacter pylori leads to chronic gastritis in all infected people. This causes gastric adenocarcinoma, atrophic gastritis, peptic ulcer disease and poorly differentiated lymphoma. The pathogenic organism is classified as a first-order carcinogen.
The bacterium is highly resistant to aggressive environments. But when the surface is treated with disinfectants, it dies within a few minutes, and when boiled, almost immediately.
Risk factors
Among the risk factors are the following:
- male gender and middle age;
- inadequate social and living conditions;
- ignoring the rules of personal hygiene;
- the presence of a microorganism in parents;
- working with carriers of bacteria (medical staff);
- promiscuity;
- swimming in open springs and drinking water from them;
It is worth noting that strong immunity is not always able to protect against bacteria. It multiplies well in the intestines even with normal natural defenses, since it can hide from immune mechanisms.
Prohibited Products
When following a diet against Helicobacter pylori, you must strictly limit or completely exclude from your menu any fried, fatty, pickled, smoked and canned foods. They activate the growth and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms, causing an exacerbation of pathologies.
Prohibited products:
- rich soups, borscht, beetroot soups in mushroom, meat or fish broth;
- bakery products - butter pastries, freshly baked wheat and rye bread;
- meat - fatty pork, ham, lamb, duck, goose;
- offal - animal fats;
- fish - fatty varieties, dried, smoked and salted fish;
- cereals - corn, pearl barley, millet and barley;
- dairy products - smoked, spicy, salted and processed cheese, margarine, spread;
- vegetables - white and red cabbage, cucumber, spinach, sorrel, peas, beans, green and onions, radishes, garlic, all varieties of mushrooms;
- fruits and berries - cherries, grapes, cherries;
- sweets - cakes, pastries and other confectionery products, ice cream, chocolate.
What drinks should not be consumed: strong black tea, coffee, cocoa, alcoholic and low-alcohol drinks, carbonated lemonades, store-bought juices.
Routes of transmission
The bacterium is transmitted from person to person and from animal to person. Research has found it in some species of monkeys and cats. There are three routes of infection that have been proven, and one more that has not yet been scientifically proven.
Fecal-oral
Helicobacteriosis is a social disease; it requires strict adherence to the rules of personal hygiene.
Heliobacter is excreted from the body in the feces and turns into a coccal form. In the latter, it can exist in the external environment for a long time. The microbe can enter the body of another person through objects on which it ends up and through contact with the dirty hands of the patient. You can become infected by not washing your hands before eating or by licking certain objects. This mechanism is typical for children who like to taste everything.
You can become infected through the fecal-oral route from sick animals. Most often this applies to cats. Infection is also common in Africa, where there are many monkeys, and the population has an extremely low level of hygienic education.
A variant of this route of transmission is infection of infants. During lactation, a mother does not properly handle her nipples, and bacteria can be transferred to them from her hands. The child swallows it with milk, then it inseminates the intestinal mucosa and develops rapidly.
Oral-oral
This method of transmission mainly occurs in adults, family members or couples. You can become infected through kissing. To some extent, the bacterium lives on the oral mucosa and dental plaque. The risks of infection increase if hygiene rules are not followed . When kissing, the bacterium can be transmitted to children from parents, but such cases are very rare.
Through the water
When the bacterium was first discovered, it was believed that it did not live in water. However, over time, research has discovered that Heliobacter is present in large quantities in water reservoirs and can be transmitted through water. Interestingly, chlorination, which prevents many infections, does not prevent the transmission of this microbe. It was discovered that in water with the addition of chlorine, pylori transformed into a coccal form and stopped growing, but did not die and retained its infectious properties.
Transplacental route
A blood test of babies born to infected mothers can detect antibodies to the microorganism. The child does not develop any symptoms of pathology. Observation of newborns with stool analysis shows the absence of bacteria in the intestines. Shortly after birth, the antibody titer decreases. All this is reason to believe that antibodies are transmitted to the baby through the mother's blood. The bacteria themselves in the blood do not penetrate or pass through the transplacental barrier, and infection does not occur.
Video on the topic: How to get rid of Helicobacter pylori and excess weight
Helicobacter treatment regimens
Eradication therapy is one of the most modern and popular methods of treating infection caused by Helicobacter pylori. Achieving complete recovery is achieved through the use of a complex of the following drugs:
- antibiotics;
- antibacterial agents;
- medications that reduce gastric acidity.
