Since ancient times, doctors in different countries have diagnosed various diseases based on the state of the tongue. In some situations, this symptom may appear even before the onset of pain and other clinical manifestations of the pathology. Previously, it was generally accepted that a person had not yet been cured if his tongue did not acquire a healthy appearance. When faced with white plaque for the first time, many people are in no hurry to visit a doctor, considering it a temporary phenomenon. But what to do if this symptom does not go away over time? During an examination, a doctor will be able to understand the reasons for its formation, diagnose the primary disease and select the correct treatment.
- 6 Treatment prognosis and possible complications
- 7 Prevention
- 8 Features of plaque in older people
- 9 Features of plaque in children
- 10 Reviews
What does a white coating on the tongue in adults mean?
Normally, the human tongue should be moderately moist, have a pale pink tint, a transparent whitish coating is allowed, which can be easily removed with a toothbrush or a special scraper. However, under certain conditions in the body and diseases, a strong white coating may appear. It develops due to various disturbances in the processes of keratinization of the surface cells of the papillae of the tongue. In this situation, it is quite difficult to eliminate such a problem, and the plaque appears again as soon as possible.
Patients may put off going to the doctor for a long time because they no longer see any other unpleasant symptoms. However, it is important to understand that white plaque is sometimes an indication of the development of serious pathologies for which it is necessary to begin treatment immediately. In most cases, the cause of this symptom is all sorts of problems in the gastrointestinal tract, infection with various infectious pathogens, poor hygiene and taking certain medications.
White plaque can be a symptom of various diseases
Video about the appearance of a white coating on the tongue in Elena Malysheva’s program “Live Healthy!”
Plaque color
As mentioned above, the darker the plaque, the more serious the patient’s condition.
- White and not too abundant plaque is usually not a cause for concern.
- A thick layer of white plaque with an unpleasant odor indicates a malfunction of the intestines; it usually accompanies food poisoning.
- Yellow plaque may indicate both malfunctions of the digestive system and diseases of the gallbladder and liver. In this case, the final word remains with the doctor.
- Dark colored plaque should cause the most concern.
- Gray, black or brown deposits usually indicate the presence of chronic forms of gastrointestinal disease.
The tongue itself can tell about the work of a person’s internal organs, even if it is not covered with plaque:
- pale - vitamin deficiency and anemia;
- red - heart or hematopoietic system;
- cyanotic - lungs and kidneys.
In conclusion, I would like to advise you to acquire the good habit of examining the condition of your tongue every morning, during hygiene procedures. If something seems doubtful to you, consult a doctor for advice. Be attentive to your health!
Types of white coating on the tongue
There are many varieties of white plaque based on its color shade, location on the tongue and accompanying symptoms. Each of these signs is very important in diagnosing diseases and allows us to reduce the list of possible pathologies in a patient.
Features that white plaque may have:
- does not go away within 24 hours;
- occurs in the morning after sleep;
- has a bad smell.
Associated symptoms:
- an unpleasant bitter or sour taste appears in the mouth;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- the tongue changes its size, swells and swells, teeth marks are imprinted on it;
- viscous saliva is secreted;
- the surface of the tongue becomes rough, loose, or cracks form on it;
- the tongue becomes painful, stings, burns, and sometimes even goes numb;
- taste sensitivity is impaired;
- dryness appears in the mouth and on the surface of the tongue.
Bad breath is a common symptom of gastrointestinal diseases
Also, sometimes various formations may appear on the tongue:
- pimples;
- sores;
- blisters;
- red spots;
- red dots, pimples.
Sometimes spots, pimples and ulcers may appear on the tongue
The location of plaque on the tongue is also an important diagnostic sign, as it may indicate pathology of a specific internal organ.
- if plaque appears in the central part of the tongue, then this may indicate stomach diseases;
- at the very base of the tongue - intestinal diseases;
- plaque on the tip of the tongue is associated with heart disease;
- the edges of the tongue indicate diseases of the liver and spleen;
- plaque on the back of the tongue may be a symptom of problems with the pancreas;
- a white coating on the palate may appear due to candidiasis;
- on the tongue and tonsils, near the throat - with sore throat.
