Pediatric gastroenterology deals with the diagnosis and treatment of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) in children under 18 years of age.
Digestive problems in a child lead to serious consequences: lack of nutrients, delayed physical and mental development, constant weakness and apathy. Not every disease manifests itself with severe symptoms: many infections proceed silently for a long time, the child does not complain of pain or discomfort. Digestive disorders can be caused by:
- genetic predisposition or congenital pathologies of the esophagus, stomach, intestines;
- unbalanced diet, which is dominated by flour, sweet, smoked dishes;
- unfavorable environmental conditions: for example, living in an industrial area;
- high levels of stress;
- increased mental and physical stress;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- abdominal injuries;
- pathologies of metabolic processes that occur against the background of chronic diseases (for example, diabetes mellitus).
A sudden disturbance in the functions of the gastrointestinal tract can also occur as an acute reaction to a toxin or allergen if a child eats a spoiled product. Regardless of the causes and factors that caused the indigestion, it is recommended to contact the pediatric gastroenterology department.
Which doctor specializes in the digestive tract?
A gastroenterologist is a doctor who treats the stomach. His responsibilities include establishing an accurate diagnosis by examining the patient, as well as prescribing treatment to eliminate the disease.
Consequently, gastroenterology is a science that studies the functioning of the human digestive organs, identifying the norm or the presence of pathological processes.
When a patient first encounters diseases of the digestive system, he often does not know who to contact with this problem. A therapist comes to the rescue, who will explain which doctor treats the stomach and give a referral to a more specialized specialist in this activity.
Gastroenterologists are divided into several types:
- coloproctologist: deals with diseases of the rectum, as well as diseases of the large intestine;
- hepatologist: specializes in the treatment of diseases of the liver, biliary tract, and gallbladder through diagnosis, examination of tests and interviewing the patient;
- proctologist: treats diseases of the rectum (often patients who have problems with hemorrhoids, polyps, anal fissures come to him).
A gastroenterologist-surgeon is another important specialist in this field. He treats patients who require surgical intervention due to pathologies that cannot be treated conservatively. The doctor performs operations to eliminate intestinal bleeding, abdominal hernia, intestinal obstruction, intestinal adhesive disease, etc.
The most common gastrointestinal problems
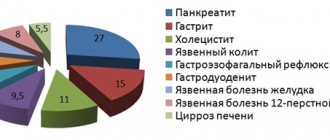
People often ask the question: what diseases does a gastroenterologist treat? Below we highlight the most common:
- Gastritis, ulcerative lesions of the duodenum, small and large intestine.
- Irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease.
- Biliary dyskinesia.
- Refluxes and esophagitis.
Now you know who a gastroenterologist is and what he treats . Often he has to identify and treat diseases of the liver or bile ducts. It also happens that the gastroenterologist refers to other doctors. The digestive system consists of a huge number of organs, which is why highly specialized doctors deal with certain diseases:
- Proctologist - identifies and treats diseases of the colon.
- Hepatologist is a doctor who specializes in liver diseases.
If the gastroenterologist cannot find the cause of the symptoms, or he is sure that the cause is not in the gastrointestinal tract, then he will refer the patient to a general practitioner.
Have questions?
You can get detailed information about services and prices and make an appointment by phone.
Information about the location of our clinic and directions can be found in the Contacts section. gastroenterologist
ASK A QUESTION
Pediatric gastrointestinal specialist
A child has a stomach ache, which doctor treats such diseases? It is logical that in addition to adult gastroenterologists, there are also pediatric ones. A child’s body is different from an adult’s, so such patients should be dealt with by a more specialized specialist. This doctor cares for children from birth to adulthood.
Currently, more and more children have problems with the gastrointestinal tract due to poor nutrition, consumption of harmful foods and drinks: chips, lemonade, crackers and much more that the child craves.
But it is worth noting that in addition to acquired diseases of the stomach, there are also congenital anomalies that require timely therapy and treatment: intestinal polyposis, tracheoesophageal fistula, esophageal atresia, stenosis and others.
The important point is that the disease detected in time is almost always cured, but the advanced form leads to the fact that it becomes chronic and permanent.
The most common reason for visiting a pediatric gastroenterologist with newborn babies is considered to be severe colic; this is often a temporary, passing phenomenon that requires taking medications that help the passage of gases and normalize the intestinal microflora.