Honored Doctor of Moscow Alexander Myasnikov about antibiotics against Helicobacter pylori:
There are 3 treatment regimens for the infection. The idea is that if the first regimen does not produce results and turns out to be ineffective, then the next one is applied and so on until the patient recovers. Usually the 3rd scheme (or line as it is called differently) is a radical measure and not every patient will reach it.
1st treatment regimen for Helicobacter pylori
This regimen is aimed at suppressing infection in most patients and includes the antibacterial agents Clarithromycin and Amoxicillin. In addition, the regulation of gastric acidity is ensured by Omeprazole or another PPI (proton pump inhibitor) - Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole, Esomeprazole or Rabeprazole. Such medications relieve the symptoms of ulcers and gastritis, and also allow you not to follow a strict diet while undergoing eradication therapy.
Important!
In some cases, Amoxicillin can be replaced with Metronidazole (an antibacterial agent) or Nifuratel.
Since the patient is taking antibiotics, the specialist usually supplements the treatment with drugs that reduce the effect of these potent drugs on the body. In such cases, for example, Enterol is used.
As an alternative to the three-component regimen (Clarithromycin, Amoxicillin, Omeprazole), a four-component regimen can also be used, which includes the additional drug De-Nol. Also, if the patient does not produce hydrochloric acid, then the prescription of proton pump inhibitors is pointless, so he is excluded from the regimen.
The minimum course of treatment is 7 days, the maximum is 14. A number of studies in the field of gastroentrology prove that it is more effective to take drugs according to the first regimen for 10-14 days. This period will reduce the risk of relapse and effectively destroy Helicobacter.
1st treatment regimen for elderly patients
The first line of eradication therapy for older people is different, since 2 antibiotics in combination can cause a number of complications in the body. That is why doctors exclude 1 antibiotic from the regimen and leave only the following drugs:
- Amoxicillin;
- Any variant of the IPP;
- Bismuth tripotassium dicitrate.
Need to know!
Bismuth tripotassium dicitrate is intended to provide protection to the mucous membrane from the effects of various damaging factors, as well as to reduce the resistance of Helicobacter pylori to antibiotics. This greatly increases the effectiveness of the therapy.
In some cases, elderly patients are prescribed a treatment regimen without antibiotics at all, but only with bismuth and PPI preparations. The course of treatment is 28 days and is used only for certain indications. The usual course of treatment is from 7 to 14 days.
Important!
The first regimen gives positive results in 95% of cases, but if improvements are not observed, a 2nd line of therapy is prescribed.
2nd treatment regimen for Helicobacter pylori
Since the bacterium has developed resistance to antibacterial drugs from the 1st regimen, it is useless to use them in the 2nd line of therapy. The following tools are used here:
- Tetracycline;
- PPI;
- bismuth salts;
- Metronidazole.
As we can see, in this scheme 4 active drugs are prescribed, so the 2nd line is usually called quadruple therapy. In addition, if the bacteria in the patient’s body is resistant to these drugs, the following replacement can be made:
- any version of a proton pump inhibitor, Amoxicillin, De-Nol, Furazolidone or Nifuratel;
- any version of PPI, De-Nol, Amoxicillin and Rifaximin.
Therapy lasts, as in the case of the 1st line, 10-14 days. If there are no results, they move on to a radical scheme.
Need to know!
The drug bismuth tripotassium dicitrate has protective properties, which may be reduced due to the consumption of fruits, juices and milk.
3rd treatment regimen for Helicobacter pylori
3rd line therapy for Helicobacter is resorted to in rare cases, but such cases exist. The use of antibiotics from the 1st and 2nd schemes does not make sense, since the bacteria have become resistant to them. Therefore, other drugs are selected in combination with the already familiar bismuth and PPI. For example, Rifabutin and Levofloxacin, however, Helicobacter pylori often develops resistance to Levofloxacin.
Important!
Before prescribing the 3rd line of therapy, a thorough examination is required, including endoscopy, biopsy, and bacteriological culture of the biopsy to determine its sensitivity to antibiotics. It is these individual results that will allow you to prescribe the correct treatment.