By the area of the tongue covered with plaque, one can judge about diseases of a particular organ.
The coating on the tongue is not always pure white; sometimes it takes on a slightly different color:
- white-yellow;
- white-brown;
- white-gray;
- white-green.
Sometimes the tongue can take on various shades, including white and yellow.
Based on saturation, the following types of plaque can be distinguished:
- light, small, easily removable;
- dense and thick;
- unevenly distributed;
- curdled.
Should I worry?
At first glance, this problem seems trivial to some. But we must not forget that the tongue is an important organ. With its pathology, a person is reluctant to communicate with others, and the full process of eating is disrupted. Therefore, if a symptom such as discoloration or soreness appears, the tongue is covered with a white coating or it stings, such discomfort and unpleasant sensations cannot be tolerated.
What does a healthy organ look like? Firstly, it is medium in size. It is pale pink in color. His papillae are not enlarged, they are of normal size. As for humidity, it should be moderate. There are no films or ulcers. Its lower part has a thin mucous membrane. By the way, by her condition you can always find out whether the patient has negative changes in the body.
If the tongue is covered with a dense white coating, and besides, it cannot be cleaned off, this is an alarming sign. In this case, as a rule, sensitivity increases and functionality is impaired. Dense plaque can be a sign of chronic infections and pronounced development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Visit a doctor when the deposits are constantly present and there is an unpleasant odor. Do not delay your visit if standard hygiene measures do not clean your tongue, tooth marks and swelling have appeared on it, and the color has become grey, yellow or white. Make an appointment with your dentist if your papillae become enlarged and you experience dry mouth, burning sensation, and loss of taste sensitivity.
Why is the tongue covered with a white coating, what is the reason for this?
White coating on the tongue is not always associated with diseases. Sometimes this can be a temporary phenomenon that goes away in a few hours or days. However, in some situations, various diseases may be detected during diagnosis.
Many doctors begin examining the body when white plaque appears on the gastrointestinal tract. In most cases, detected diseases are accompanied by a pronounced clinical picture.
- Acute gastritis is a very common type of gastrointestinal disease and is diagnosed in people of all ages. The pathology is sometimes accompanied by heartburn, acute pain in the stomach, and nausea. Patients are concerned about dry mouth and tongue. A coating with a grayish tint forms, although the tongue usually remains clean on the sides and at the very end. A common symptom of gastritis is bad breath.
- Chronic gastritis occurs in a more smoothed form, pain may be less pronounced. Many patients note heaviness in the abdomen after eating and frequent belching. The tongue is coated with a white-yellow or grayish coating, and the taste buds may be enlarged. Also, sometimes red spots on the mucous membrane stand out clearly.
- Stomach and intestinal ulcers are serious diseases that can lead to various complications. Patients note acute pain that may go away after eating, and sometimes bleeding occurs. The coating on the tongue is located at the root, has a whitish-gray color and a dense consistency. It is quite difficult to remove it, since it is tightly attached to the taste buds.
- Acute pancreatitis occurs when the pancreas becomes inflamed. Taste sensitivity is impaired, and a white-yellow coating is found on the tongue. Patients suffer from dry mouth and severe pain in the left hypochondrium.
- Chronic pancreatitis has less pronounced symptoms, and a white coating forms on the tongue due to candidiasis, which develops against the background of metabolic disorders and lack of vitamins.
- Malignant formations in the stomach are accompanied by general weakness, weight loss, lack of appetite and severe pain in the abdominal area. A dense white coating appears on the tongue due to the large number of leukocytes.
- Dysbacteriosis can also cause plaque to appear. It is usually pure white, but in severe forms a yellow tint may appear. This coating is easily removed, but soon it appears again, sometimes even with greater force. Most often found on the left side of the tongue. Sometimes the plaque forms such a thick layer that it is impossible to see the color of the taste buds underneath.
- Poisoning is accompanied by vomiting, nausea and severe digestive upset. Also, sometimes the temperature rises and severe sharp pains in the abdominal area are tormented. A white coating with an unpleasant odor may appear. If poisoning occurs due to various toxic substances, then the surface of the tongue becomes covered with ulcers and erosions with a large number of dead cells.
In addition to gastrointestinal diseases, the cause of white plaque can be other pathologies that appear due to various pathogens.
- Various colds that occur with complications can cause the tongue to turn yellow. Moreover, the higher the patient’s temperature and the more severe his condition, the greater the thickness of the plaque. A severely weakened body cannot fully cope with pathogenic microorganisms that begin to rapidly divide in the oral cavity. Due to various pathologies that lead to difficulty breathing through the nose, a white-yellow coating may occur. It often disappears when the consumption of clean drinking water increases.
- Syphilis is a serious sexually transmitted disease. Its consequences can be very serious. The plaque forms on the back wall of the throat and on the root of the tongue, has a dense structure and is white in color.
- HIV infection leads to a significant decrease in immunity and weakening of the entire body. Against this background, pathogenic microorganisms, including fungi of the genus Candida, often begin to multiply. Painful ulcers may also form on the tongue.
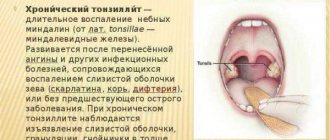
- Tonsillitis can contribute to the occurrence of various concomitant diseases. Very often, inflammation of the tongue occurs, which becomes covered with a dense white coating. Sometimes its base may hurt.
- Scarlet fever is a very serious disease that can lead to various complications. Patients complain of very high fever, headaches and skin rashes. The plaque spreads not only to the tongue, but also to the throat.
When suffering from scarlet fever, the tongue becomes covered with a white coating on the first day.
- Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted sexually transmitted disease. The causative agent is gonococcus, which can also infect the oral cavity. A whitish-yellow coating appears in it and on the tongue, as well as purulent ulcers. Patients experience itching, burning and dry mouth, pain when swallowing, and the voice becomes hoarse. There is also increased salivation, an unpleasant odor, and the lymph nodes become enlarged and painful to the touch.
- Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx. Accompanied by severe pain in the throat, difficulty swallowing, swelling of the walls of the larynx. A white coating appears on the back of the throat and can also spread to the surface of the tongue.
- Sore throat is accompanied by high fever, severe sore throat and general weakness. The tonsils, palate and tongue may be coated with a thick white coating. Sometimes the color may take on a yellowish tint.
- Candidiasis can affect many internal organs and is a very common disease. It can appear after long-term use of antibiotics, during which the content of microorganisms is disrupted and pathogenic flora begins to multiply intensively. Reduced immunity, oral contraceptives, drugs, and alcohol may also be the cause. The tongue with thrush sometimes burns, turns red and swells. The plaque is very dense, thick, white, difficult to remove, and in its place an ulcerated surface is found. Sometimes it is unevenly located on the surface of the tongue.
- Galvanic stomatitis occurs in people who wear various dental devices made of metal. A white coating appears on the tongue, which may have a heterogeneous structure and sometimes forms pimples. In some cases, there may be erosion and a burning sensation.
- Desquamative glossitis or geographic tongue is often detected against the background of dysbacteriosis. In this case, a white coating and red spots appear.
- Dental diseases can also cause plaque to appear. Due to pathological processes occurring in the oral cavity, bacteria begin to multiply rapidly and form a white film on the surface of the tongue. The cause of the white coating is not always the disease. Sometimes it can occur after taking various medications and even foods.
There are other reasons for the appearance of plaque:
- A white coating on the tongue may appear after eating various fermented milk products, such as cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt, and cheese.
- Sweet foods are a favorable environment for the growth of various bacteria, which leads to the appearance of white plaque. This phenomenon is temporary and can be easily eliminated after rinsing the mouth or brushing the tongue.
- Individual intolerance to toothpaste or mouth rinse. This happens quite rarely, but for some people, frequent contact with these products causes unpleasant chemical and allergic reactions, which can subsequently cause a white coating on the tongue.
- Violation of hygiene rules, in which teeth and tongue are rarely brushed, and food debris and various bacteria accumulate on them every day.
- Bad habits are a common cause of the problem. Abuse of alcohol and cigarettes negatively affects the condition of the entire body. When smoking, the tongue is exposed to high temperatures and harmful chemicals, and its mucous membrane is damaged. After alcohol abuse, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, and dehydration occurs. Very often, after drinking drinks, the next morning people suffer from dry mouth, unpleasant odor and a coating on the tongue.
- Taking antibiotics seriously affects the balance of microflora in the human body. There is also an increased load on the liver, which sometimes cannot cope with the amount of harmful substances received. In these situations, either white or white-yellow coating may appear on the tongue.
Eating fermented milk products may cause white plaque to appear, but this is not a sign of disease.
In some cases, the cause of the appearance of white plaque may be a violation of the division of tongue cells. Various hereditary and systemic diseases can lead to this.
- Leukoplakia is common in people who smoke. Plaque is formed as a result of the death of cells that die due to tobacco smoke. The disease can affect the mucous membrane of the mouth, respiratory tract and other organs. It is most often found in people aged 30–40 years.
- Lichen pilaris is a skin disease that can also affect the mucous membranes. With the erosive form, an inflammatory process begins in the oral cavity, grayish plaques and ulcers appear. The top of the tongue is covered with a white coating, and if you try to remove it, bleeding may begin due to open wounds.
- Brunauer syndrome is a serious disease that is inherited. With it, hyperhidrosis (increased sweating) and keratoderma (impaired keratinization processes) are observed. A very common sign of this disease is a white coating on the tongue.
- Christ-Siemens-Touraine syndrome is an extremely rare genetic pathology in which atrophy or congenital cutaneous hypoplasia is detected; the skin of patients is very smooth, fragile, and practically hairless. One of the symptoms of this syndrome is also a white coating on the tongue.
Video: 5 problems your tongue will tell you about
What diseases can plaque indicate?
Among the pathologies that provoke the formation of whitish deposits on the tongue: infections, gastrointestinal diseases, immune pathologies and others. Below are the most likely ones:
- colds, acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, flu, sore throat. The formation of plaque on the tongue indicates an uncontrolled proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms;
- glossitis or “geographic tongue”. Inflammation of the tongue caused by injury and of an infectious nature. Red spots form on the tongue, which often go away on their own.
- gastritis, gastric ulcer, enterocolitis. Inflammation of the gastric mucosa, in which a grayish-white coating appears on the tongue;
- candidiasis or thrush. The plaque caused by a fungal infection is localized under the tongue, it is uneven and appears in spots;
- chlamydia. Failure of the immune system, which leads to the formation of a thick sticky coating not only on the tongue, but also on the palate;
- bronchitis and pneumonia. Diseases of the upper respiratory tract stimulate the formation of a whitish film along the edges of the receptor organ;
- first stages of cancer. Whitish lesions lack clear boundaries. They are formed in all forms of cancer;
- lichen planus. Small grayish-white nodules appear in the patient’s mouth, which form a layer similar to lace;
- jaundice and liver disease. The color of the plaque is predominantly yellow; when bile stagnates, it acquires a greenish tint;
- diabetes. The film appears in response to a deficiency of saliva in the mouth, the disease is accompanied by the development of candidiasis in the oral cavity;
- chronic constipation. The film is thick, dense, with a repulsive odor;
- acute and chronic radiation sickness. The tongue swells, becomes covered with a thick film, cracks, hemorrhage and necrosis appear in the root area of the organ.
As you can see, plaque on the tongue can be a symptom of both minor health problems and serious pathologies that require an immediate comprehensive approach.
How to get rid of the problem
First of all, it is necessary to find the primary disease that led to the appearance of a white coating on the tongue. Depending on the diagnosis established for the patient, the doctor prescribes an individual course of treatment. This can be either taking medications, following a strict diet and using traditional methods, or special preventive measures that will help get rid of the unpleasant manifestation. It is necessary to sanitize the oral cavity at the dentist, eliminate all carious formations, and get rid of tartar.
