Unfortunately, constipation in older people is a common phenomenon these days. Treatment of such diseases does not always occur, since they often prefer not to talk about such a delicate problem. At the same time, some not only do not know what to do when constipation occurs in older people, but also what it is in general. For example, some call it irregular trips to the toilet, while others call it difficulty in bowel movement itself. It is necessary to understand in more detail the accuracy of the definition and symptoms in order to discuss the treatment of constipation in bedridden elderly people (and healthier people, however, are also not immune from the disease, but it is the bedridden who are in greater need of help, in particular, from medical specialists).
Boarding houses
for the elderly
About us
"Strelna"
25
people
from 1300 R
Find out more about the boarding house ›
Causes of constipation in the elderly
Physiological features
According to statistics, about 60% of people after 60 years of age suffer from defecation disorders. Constipation significantly impairs the quality of life and contributes to the occurrence of organic pathologies of the lower gastrointestinal tract. In the vast majority of elderly people, stool retention is caused by natural changes in nervous regulation and age-related dystrophy of the smooth muscles of the digestive tract. The main physiological causes of disruption of the normal frequency of bowel movements:
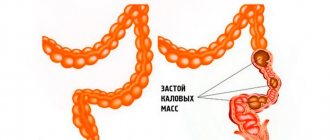
- Intestinal atony
. Elderly people with weakened intestinal wall tone are characterized by the absence of feces for 3 days or more, not accompanied by other dyspeptic symptoms. Due to innervation disorders, patients do not feel the urge to defecate. It takes effort to have a bowel movement. Often patients resort to various manipulations - they press their hands on the perineum, spread their buttocks to the sides, which promotes the release of feces. - Physical inactivity
. Constipation occurs in older people who, for medical reasons, need to adhere to bed rest. As a rule, spontaneous passage of feces is difficult or impossible. Against the background of prolonged retention of feces, bloating or pain in the left iliac region is noted. Defecation often occurs only after a cleansing enema, oil microenemas or laxatives. - Weakness of the abdominal muscles
. Normal emptying is disrupted due to dystrophic and degenerative changes in the muscles of the abdominal wall. The urge is felt, but excretion of feces is difficult. In severe cases, patients are forced to resort to manual assistance. When defecating, you have to strain; excessive strain can be accompanied by severe pain in the anus. - Features of the diet
. Elderly people experience problems with bowel movements after eating large amounts of baked goods, milk porridges, and white bread. Usually there is no feces for 2-3 days, after which defecation occurs independently with the release of dry feces in the form of lumps. Stool retention can also be caused by drinking several cups of strong tea a day and overeating. - Endocrine system disorders
. In the elderly, a special category of disorders is distinguished - endocrine constipation, associated with age-related hypofunction of the thyroid, parathyroid and gonads. Spontaneous emptying is extremely rare (1-2 times a week); patients complain of heaviness and discomfort in the left iliac region. When defecating, hard lumps of feces are released, which injure the mucous membrane of the rectum. - Stressful situations.
Due to disruption of the coordinated work of different structures of the brain and the autonomic nervous system, constipation in the elderly becomes a reaction to severe emotional shocks. Many patients complain of fecal retention after a change in their usual living conditions: moving, hospitalization in a hospital. These disorders are short-lived and can be treated well with non-drug methods.
Proctological diseases
Various pathologies of the rectum are accompanied by constipation, which is caused not only by mechanical obstacles to the movement of feces, but also by a reflex spasm of the sphincter in response to pain. Due to the fear of pain during bowel movements, many older people hold back the urge, which further aggravates the situation. In case of proctological diseases, stool retention can be combined with the release of mucus and blood from the rectum both during the act of defecation and during the day. Constipation is most often caused by:
- Haemorrhoids
. Patients experience difficulty with bowel movements, and a subjective feeling of incomplete bowel movement may occur. Sometimes, with strong straining, patients notice the loss of red-bluish formations from the anus (varicose nodes). Over time, constipation becomes chronic, with no bowel movements for 7 days or longer. Defecation is accompanied by intense pain. - Proctitis
. Defecation disorders are characterized by short-term constipation, after which spontaneous excretion of feces always occurs, requiring increased effort. When passing stool, older people report increased pain. Depending on the degree of inflammation, fecal retention may alternate with frequent false urges to defecate, during which mucus and blood are separated. - Rectal polyps
. Constipation in tumor formations is associated with partial intestinal obstruction. A gradual decrease in the frequency of bowel movements is typical. Feces are excreted in small lumps; with a pronounced narrowing of the intestinal lumen, “pencil” or ribbon-like feces are formed. A similar type of constipation occurs in the elderly in the case of acquired rectal diverticula.