Look for a gastroenterologist!
print version- home
- >
- For patients
To be treated well, you need to understand your illness
Gastroenterologists are better at treating gastroenterological diseases than general practitioners
Having fallen ill, we all dream of getting to an experienced doctor who will carefully understand what happened to us, take into account the characteristics of our body, lifestyle and prescribe treatment that will definitely help and will not give side effects, either now or in the future. Statistics show that today gastroenterologists are better at treating gastroenterological diseases than internists or general practitioners.
| Stomach acidity is examined by a gastroenterologist, MD. G.O. Smirnova (City Clinical Hospital No. 15, Moscow) |
| Unfortunately, even gastroenterologists are often forced to prescribe standard treatment aimed at the average patient, because Hospitals do not always have the necessary diagnostic equipment to prescribe individual treatment. If it helps, good, if not, they will prescribe another medicine, etc. It is not customary to talk about this to patients, since recovery is faster if the patient believes that he is being treated in the best possible way. In gastroenterology, the effect of “faith in the doctor” (the so-called “placebo”) provides up to 60% of the treatment effect. However, modern man in the Internet era does not have blind faith. In order for the patient to trust the gastroenterologist, the doctor must explain to the patient the features of his disease, why he needs to be treated in this particular way, what contraindications this treatment has, what side effects of treatment there may be in order to immediately notice them, etc. The purpose of this section is to help the patient understand the basic terms in order to correctly tell the attending gastroenterologist about the symptoms in order to understand the diagnosis. And understand whether the gastroenterologist has modern diagnostic capabilities to prescribe quality treatment. |
What is your acidity?Experienced gastroenterologists ask this question to their patients with gastrointestinal diseases when they do not have the opportunity to conduct an acidity test themselves. in accordance with state equipment standards. Such treatment without high-quality diagnostics can take a long time. As the head of the gastroenterology department of a large hospital once noted: “30% of errors in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases is a very good result.” According to Trush O.V. (2007), 60-70% of patients with chronic gastroduodenitis and peptic ulcer disease receive poor-quality medical care, half of them due to failure to carry out pH-metry of the stomach . | Acidity of different solutions |
Increased and decreased acidity
| Professor Grozdova T.Yu. said that in Soviet times, during an expedition to the northern regions, she performed intragastric pH measurements on indigenous reindeer herders. It was discovered that there was no acid in their stomachs between meals! But they eat at precisely certain times of the day. After eating, acid was produced. After a few hours, the food left the stomach and the acid stopped being released. In people spoiled by civilization, physiological rhythms are disrupted: acid is produced both when needed and when not needed, causing inflammation and ulcers on the mucous membrane. Low acidity is also bad, because... acid is needed to digest food and, less known, to disinfect food. Acid prevents infections that are present in food from entering the body. If there is little acid, then a person is more likely to experience all kinds of gastrointestinal disorders and infectious poisoning. If the acid is low, then you need to pay more attention to the quality of food and the cleanliness of your hands. |
The future reindeer herder eats raw meat |
When talking about the acidity of the stomach, we mean acidity in its middle part (in the so-called body of the stomach). The lower (antral) part of the stomach produces alkaline mucus, which must neutralize acid before food enters the duodenum. If little alkaline mucus is produced, then food saturated with acid stagnates in the stomach, corroding the stomach walls. And if food with acid still passes into the duodenum, it corrodes the walls of the duodenum. Daily pH-metry
, carried out simultaneously in three sections of the gastrointestinal tract, makes it possible to detect deviations from the norm in a particular patient: either a lot of acid is released, or little alkaline mucus is released, or some other dysfunction, and prescribe adequate treatment.
Stomach cancer
The standard approach to treating most diseases of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum is to reduce acidity in the stomach. Typically, in patients with stomach pH = 1-2. For treatment, it is necessary to maintain the pH in the stomach above 3-4 units using antisecretory drugs. In different people, the same dose of medicine gives different pH levels, so to ensure healing, a larger dose is given. However, if you overdo it and raise the pH above 5 units, then the transformation in the stomach of harmless nitrates, which we receive with food, into strong carcinogens: nitrites and nitrosamines (N-nitrosoamines) is accelerated tenfold. If the hospital has pH testing, the doctor can choose the correct dose and regimen for taking the medication without increasing the risk of cancer by reducing the acidity too much.
Increased bone fragility
| It would seem, what is the connection between gastrointestinal diseases and increased bone fragility? However, US health authorities issued a warning in May 2010 about an increased risk of hip, wrist and spine fractures when taking large doses of the common stomach acid-lowering drugs proton pump inhibitors or taking them for a year. “When prescribing proton pump inhibitors, the physician should choose the lowest possible dose or shorter course of treatment that would be adequate to the patient’s condition,” the publication states. The only way to select the optimal dose of proton pump inhibitors is to perform intragastric pH measurements . |
Infectious Helicobacter theory of peptic ulcer
The infectious theory states that ulcers in the stomach and duodenum are caused by the microbe Helicobacter pylori.
Despite serious contradictions, this theory has become widespread due to its simplicity and the ability to use expensive drugs to eliminate (eradicate) this microbe. During the years of the greatest popularity of this theory, it was argued from a high rostrum that eradication should be carried out not only in the patient, but also in all family members and pets, and in Russia eradication therapy must be prescribed without understanding whether a particular patient has this microbe, because most have it. Helicobacter eradication therapy with large doses of antibiotics has become firmly established in the standards of treatment of the gastrointestinal tract, although 30-40% of patients experience side effects in the form of colonic dysbiosis and antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Now, despite the Nobel Prize, the excitement is subsiding. Experienced gastroenterologists consider Helicobacter to be just one of a dozen other risk factors. Academician V.T. Ivashkin at one of the conferences spoke about foreign studies that showed that taking vitamin C and beta-carotene (vitamin A) compensates for the negative effect of Helicobacter on the gastric mucosa. However, when it reaches ordinary doctors...
Where to start if you get sick?
Analyze your feelings, identify the symptoms of the disease, try to identify the disease itself, but remember that only a good doctor can make the correct diagnosis. The fact is that the same symptom can be a consequence of different diseases. For example, chest pain may be caused by heart disease, gastrointestinal disease, spinal disease, or a related combination of these. Another example. Gastrointestinal diseases with the same name sometimes need to be treated differently depending on your condition (acidity has already been discussed), so it is important that the doctor can prescribe all the necessary tests for you.
Is self-medication acceptable?
It is commonly said that self-medication is unacceptable.
However, this is the reality of our time. In 2008, the international community adopted the “Gstadt Guidelines for the Treatment of GERD,” which recognized the correctness of self-medication without consulting a doctor for uncomplicated forms of gastroesophageal reflux disease using over-the-counter drugs: antacids, alginates, H2-blockers, proton pump inhibitors. For other gastrointestinal diseases, there is no evidence that self-medication is admissible. Therefore, if you value your health, look for a good gastroenterologist. A modern good gastroenterologist not only treats, but also shares his experience with colleagues through publications in scientific and practical journals, conference proceedings, etc. All this ends up on the Internet and provides food for thought. If you are at a loss, start with the list of medical institutions that seem to have devices for diagnosing functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, with the list of authors of gastroenterologists, or with the list of articles on functional gastroenterology on our website. Use the search on the site, enter your city and disease into it.
We constantly update the site with new information. We wish you to find answers to your questions.
What diseases do gastroenterology specialists treat?
Specialists in this category treat the digestive tract. A person may have problems ranging from the esophagus, where chewed food ends up, to diseases in the rectum. The patient should contact this specialist if problems such as:
- pathology in the work of the sphincters, which are located between the border of the stomach and esophagus;
- diseases of the esophagus: the presence of polyps, achalasia, dilated veins in the esophagus, diverticula;
- diseases in the stomach: ulcers, gastritis, papillitis, erosion, tumors, polyps;
- diseases of the pancreas: pancreatic necrosis, pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, diabetes mellitus, cyst, oncology;
- pathology in the duodenum;
- diseases occurring in the spleen: cyst, abscess, malignant neoplasms;
- pathology of the rectum and anus;
- intestinal diseases: colitis, duodenitis, adhesions, enteritis, obstruction, ulcers, flatulence, tumors, worms, dysbacteriosis;
- various liver diseases, pathologies in the gallbladder and biliary tract: cholecystitis, hepatitis, Gilbert's syndrome, oncology, cirrhosis of the liver, curvature of the biliary tract.
When should you visit a doctor?
Having dealt with the question of which doctor treats the stomach and intestines, the patient should then know the specific symptoms that require a visit to the gastroenterology department. These symptoms include:
- heartburn;
- frequent belching;
- frequent persistent hiccups;
- sudden weight gain or rapid weight loss;
- severe gas formation, bloating;
- nausea that does not go away for a long time;
- bowel disorders (constipation, indigestion);
- the presence of persistent heaviness in the abdomen;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- pain that occurs on an empty stomach;
- specific odor from the mouth;
- pain that occurs when eating;
- coating on the tongue that has uncharacteristic signs (high density, yellow, white, large quantity);
- cramps in the intestines;
- changes in the color of stool not related to food intake, etc.
If a person does not have direct symptoms indicating gastrointestinal diseases, but has a rash on the body that is not related to an infectious origin, then a gastroenterologist can also help him. Having dealt with the question of which doctor treats the stomach, you should know that he also deals with patients who have metabolic disorders and improper absorption of mineral nutrients. The presence of this pathology is indicated by a sharp deterioration of hair, teeth, skin, rapid weight gain or loss.
Visit to a therapist or gastrologist
If you have already previously visited a therapist who has sent you to see a specialized doctor, then you need properly selected treatment, since gastritis and other gastrointestinal diseases are a very serious problem, and this should not be joked about under any circumstances.
Diagnostics
Well, you are already at an appointment with a gastroenterologist. Experts recommend using special expressions to describe your condition and pain. Pain in this area may be:
- piercing;
- cutting;
- pulling;
- aching;
- twitching;
- pushing.
In addition, pain in the stomach area is not always associated with digestion. These may be disturbances in the functioning of the liver or gall bladder. And only a doctor can determine what the problem is.
Surveys
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an examination. If a gastroenterologist diagnoses you at your first appointment, you need to think about whether this doctor is really a specialist in his field?
Usually, at the first appointment, the doctor will find out about your diet, the nature of stomach pain or other unpleasant sensations. Next, the specialist recommends undergoing a digestive system examination. After all, only a deep study of the problem can correctly diagnose and cure the body in a short period. Among the most popular examinations are:
- basic tests (blood, urine, etc.);
- fibrogastroscopy - examination of the stomach using an endoscope;
- biopsy of the stomach and intestines (if indicated);
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
At the first symptoms of gastritis or a stomach ulcer, a gentle diet and medications that can remove the signs of the disease are prescribed.
Repeat visit to the doctor
In addition to the main types of examinations, a specialist may prescribe additional types of symptomatic studies:
- Breathing test - the patient breathes into a special bag that is evacuated. After this, the air in the bag is examined for the presence of harmful microorganisms.
- Analysis of gastric juice - the analysis is taken using a specialized rubber device - a probe.
- X-ray of the gastrointestinal tract.
The first stage of treatment involves a specialized diet. The patient should refuse fatty, spicy, i.e., foods harmful to the stomach. In addition to diet, medications are prescribed that can relieve pain. They do not cure the disease, but only make it easier to tolerate the disease.
At the second stage, after a full examination, the specialist prescribes specialized drugs that fight the inflammatory process of the stomach and intestines.
Stomach ulcer: symptoms and signs
If a person is bothered by stomach pain that wakes him up even in his sleep, heartburn and upset, as well as vomiting and anemia, then this indicates the presence of a stomach ulcer. Which doctor treats this disease? A gastroenterologist deals with this type of health problem. Experts note that most often an ulcer does not bother a person much until it completely destroys the intestinal walls, which leads to perforation, damage to blood vessels, and, most dangerously, internal bleeding. Such complications are extreme.
Stomach ulcers are not something to joke about; if left untreated, this disease can lead to a very bad outcome. Therefore, a person needs to be attentive to the symptoms indicating the presence of an ulcer:
- burning, aching pain in the abdomen, namely between the navel and chest;
- causeless pangs of hunger;
- dull pain in the gastrointestinal tract;
- bloating, belching.
In advanced cases, when a person has developed bleeding, he will feel constant fatigue and weakness. The presence of blood in the stool and vomit indicates severe bleeding. In this case, the stool will contain mucus and its color varies from black to red.