It is very important to properly clean the surface of the tongue. It would be best to purchase a special brush or scraper that is designed specifically for these purposes. You should not use iron spoons or any other objects, as they can damage the already inflamed surface of the tongue. You can take regular toothpaste and squeeze a small amount onto your brush. It is better to start cleansing from the root, gradually moving to the tip with slow and gentle movements. After completing the procedure, you can rinse your mouth using special products.
Video about the treatment of oral thrush in the program of Dr. Komarovsky
Drug therapy
Medicines are prescribed based on the primary disease that was detected in a person.
- Antifungal drugs are necessary if candidiasis is present (Amphotericin B, Fluconazole, Diflucan). Nystatin and Decamine ointments are suitable for topical use.
- Eubiotics with live lactic acid bacteria are necessary to normalize microflora and improve intestinal function (Bifiform).
- Prebiotics are needed to restore microflora after the use of antibiotics (Linex, Bifiform, Hilak-Forte).
- A solution of 3% sodium and potassium iodide is suitable for the prevention of fungal diseases.
- Multivitamin complexes are prescribed to improve the overall health of the patient.
- Antiseptic agents are necessary for treating the surface of the tongue (Chlorhexidine, Corsodil).
- Local non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are necessary for the treatment of sore throat and other similar diseases (Tantum Verde Forte).
- Kalgel is suitable for numbing the surface of the tongue. It can be used even by children.
- Antimicrobial anti-inflammatory drugs are used for inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract and infectious diseases affecting the mucous membranes (Romazulan).
- Enzyme medications are necessary to improve digestion (Festal, Penzital, Pancreatin).
- Sorbents are needed to cleanse the body of toxins (activated carbon, Smecta, Enterosgel).
- Laxatives will be needed for periodic bowel cleansing (Dulcolax, Regulax).
- Anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed for various respiratory diseases (Ibuprofen, Imet, Ketorol).
- Antibiotics are needed for sore throat (Amoxicillin, Flemoxin, Amotit).
- Hepatoprotectors are prescribed to support the liver under heavy loads (Heptral, Phosphogliv, Essentiale Forte).
Medications - photo gallery
Heptral - a hepatoprotective agent, has a positive effect on the liver Diflucan - an antifungal drug Dulcolax - a drug that has a laxative effect Ibuprofen - a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug Kalgel - a combined drug with antimicrobial and local anesthetic action Romazulan - an antimicrobial anti-inflammatory drug of plant origin for local, external and systemic use Tantum Verde - a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug for topical use Festal - a digestive enzyme agent Flemoxin - a broad-spectrum antibiotic of the group of semi-synthetic penicillins Hilak Forte - a drug for intestinal dysbiosis Chlorhexidine - a local therapeutic and prophylactic broad-spectrum antiseptic and disinfectant Enterosgel - a medicinal product, an enterosorbent, serves to remove harmful substances from the body
Diet
Since most cases of white coating on the tongue occur due to problems with the gastrointestinal tract, many patients need to reconsider their diet and give up harmful foods. The following dishes should be excluded:
- smoked, fried, spicy and canned food;
- sweets, chocolate;
- pastries, white bread;
- alcoholic drinks;
- carbonated drinks;
- products with artificial food additives;
- fast food.
Eating plenty of fresh vegetables and fruits promotes good health
For diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, it is necessary to diversify your diet with low-fat meat and vegetable broths, cereals with milk or water. Eating fermented milk products will also be beneficial, and raw solid vegetables and fruits will help mechanically cleanse the surface of the skin of the tongue.
Traditional methods of treatment
There are many folk recipes that can help in the fight against white coating on the tongue. However, it is worth remembering that before using any product, you must first consult a doctor, as there are contraindications and individual intolerance is possible.
Flax seed decoction
With daily use of this recipe, you can significantly improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, improve intestinal motility and eliminate constipation. When cooked, flax seeds release a special mucus that has enveloping and antiseptic properties.
- Take three tablespoons of seeds.
- Pour in 250 ml of clean water.
- Bring to a boil and then simmer over low heat for ten minutes.
- Remove from heat and cool the resulting mixture for twenty minutes.
- Then strain the broth and drink half a glass twice a day before meals.
A decoction of flax seeds is prescribed for various gastrointestinal diseases.
Rinse with medicinal herbs
Many herbal remedies are known for their antiseptic properties. Also, using them can significantly improve the smell of your mouth and make your breath fresher.
- Take strawberry, mint, sage and chamomile leaves.
- Dry them in a dark place for a week, placing them on paper or gauze in a dark room.
- Once the plants are completely dry and brittle to the touch, puree them in a blender until smooth.
- Take two tablespoons of the mixture, pour them into a thermos, add 250 ml of boiling water and let it brew for one hour.
- Strain the resulting product and rinse your mouth with it every time after eating for three minutes.
Mint and sage mouthwash promotes fresh breath
Baking soda solution
This recipe is especially suitable for inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and diseases such as sore throat. Take a glass of warm, but not hot, boiled water, add 30–40 grams of baking soda. Rinse your mouth with the resulting solution up to four times a day. After the procedure, it is necessary to rinse the mucous membrane with clean drinking water.
Baking soda helps clean the surface of the oral cavity from pathogenic bacteria
Oil rinses
Oil has special binding properties; it is able to “collect” food debris and bacteria. You can use olive, sunflower, grape or any other oil. For twenty minutes, you must continuously rinse your mouth with the chosen product. If after this the oil becomes cloudy and has a whitish tint, this indicates that the procedure was carried out correctly and the oral mucosa is cleansed.
When rinsing, the oil absorbs food debris and accumulated plaque.
You can also treat the surface of the tongue using the following means:
- rosehip oil;
- sea buckthorn oil;
- aloe juice;
- tea tree oil.
Types of plaque
When assessing the nature of the phenomenon, it is worth taking into account not only the amount of deposits, but also their color and structure. Below we will tell you what the color of the plaque says:
- white. A thin white mucous coating after night is not a deviation. An increase in the density of the membrane indicates chronic constipation. A cheesy light coating is a symptom of Candida infection.
- red. Indicates the development of an infection, such as a sore throat. A dark red tint will indicate problems with the kidneys; the plaque acquires this color when the body is poisoned by various poisons;
- yellow. A bright color indicates the development of hepatitis A. If there are problems with the gallbladder, in addition to the yellow film, cracks appear on the tongue;
- green. Visualized during inflammation of the organ - glossitis. Most often, the provoking factor is a fungal infection (yeast glossitis);
- brown. This purulent tint is associated with liver intoxication (alcohol addiction). However, coffee, tea, and chocolate can also give brown color to deposits;
- grey. A characteristic symptom of pathologies of the stomach and duodenum, and also appears when the immune system is damaged. The same diseases also affect tooth enamel (it also takes on a dark shade);
- bluish. This is a symptom of an experienced smoker. The root of the tongue becomes blue and becomes slightly thicker;
- orange. A rare phenomenon that indicates the release of acid from the stomach into the oral cavity. However, this condition should not be confused with staining the surface of the organ with food coloring;
- black. A dangerous sign indicating a strong sludge in the body or a specific disease, for example, Crohn's disease. Black spots on the tongue are visualized due to metal intoxication.
A spotted coating on the tongue (when the surface of the organ is covered with uneven spots) appears in people of different age categories. Most often, this condition does not pose any danger and goes away on its own. Today, the reason for this phenomenon has not been fully identified. Each clinical case is individual - the cause of the spots can be either candidal stomatitis and allergies, or the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
The prognosis for treatment of white plaque on the tongue very much depends on the primary disease. In most situations, it can go away on its own with normalization of nutrition and daily hygiene procedures. If serious diseases are detected, the treatment prognosis is determined individually, depending on the severity of the pathology and the patient’s health status. If you have gastritis or a stomach ulcer, then with proper therapy, most people experience a significant improvement in their condition. In the case of such a serious infectious disease as HIV, the treatment prognosis is unfavorable; it is only possible to temporarily support the human body.
Diagnostics
After a visual examination of the oral cavity and analysis of the patient’s complaints, the patient is sent for a general blood test and a mouth smear for bacterial culture (bacteriological culture).
Next, based on the results of the studies, the patient is referred to the appropriate specialist.
It depends on the underlying disease and then treatment is prescribed.
But if gastrointestinal diseases or hormonal disorders are suspected, are prescribed by appropriate specialists.
Prevention
In some cases, it is impossible to predict the appearance of a white coating on the tongue. However, there are general recommendations that will help reduce the likelihood of its formation:
- First of all, get rid of bad habits. It is very important to give up cigarettes and alcohol consumption;
- drink about two liters of clean drinking water every day. This will help improve your health and quickly eliminate toxins and waste accumulated in the body;
- undergo preventive examinations at the dentist, monitor the condition of your teeth;
- after eating food, use a mouthwash and clean your tongue with a toothbrush or scraper;
- carry out timely treatment of the gastrointestinal tract, undergo examinations by a gastroenterologist;
- watch your diet, try to reduce your consumption of sweet, fatty and other unhealthy foods;
- Brush your teeth thoroughly at least twice a day. Find a toothpaste and mouthwash that's right for you.
Video on how to properly clean the surface of your tongue
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To reduce tingling and burning, doctors recommend following a diet. All hot and spicy dishes are excluded from the menu; food should be warm, but not hot. Products are prepared by steaming, boiling or stewing so that they are soft and do not injure the surface of the tongue. It is necessary to regularly rinse your mouth with water or a weak solution of chlorhexidine: this helps get rid of tingling and also prevent inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
Conservative therapy
Treatment for a tingling tongue begins with dental care. The doctor sanitizes the oral cavity and, if necessary, changes fillings and incorrectly selected dentures. If after this the symptoms do not disappear, treatment is prescribed for the underlying disease causing glossalgia. Therapeutic regimens are selected by a specialized specialist: neurologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist.
Pathogenetic treatment includes medications that affect the nervous system, which help reduce painful paresthesias. Herbal sedatives, bromine preparations, and “daytime” tranquilizers are effective. For refractory symptoms, injections of B vitamins and trimecaine blockades are used. Local remedies provide a quick effect: lubricating the tongue with anesthesin, pyromecaine, oil solutions (vitamin A, rose hips).
Those suffering from desquamative glossitis are often prescribed physiotherapy, which includes medicinal electrophoresis, ultrasound therapy, and SMT therapy. For prolonged glossalgia, reflexology and ozone therapy help relieve tingling. To reduce the intensity of symptoms, laser therapy is used, which has an additional anti-inflammatory effect. Paresthesia of a neurogenic nature requires psychotherapy sessions.
Features of plaque in older people
In older people, the appearance of a white coating on the tongue is often associated with the presence of dentures. They often develop stomatitis, which is a provoking factor. The thing is that a foreign object in the oral cavity promotes the rapid proliferation of bacteria. Also, some older people become unable to fully maintain personal hygiene. Among other things, older people are more likely than usual to experience all sorts of diseases and reduced immunity.
Plaque and dental problems
The topic of plaque and dental problems deserves special attention. Any dental disease occurs against the background of active activity of pathogenic microorganisms. Obviously, this factor contributes to the formation of pathological plaque in the mouth.
Plaque on the tongue, cheeks and palate can appear as a result of a banal failure to comply with the rules of oral hygiene, or the picture can be much more serious. In particular, such a dangerous disease as Vincent's stomatitis manifests itself by the formation of a whitish film.
The conclusion is obvious: if the amount of plaque increases or its structure changes, you must immediately contact your dentist to undergo a detailed diagnosis and, by starting timely treatment, prevent undesirable consequences.
Features of plaque in children
Children may also develop a white coating on the tongue. In infancy, such a symptom may be an indicator of thrush. This fungal disease occurs quite often due to breastfeeding, premature birth, hypothermia and poor hygiene. At the same time, the baby may cry and refuse to eat. This occurs due to a burning sensation on the tongue that constantly worries the child. The mother's consumption of sweet foods may also be a contributing factor.
In infants, a white coating on the tongue is usually a consequence of breastfeeding.