Bowel diseases
Constipation in elderly patients may be associated with organic lesions of the intestinal wall, which contribute to the retention of feces in the intestines, its compaction and difficulty in excretion. Colon pathology develops primarily or as a complication of other gastroenterological diseases. If the disturbances are caused by damage to the colon, they are complemented by diffuse abdominal pain and a deterioration in the general condition. Constipation is caused by:
- Chronic colitis
. Inflammation of the large intestine is characterized by retention of feces in combination with periodic discharge of blood and mucus from the anus. The frequency of bowel movements decreases; when emptying, you have to make additional efforts and strain your abdominal muscles. Constipation is combined with painful, fruitless urges. Stool retention increases the pain, so patients begin to take laxatives on their own. - Acquired megacolon
. Elderly people complain of chronic constipation, the duration of which reaches a week or more. There is practically no urge to stool. During defecation on its own or due to the use of laxatives, severe pain in the anus associated with the release of large hard lumps of feces is disturbed. The disorder is always accompanied by severe flatulence. - Pneumatosis intestinalis
. The pathology is characterized by prolonged constipation with bloating and paroxysmal pain. The absence of feces for 4-5 days is replaced by watery diarrhea with a large amount of mucus. Pneumatosis is characterized by periodic retention of feces, the severity of which correlates with the degree of morphological changes. Stool retention is not associated with errors in the diet. - Adhesive disease
. In elderly patients, constipation can be caused by compression of a section of the intestine by connective tissue bridges. The duration of stool retention ranges from several days to a week or more. In case of spontaneous emptying, a small amount of dry feces is released. Defecation is accompanied by pain in the anus due to trauma to the mucous membrane.
Tumors
Malignant neoplasms of the large intestine are a common cause of constipation in the elderly, as they develop mainly after 55-60 years. Patients are concerned about chronic stool retention, which does not disappear even after the use of laxatives. Defecation is difficult; you have to strain hard to empty it. The discharge of feces is accompanied by severe pain in the anal area; sometimes patients notice dark blood in the stool. General changes increase: loss of appetite, weight loss.
Intestinal obstruction
The absence of feces with sharp abdominal pain and repeated vomiting is a characteristic sign of acute intestinal obstruction. It is possible that both a mechanical form of the disease may occur (when the intestinal lumen is obstructed by a tumor, a fecal stone, or when a hernia is strangulated along with an intestinal loop or mesentery), and a dynamic form—intestinal paresis. Normally, in the elderly, stool can be delayed for 2-3 days, therefore, with chronic intestinal obstruction, patients pay attention to the presence of problems with the gastrointestinal tract only if there is no bowel movement for 5 or more days.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
Fecal retention is an adverse reaction to many medications used to treat hypertension, anemic conditions, emotional and cognitive disorders, and other chronic diseases in the elderly. Drug-induced constipation most often develops with the abuse of secretory laxatives and the systematic use of pharmaceutical drugs from the following groups:
- Calcium antagonists
: verapamil, finoptin, nifedipine, corinfar. - β-blockers
: atenolol, bisoprolol, corvitol. - Anticholinergics
: atropine, pachycarpine, cyclodol. - Diuretics
: furosemide, hypothiazide. - Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
: aspirin, ibuprofen, indomethacin, naproxen. - Narcotic analgesics
: morphine, codeine, their derivatives. - Antidepressants
: nialamide, tranylcypromine, pyrazidol, befol. - Neuroleptics of the phenothiazine series
: aminazine, thioridazine, pipothiazine. - Barbiturates
: barboval, corvaldin, corvalol, reladorm. - Antiepileptic drugs
: diphenin. - Antianemic drugs with iron
: iron sulfate, fumarate, iron gluconate. - Antacids
: aluminum hydroxide, calcium carbonate. - Antidiarrheals
: phthalazole, activated carbon, loperamide.
Laxatives for constipation in the elderly
For older people, as for younger people, many types of medicinal laxatives are prescribed, depending on the type and severity of constipation3:
- Drugs that increase intestinal volume. Such preparations include products that can retain a large amount of moisture - flaxseed, seaweed, bran, etc.
- Chemical irritants. Drugs that irritate intestinal receptors, thereby increasing peristalsis. They act quickly, but such drugs are addictive, which negatively affects intestinal functions.
- Osmotic drugs. These products create osmotic pressure inside the intestines; this effect allows them to retain moisture, which greatly facilitates the process of defecation. An example is lactulose, which can be consumed over a long period of time. The well-known drug Duphalac® is produced based on lactulose, which, in addition to the laxative effect, helps improve intestinal microflora, which is very important for older people4.
- Enemas. The use of an enema is an emergency method of cleansing the intestines, which cannot be used frequently and independently.
In addition to taking laxatives, an elderly person needs to understand that a laxative may not be enough and he needs to change his lifestyle, eat better, and give up bad habits.