Gastritis: causes, symptoms
Inflammation of gastritis is promoted not only by poor nutrition and environment, but also by the presence of various irritants and bacteria in the human body.
Main reasons:
- Helicobacter pylori bacteria, which can settle in the human stomach.
- Environmental and chemical irritants that adversely affect the gastric mucosa. This includes cigarette smoke, alcohol, painkillers and antipyretics.
- Various viral infections that provoke attacks of gastritis.
Which doctor treats gastritis of the stomach and how? A gastroenterologist is a doctor with special skills and training in diagnosing, treating, and preventing diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The risk group for these diseases includes people who abuse alcohol, smoke, regularly take painkillers and antipyretics, as well as those whose age is over 60 years.
Symptoms of gastritis include:
- frequent pain between the lower ribs and the navel;
- discomfort in the abdominal area;
- nausea, vomiting;
- loss of appetite;
- constant feeling of overeating, bloating, belching;
- in severe form there may be stool and vomiting with blood.
What other doctors treat this diagnosis?
In addition to the therapist and gastroenterologist, those with characteristic pain are referred to the following doctors:
- oncologist;
- endocrinologist;
- proctologist;
- surgeon
What does an oncologist treat?
People are sent to an oncologist for stomach cancer. It is determined using ultrasound, endoscopic and histological examination, and biopsy. After a long examination, either a general practitioner or a gastroenterologist refers you to an oncologist. This type of cancer does not occur in a healthy organ. It is preceded by a precancerous condition.
Stomach cancer is a terrible disease, but there is a possibility of a complete cure for the disease. It depends on the stage of the disease.
For stomach cancer, the following types of tests are usually prescribed:
- ultrasound endoscopy;
- fluoroscopic examination;
- computed tomography;
- measurement of tumor tumor markers.
A competent doctor is able to prescribe quality treatment.
What does a proctologist treat?
The main area of research of a proctologist is diseases of the colon and intestinal sections. Thus, the scope of specialization of this doctor includes diseases of inflammatory, infectious, oncological and other nature.
If discomfort occurs in the intestines and duodenum, experts recommend immediately contacting this doctor. This approach will help stop the development of the disease and complications.
Features of gastroenterology
Which doctor treats the stomach and pancreas and when to seek help? Of course, if a person has previously suffered from a similar disease, he will immediately contact a gastroenterologist. But when he first encounters gastrointestinal diseases, he first goes to a therapist, who will refer him to a more specialized specialist. Which doctor treats the stomach and pancreas, and how does this happen? A competent gastroenterologist is currently in great demand. His primary task is to determine the most accurate diagnosis of the patient. To do this, the patient is prescribed a series of tests and studies. After the doctor is convinced of the correctness of the diagnosis, he prescribes treatment. It will depend on the specifics of the disease.
Treatment methods in gastroenterology
Treatment methods include:
- medicinal;
- physiotherapy;
- special diet;
- correct lifestyle;
- surgical intervention if necessary.
Which doctor treats the stomach if a person has signs of infectious poisoning? In this case, you should contact an infectious disease specialist. If the patient’s condition is serious, the patient is a child or an elderly person, then first of all it is necessary to call an ambulance and, if necessary, be hospitalized in a hospital.
First aid for poisoning
Common to all types of toxic infection are:
- rapid development of the disease;
- often manifests itself in a group of people at once;
- does not last long: on the fifth day all symptoms disappear completely, and health returns to normal;
- there is a clear connection with a specific product;
- sick people are not contagious to others.
In case of poisoning, the help of a doctor is necessary. But it is not always possible to see a doctor or go to the hospital, so you have to treat the disorder at home. First of all, it is necessary to stop the process of intoxication, prevent dehydration, and restore the intestinal microflora.
For this purpose the following is used:
- potassium permagnate for gastric lavage. The solution should be pale pink. The volume of the resulting liquid, which must ultimately be drunk completely, is two liters. Instead of potassium permanganate, water with sea salt or soda is suitable;
- in the absence of diarrhea, it must be provoked with laxatives;
- sorbents (the simplest is activated carbon) remove toxins;
- It is important to drink plenty of liquid: boiled water is suitable;
- after the end of the acute period, it is necessary to normalize the balance of microflora by taking medications with probiotics and prebiotics.