Bismuth tripotassium dicitrate helps get rid of symptoms of dyspepsia (stomach pain, bloating, heartburn), and also stimulates the regeneration of the gastric mucosa.
With such a long treatment, the intestinal microflora may suffer, so in most cases a course of probiotics is prescribed to reduce the load on the digestive tract and protect the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as gastroprotectors to prevent relapses.
What precautions should be taken to prevent family transmission?
If one of the family members has become infected with the bacteria, it is important to prevent its occurrence in other relatives. First of all, it is important to get tested. Precautionary measures focus on personal hygiene. Each family member should have their own dishes, towels and other household items . Bed linen, door handles and other items must be constantly processed. It is important to take care of proper nutrition, giving up bad habits and strengthening the immune system.
How to detect the disease
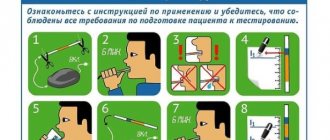
The bacterium can reside in the body without causing any inconvenience to the host. In this case, only research - blood and stool tests - will help identify it. It is also worth paying attention to the characteristic symptoms of its presence, which are listed above.
Is it possible to get infected again?
It is possible to become infected again, since a person does not have immunity to this microorganism. Often, re-infection occurs in the first 10-12 months after completion of therapy. This may be due to just one surviving bacterium.
Secondary pathology is very dangerous, as it can provoke relapses of ulcers, gastritis and gastric erosion.
What diseases are caused by Helicobacter pylori infection?
Is joint treatment necessary in cases where one of the family members tests positive for Helicobacter pylori?
First, all family members need to be tested for helicobacteriosis. Moreover, this is also recommended for friends, other relatives and neighbors, since you can catch the bacteria even through a door handle. If the analysis confirms the presence of the microbe, then therapy is necessary.
What causes Helicobacter in dogs? How do we know if our pet is contagious?
One of the reasons for poor health may be the bacterial infection helicobacter pylori. In humans and animals, the bacterium spreads in the same way - through contaminated food and water. Naturally, protecting a pet is more difficult. The main sign of bacteria in dogs and cats is vomiting.
Healthy carriage is also common, when the microorganism is present but does not cause any inconvenience. In any case, only an examination by a veterinarian can reveal it. Pets can be carriers of many pathologies that are dangerous to humans, so owners must carefully monitor their health and observe hygiene standards that are necessary for the health of all family members.
What is Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori is a unique microorganism that leads to such a dangerous disease as helicobacteriosis.
This is a pathology that can develop in the duodenum, but most often it affects the stomach. The bacterium received this name due to the fact that it lives in the pyloric section of the stomach. One of its main features is that the microorganism is resistant even to stomach acid. Helicobacter pylori has flagella, with the help of which it can easily move along the walls of the stomach or be firmly attached to them.
Helicobacter Pylori is the causative agent of many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, since when it multiplies, the pathogen leads to irritation of the mucous membranes. This provokes the occurrence of inflammatory processes. This is not just about ulcers or gastritis. Pathological processes can even lead to oncology. But if you start therapy in time, then the dangerous consequences for the body caused by the vital activity of the bacterium can be prevented.
It is believed that more than half the world's population is infected with Helicobacter pylori. After analyzing the statistics, experts came to the conclusion that the prevalence of helicobacteriosis depends on the material level of people. In developed countries, this disease is less common than in developing countries. More often, helicobacteriosis is diagnosed in people over 60 years of age. Also, patients with a weakened immune system have an increased susceptibility to this microorganism.
Prevention
Prevention of helicobacteriosis comes down to the following measures:
- The main thing is compliance with the rules of personal and household hygiene. It is important to thoroughly wash dishes and hands before eating, not touch dirty objects, and use personal household items. Children should be supervised to ensure that they do not put any foreign objects in their mouths. Only boiled water should be used.
- The body must receive sufficient amounts of vitamin C and beta-carotene. Their regular use helps reduce the likelihood of infection.
- To reduce the risk of infection, it is recommended to avoid promiscuity. Couples need to undergo appropriate examinations regularly.
Secondary prevention also includes the listed measures. It is also important that all family members are treated with antibiotics and regularly tested for bacteria in stool and exhaled air.
Prevention also includes strengthening the immune system. Proper nutrition and giving up bad habits are important.