In cases where medication is required to treat constipation in older people, the optimal choice would be Duphalac®. Leader of the Russian market of drugs containing lactulose. Due to its qualities, mechanism of action, high level of safety and effectiveness, it is successfully used to treat constipation in any patient, including newborns and infants, pregnant and lactating women, as well as the elderly.
RUDFL174433 from 07/03/2018
Co-author of articles, editor - Shimbaretsky Georgy Alekseevich.
Survey
A gastroenterologist is involved in finding out the causes of constipation in the elderly. A diagnostic search involves a comprehensive examination of the gastrointestinal tract, which is aimed at studying the morphological features and functionality of the digestive system. If necessary, consultations with other specialists are prescribed. The most informative are:
- Rectal examination
. A digital examination of the rectum is performed to study the structure of the mucous membrane, identify enlarged hemorrhoids, cracks and space-occupying formations. According to indications, the examination is supplemented with anoscopy or sigmoidoscopy to visualize the lower parts of the large intestine. - Endoscopy
. Colonoscopy is prescribed to all elderly people with complaints of delayed bowel movements for a detailed study of the structure of the colon and sigmoid colon, and to identify tumors. If suspicious areas are detected, a biopsy is performed for further histological analysis. - X-ray examination
. Taking X-rays after oral contrasting of the gastrointestinal tract with barium sulfate is necessary to detect organic changes in the intestinal wall, signs of ulcerative defects, and inflammatory processes. Delayed images are taken to determine the rate of passage of chyme through the intestines. - Sonography.
Using abdominal ultrasound, the structural and functional features of the digestive tract are assessed and pathological changes that can cause constipation are identified. If necessary, an ultrasound of large vessels of the abdominal cavity is performed to exclude occlusion of the mesenteric arteries. - Stool tests
. Constipation in the elderly is accompanied by changes in the consistency and composition of stool, which is established using a coprogram. To study the microflora of the large intestine, bacteriological analysis is carried out. The Gregersen reaction to occult blood helps to exclude chronic bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract.
To clarify the diagnosis and detailed visualization of the structures of the abdominal cavity, computed tomography is prescribed. All patients undergo general and biochemical blood tests. If damage to the intestinal vasculature is suspected, contrast angiography is performed. To exclude diseases of the hepatobiliary system, duodenal intubation with microscopic and bacteriological examination of bile is used.
If you are prone to constipation, you should reconsider your diet
Treatment of constipation
How to treat constipation in older people? This is mainly determined by the reason for which they arose. In any case, elderly singles should be looked after, and it would be best to entrust them to experienced doctors and attentive staff of the Golden Time boarding houses. There, every person will receive the necessary good treatment, decent care, comfortable conditions for the treatment and prevention of many diseases. Sensitive caregivers will certainly pay attention to all necessary issues, including hygiene. In a boarding house for the elderly, no one will feel alone - the same people will gather there and you will certainly find someone to communicate with. A private home guarantees guardianship, proper supervision of the elderly, takes care of their health and organizes conditions for good examination and treatment. When older people have constipation, treatment (drugs or folk remedies) will always help restore health in a comfortable environment. This is clearly better than at home or hiring a nurse. A good boarding house guarantees a peaceful and tranquil old age.
The main ways to restore health:
- the diet for constipation in older people should consist of raw fruits and vegetables, best consumed on an empty stomach or before bed in the evening - this is proper nutrition;
- folk remedies for constipation in older people - recommends drinking an infusion of Alexandria leaf or healthy tea with brewed St. John's wort.
- Another effective remedy is ordinary laxative tea, which can be purchased at any pharmacy. It results in quick and gentle normalization of stool;
- A good exercise for constipation in older people is self-massage. Not the fifth point, as one might think, but the abdomen. Abdominal massage should be carried out every day for several weeks, then the active activity of the intestines will “start” and there will be a desire to empty it.
Symptomatic therapy
If constipation is associated with age-related changes in the body, non-drug methods are primarily used to normalize stool. It is recommended to include fiber-rich foods in your diet: whole grain bread, fresh or stewed vegetables. To restore natural bowel movements, it is useful to drink about 2 liters of fluid per day. It is better to replace tea with fermented milk drinks and compotes. To stimulate peristalsis, older people need to eat a piece of bread with butter in the morning or drink 1 spoon of vegetable oil.
To strengthen the abdominal muscles and accelerate the movement of feces, it is recommended to perform a special set of physical exercises. To eliminate constipation, you can use herbal preparations - decoctions of buckthorn bark, yarrow herbs. To quickly cleanse the intestines, enemas are prescribed. For persistent constipation, oral laxatives and rectal suppositories are used. If stool is retained for more than 3 days, which is accompanied by intense pain in the abdominal cavity, a violation of the general condition, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible.