Symptoms of salmonellosis
The incubation period of salmonellosis can last from several hours to several days. Rapid intrahospital spread of the disease is possible when salmonellosis is transmitted through household means. In this case, the first symptoms of salmonellosis appear within a week.
The clinical picture depends on the form of the disease.
Typhoid-like salmonellosis begins acutely, and the patient immediately develops intestinal disorders. After a few days they disappear, but the temperature remains high. The patient feels apathy, general weakness, lethargy, a herpetic rash appears on the body, and the skin is anemic.
The most common gastrointestinal form of the disease is diagnosed in approximately 95% of patients. The main symptoms in this case are headaches, upset stool, increased body temperature, pain in the navel, and vomiting.
In particularly severe cases, the following clinical signs may be observed:
- high fever that lasts more than five days;
- very frequent, foul-smelling stools;
- tachycardia;
- intoxication of the body;
- pressure drop;
- skin cyanosis;
- impaired renal function, up to the development of acute renal failure.
If treatment is not started in a timely manner, patients' water-electrolyte metabolism is disrupted and severe dehydration occurs. Clinically, this is manifested by dry skin, cyanosis, and convulsions. With severe loss of fluid, the functioning of other body systems is disrupted.
Septic salmonellosis. An extremely dangerous form of the disease that can lead to the death of the patient. It all starts with a high temperature, the patient’s condition rapidly deteriorates, and the following complications of salmonellosis appear:
- severe chills;
- sudden changes in temperature;
- hyperhidrosis;
- formation of purulent foci in the musculoskeletal system;
- aortitis, endocarditis.
The septic form of the disease can lead to the development of meningitis, abscess of the buttocks, and liver. The disease is severe, long-lasting and can result in the death of the patient.
Therefore, when the first suspicious symptoms appear, you must immediately contact a specialist and undergo an examination. The sooner treatment for salmonellosis begins, the faster the recovery and the lower the risk of developing complications of the disease.
Rospotrebnadzor warns!
Beware of salmonellosis!
Salmonellosis is an acute infectious disease that affects humans and animals.
Back in 1876, scientists drew attention to the connection between diseases of farm animals and food poisoning in people who consumed meat from sick animals. In 1934, the International Association of Microbiologists adopted the name "salmonellosis" for this infectious disease.
The cause of the infection is Salmonella bacteria, which are resistant to environmental factors. In open reservoirs they are stored for about 4 months, in animal feces - up to 3 years, in milk at a temperature of 6-8 ° C - about 3 weeks, in poultry eggs - up to 1 year. Salmonella are resistant to low temperatures; in meat at 0°C they survive for about 140 days and retain the ability to reproduce.
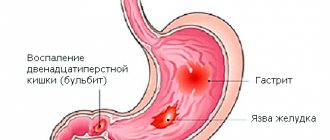
The disease occurs most often within 12-24 hours, from 3 to 6 days after infection. The disease begins acutely, with chills, increased body temperature to 38-39°C, headache, weakness, and dizziness. Signs of damage to the gastrointestinal tract, pain in the epigastric region and near the navel, and vomiting quickly appear. The vomit initially looks like undigested food, but later becomes watery and stained with bile. In most cases, diarrhea appears a little later - watery, foamy, mixed with mucus and sometimes blood. Sometimes the feces may resemble rice water.
Salmonella sepsis occurs rarely, mainly in newborns and the elderly if untreated.
Infection with salmonellosis occurs mainly through food products of animal origin, primarily meat and meat products from cattle. In recent years, the importance of poultry meat (primarily chicken), eggs and egg products has increased, since Salmonella penetrate through shells contaminated with bird secretions. Less common transmission factors are milk and dairy products, vegetables and fruits.
Particular attention should be paid to meat products, especially chopped meat and minced meat, which are a favorable environment for the proliferation of salmonella. To neutralize meat, it is necessary that the temperature inside the piece reaches at least 80°C with an exposure of 10-15 minutes. It should be borne in mind that under favorable temperature conditions, salmonella multiply faster on cooked foods than on raw ones, so meat or fish that have been previously cooked should not come into contact with tables or boards on which raw foods were cut. Salmonella contamination of foods can also occur when stored in the refrigerator; prepared meals and raw foods should not be stored together. Before storing eggs in the refrigerator, they must be washed under running water.
You can also become infected from a person with salmonellosis. The risk group primarily includes children who become infected through household items and toys.
Follow the cooking technology and storage conditions of ready-made dishes!
Wash your hands before eating and after using the toilet!
At the first clinical manifestations of salmonellosis, consult a doctor immediately!
Deputy Head of the Rospotrebnadzor Office for the city of St. Petersburg in the Vyborg and Kalininsky districts Valentina Vasilievna Chakharyan.
Prevention of helminthiases transmitted through meat and meat products.
Meat occupies a significant place in the human diet. Of all consumed foods, meat is the richest in protein, as well as microelements, primarily iron. However, meat can be contaminated with helminths.
Three helminthiases can be transmitted through meat and meat products: trichinosis, taeniarinhoz, taeniasis.
In the Vyborg and Kalininsky districts of St. Petersburg, as well as in St. Petersburg, trichinosis and taeniasis have not been registered in recent years. Teniarinhoz in the Kalininsky district was registered in 2021. and in 2021 1 case each year. Both cases are imported, imported from Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. However, you shouldn't relax. In the Russian Federation, cases of trichinosis, taeniarinchiasis and taeniasis are registered annually.
Taeniarinhoz is a helminthiasis associated with the parasitism of the “bull” tapeworm (Taeniarhychus saginatus) in the human body. Infection occurs when eating insufficiently heat-treated infected beef meat and deer brain, which are intermediate hosts of this helminthiasis.
Taeniasis is a helminthiasis associated with the parasitism of the “pork” tapeworm (Taenia solium) in the human body. Infection occurs when eating insufficiently heat-treated infected meat from animals that are intermediate hosts of the helminth (domestic pig, wild boar, bear, camel, hare, rabbit).
The clinical manifestations of teniarhynchosis and taeniosis are similar and are characterized by the following symptoms: loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, sleep disturbance, headaches, dizziness.
Trichinosis is a helminthiasis caused by parasitizing Trichinella larvae. Infection occurs when eating pork or wild animal meat (bear, wild boar) containing live encapsulated larvae, which in humans migrate into the muscles and become encapsulated, causing fever and severe allergic manifestations.
The clinical picture of trichinosis is characterized by three main syndromes: fever, muscle pain, swelling and is accompanied by hypereosinophilia of the blood.
For the purpose of personal prevention of helminth infections transmitted through meat and meat products, it is necessary:
— eat meat and meat products that have passed veterinary and sanitary examination;
- do not buy meat in unspecified places without veterinary and sanitary examination;
— follow the technology for preparing meat and meat products: from the moment of boiling, cook the meat in small pieces for at least 2 hours under the lid or fry thoroughly;
- Do not try raw minced meat.
Entomologist of the FBUZ branch
"Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the City
St. Petersburg" in Vyborg
and Kalininsky districts Korotaeva A.G.
Conditions for salmonellosis infection
Despite the high contagiousness of the disease and its widespread prevalence, not every person gets sick with salmonellosis. The following factors increase the likelihood of infection:
- Neglect of personal hygiene rules
. Banal carelessness and haste can cause illness. Salmonellosis is easily transmitted through household contact, so it is necessary to wash food before eating it and also keep your hands clean. - Contact with sick animals
. Pets often become carriers of salmonellosis and transmit the disease to their owners. The more raw meat in an animal's diet, the higher the likelihood of the pet becoming infected. - Underprocessed food
. Often there are dishes that contain thermally unprocessed meat or fish. Such food is a potential source of disease. - Swimming in unfamiliar bodies of water
. Recreation areas where there are large crowds of people are safe only if they are first checked by the sanitary and epidemiological station. - Weakened immune system
. A person with a weak immune response is at much greater risk of developing the disease than a healthy person.
Most people and animals are carriers of various pathogenic bacteria, including the causative agents of salmonellosis. However, they cannot cause any harm to the body as long as its protective reaction is strong enough.
Ways of transmission of the disease
To protect yourself from infection, it is important to know how salmonella infection most often occurs. In most cases, infection can be avoided by simply following basic hygiene rules.
Once you have had the disease, you develop a strong immunity to the pathogen, but you can become infected again.
In total, microbiologists in our country count about 500 species of salmonella. Most of them enter the body through the three most common modes of transmission.
Contact and household method of transmission
The pathogen enters the human body as a result of contact with a patient with salmonellosis, or with its carrier. Often, infection becomes widespread if a food service worker becomes ill.
Possible transmission options:
- Personal items of the patient
. These include toothbrushes, towels, and bed linen. - Unsterilized medical instruments
. All probes, dilators, and catheters must be handled thoroughly before use. - Contact with an infected animal
. An infected pet may have access to the owner's personal hygiene items. In addition, many owners take a cat or puppy to bed, kiss it, and do not wash their hands after playing with the animal. - Poorly washed dishes can also be a source of bacterial transmission
.
Often, common objects in kindergartens also become the cause of mass disease. For example, toys in groups that young children put in their mouths, or poorly processed pots.
The pathogen is released into the environment along with the feces of the infected person; transmission of Salmonella by airborne droplets is impossible.
The listed methods of transmission of bacteria are typical for most intestinal infections. The routes of infection for such dangerous diseases as dysentery and typhoid fever do not differ from the mechanisms of infection for salmonellosis.
Alimentary route of infection
The most common route of infection into the body. The pathogen enters the intestines along with contaminated foods and drinks. The following products pose the main danger:
- Milk
. Only thorough pasteurization destroys bacteria in milk obtained from a sick animal. Once in dairy products that have not been sufficiently processed by temperature, bacteria not only retain their viability, but also begin to actively multiply. Their lifespan is quite long - it reaches three to four months. Surely boiling it will help disinfect milk. - Meat products
. Animal meat that is not properly cooked can become a source of infection. Feeding raw minced meat to pets also contributes to infection of their intestines. By licking itself, the animal spreads the pathogen throughout the entire skin. In the future, the owner, by petting his pet, also runs the risk of becoming infected with salmonellosis. - Eggs
. They are an excellent breeding ground for bacteria. Eggs in waterfowl are especially dangerous, since water is one of the most common ways of spreading infection.
According to a number of studies, up to 80% of livestock products, even those obtained at large plants, are carriers of salmonella. Neglecting its heat treatment is extremely dangerous.
Transmission of salmonellosis from a nursing mother to her infant through milk is excluded, although the baby can become infected through contact.
Infection of the milk of farm animals is not explained by the passage of the parasite through the blood-brain barrier, but by insufficient treatment of the animal's udder to remove feces. As a result of such neglect, contamination of the resulting products occurs.
Diagnosis of salmonellosis
The diagnosis of this disease is carried out by a general practitioner or infectious disease specialist. If a patient complains of severe abdominal pain, he is first sent for examination to a surgeon to rule out surgical pathologies.
The main stages of diagnosing the disease are:
- Collecting anamnesis, interviewing the patient. The doctor is interested in what the patient ate, what he complains about, whether he has chronic diseases, and so on.
- Inspection. The doctor conducts an external examination of the patient, palpates the abdomen, and, if necessary, listens to the heart and lungs.
- Serological diagnostic methods.
- Stool analysis. The presence of an inflammatory process in the intestines and an increase in the number of leukocytes in the feces are determined.
- Bacteriological research. The causative agent of salmonellosis is found in the biological material taken from the patient, after which it is planted on nutrient media and antibiotic resistance is determined. Vomit, the patient's feces, urine, blood, bile, as well as food that could lead to infection can be used as biological material for research.